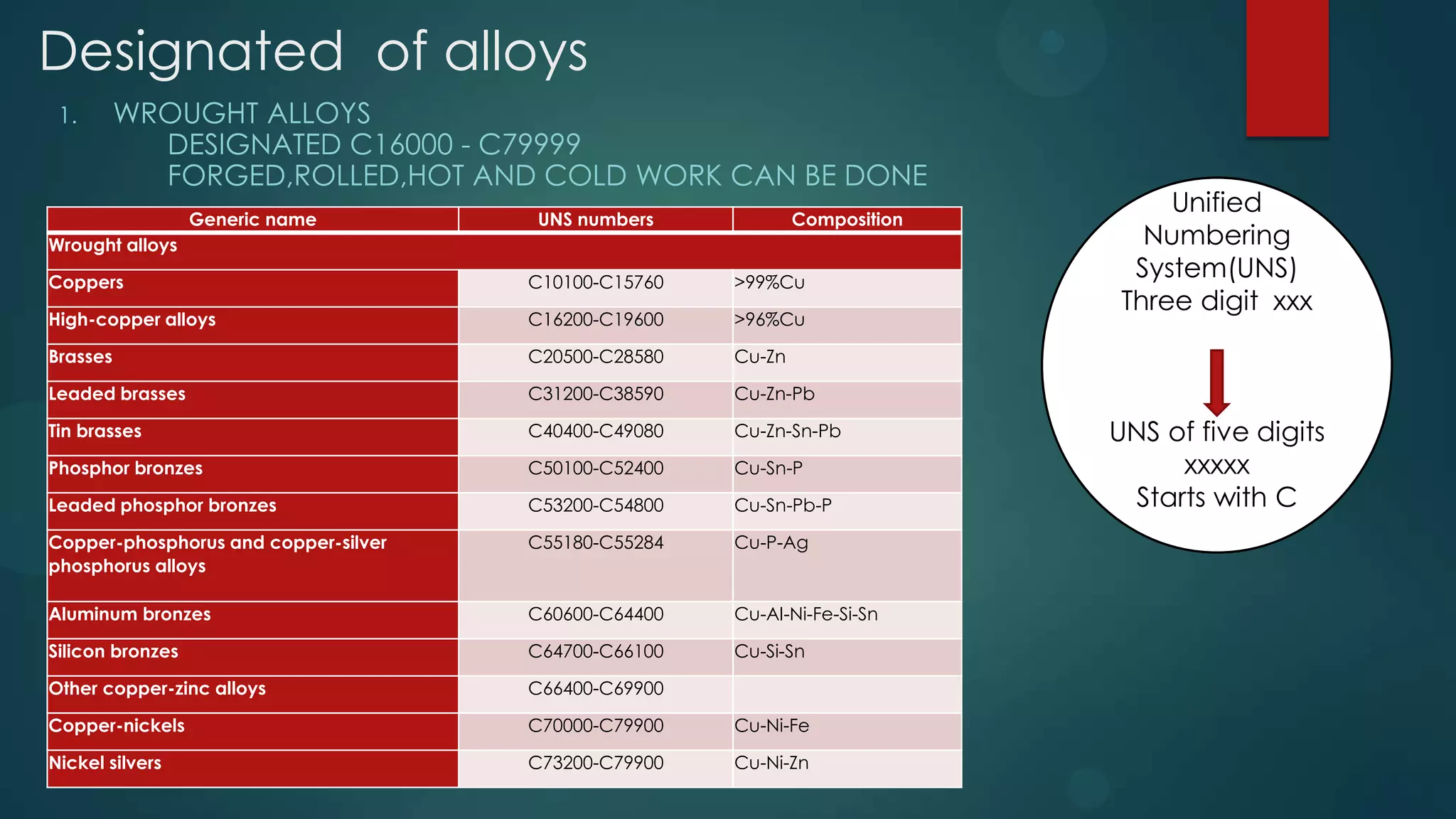
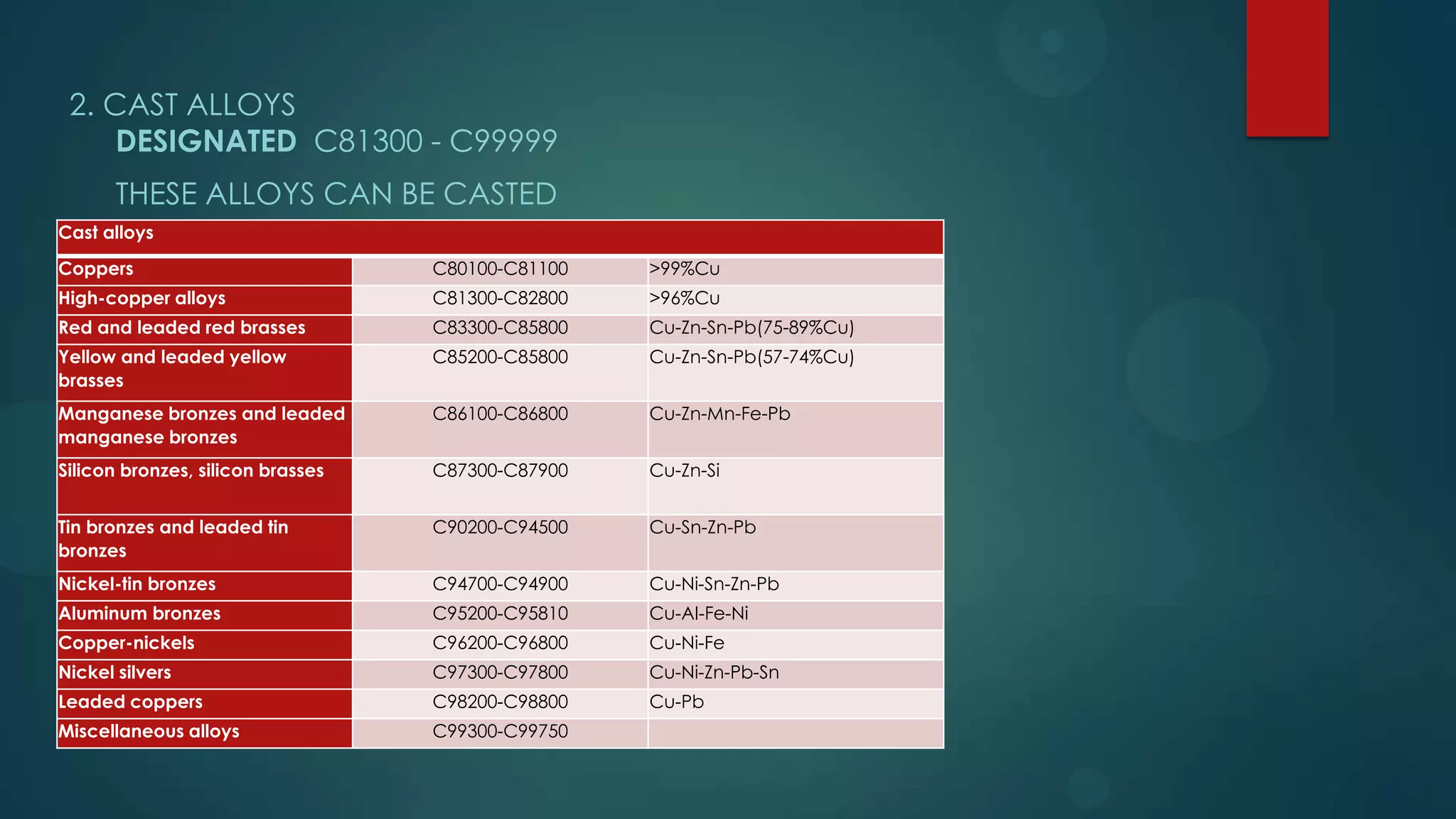
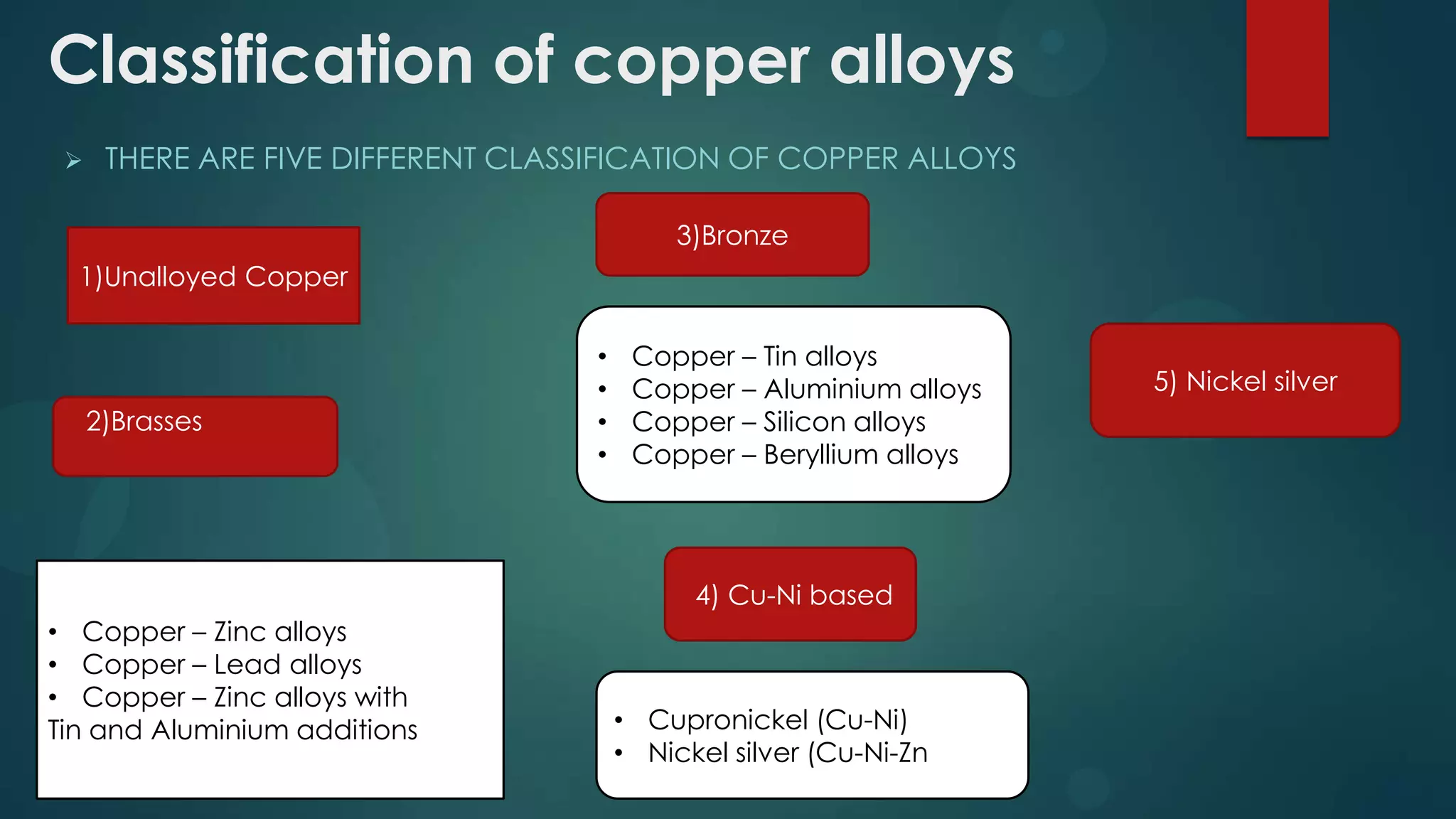
1. There are two main classifications of copper alloys - wrought alloys and cast alloys. Wrought alloys can be forged, rolled, or worked hot or cold, while cast alloys are designed to be cast.
2. Copper alloys include brasses, bronzes, copper-nickel alloys, and nickel silvers. Brasses are copper-zinc alloys, bronzes are copper-tin alloys, copper-nickels contain copper and nickel, and nickel silvers contain copper, nickel, and zinc.
