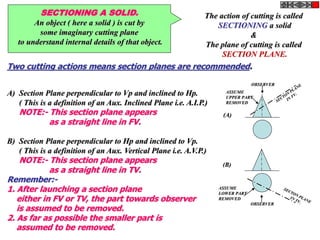
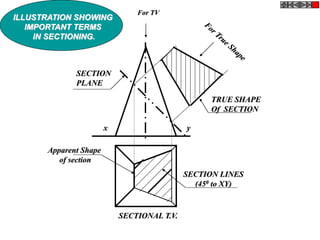
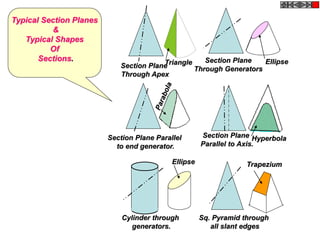
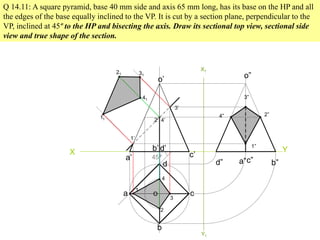
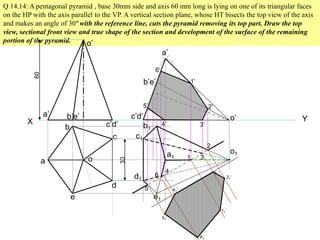
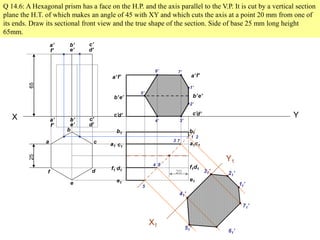
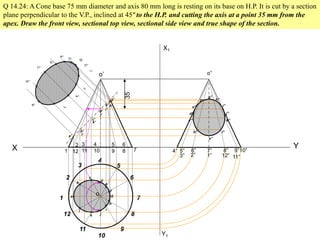
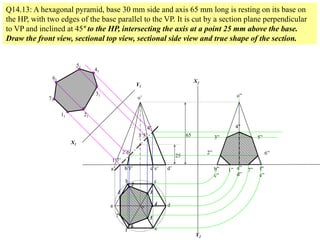
The document discusses the principles of sectioning solids in engineering applications, detailing different types of section planes and their corresponding views. It provides examples involving various shapes like pyramids and prisms, illustrating how to execute sectional views and true shapes based on cutting planes. The text emphasizes understanding the cutting process and visual representation through diagrams.