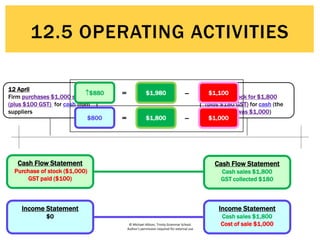
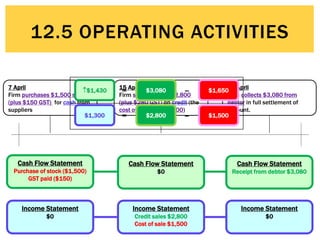
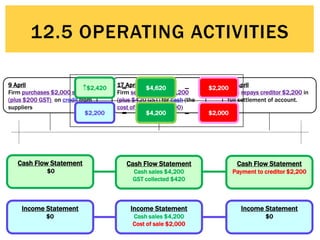
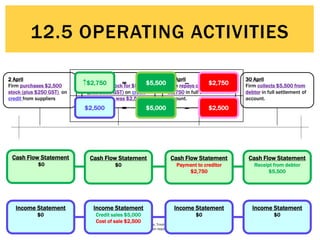
The document defines operating activities as cash flows resulting from the day-to-day provision of goods and services by a business. It notes that operating activities include cash inflows from customers for sales of goods and services, as well as cash outflows to pay employees and suppliers. The document then provides an example cash flow statement for a business for the month ended June 30, 2015, showing cash inflows of $50,000 from cash sales, $10,000 from debtors, and $5,000 in GST collected, and cash outflows of $30,000 for stock purchases, $3,000 for advertising, $14,000 for wages, $3,000 for cleaning, and $4,000