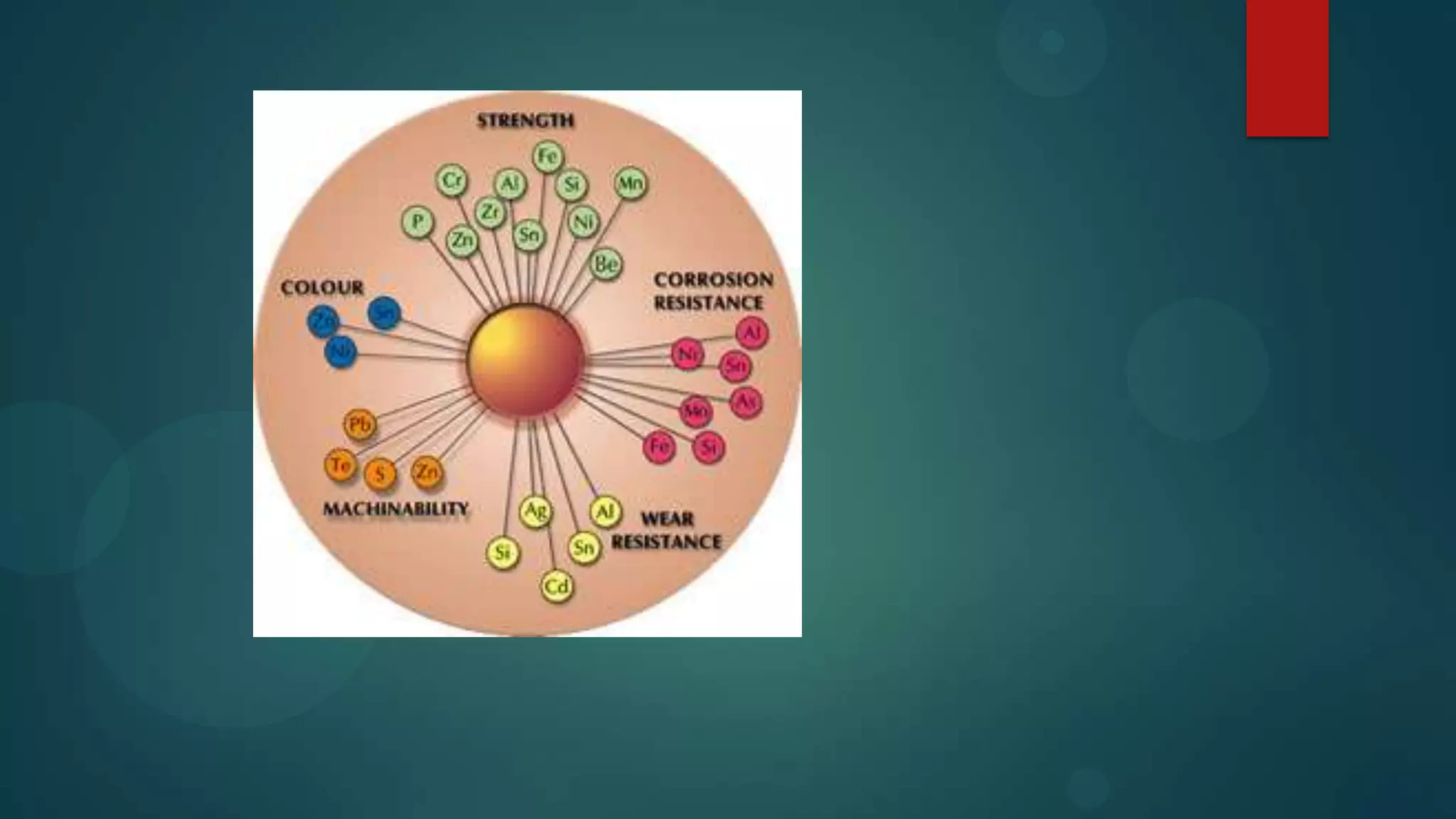
3. Alloying elements are added to copper to influence properties like strength, color, conductivity, machinability, corrosion resistance, and wear