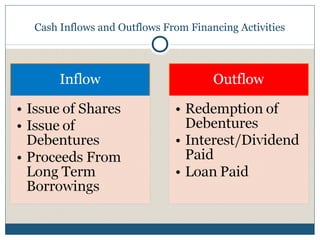
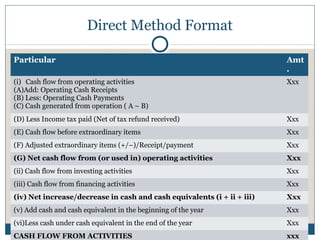
The document discusses the cash flow statement, including its importance, purposes, components, and methods of preparation. Specifically, it defines operating, investing and financing activities. It also provides examples of indirect and direct methods to prepare the cash flow statement, including working notes and calculations. Finally, it includes a sample problem demonstrating the preparation of a cash flow statement using both the direct and indirect methods.