Embed presentation
Downloaded 37 times





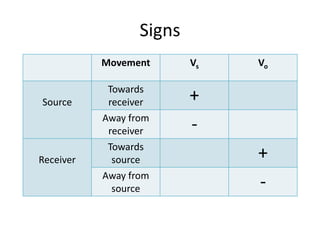


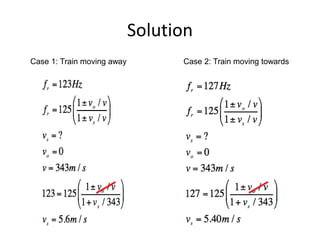
The Doppler Effect describes how the frequency of sound changes due to the relative motion of the source and the observer. Key variables include emitted frequency, observer frequency, speed of sound, and the speeds of the observer and source. Example problems illustrate how to calculate the speed of a moving train based on observed frequencies.










