This document provides an overview of creative accounting, including:
- Defining creative accounting as the manipulation of financial numbers within legal standards but against their intended spirit.
- Explaining why companies may resort to creative accounting, such as managing earnings, meeting targets, or boosting share prices.
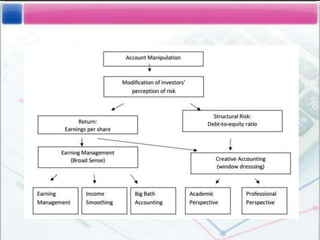
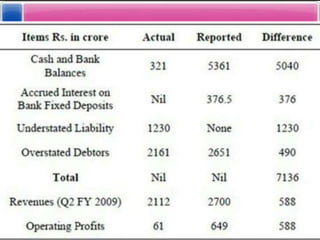
- Detailing some techniques of creative accounting like premature revenue recognition, manipulating reserves and amortization policies.
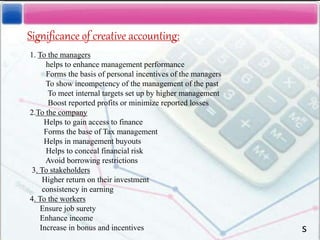
- Noting the significance of creative accounting for managers to enhance performance but its misleading nature for stakeholders; and the role of auditors in reducing its effects.