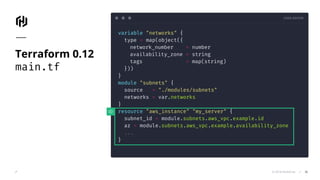
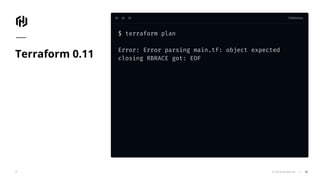
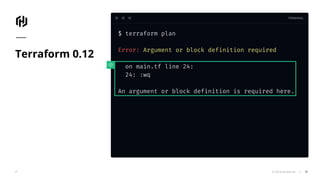
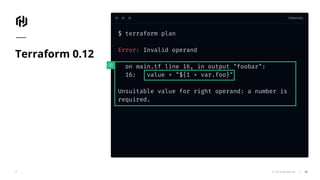
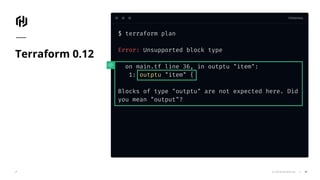
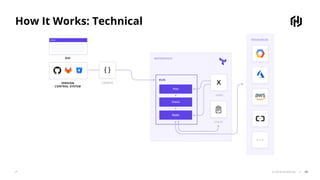
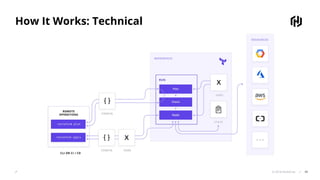
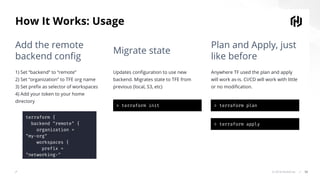
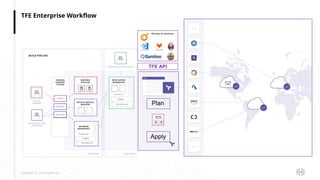
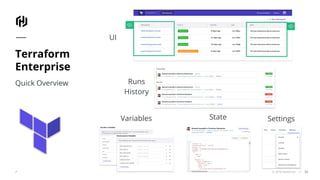
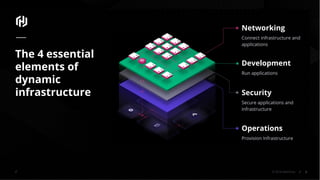
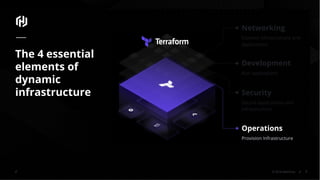
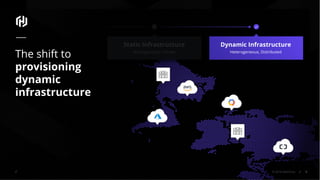
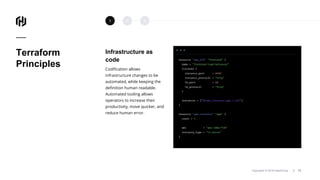
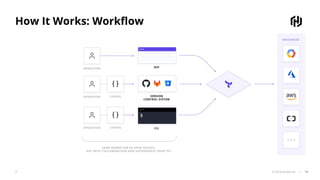
The document presents an overview of HashiCorp's Terraform 0.12, emphasizing its infrastructure as code capabilities aimed at safely provisioning and managing dynamic infrastructure across multiple cloud environments. It highlights enhancements to the HashiCorp Configuration Language (HCL), including improved error handling, robust type systems, and new programming constructs that facilitate more complex infrastructure definitions. Additionally, the document outlines the remote plan and apply features that allow for centralized management and integration of policy controls within Terraform Enterprise.
















![© 2018 HashiCorp
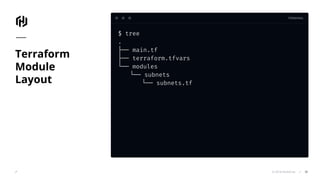
Terraform 0.12:
First-Class
Expressions
23
● Operations and variables can be used outside
of string interpolation
○ Buh-bye “${ }”
● Lists and maps can be used directly with
expressions
○ Less list(""), more []](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/terraform0-181213185854/85/Terraform-0-12-Deep-Dive-HCL-2-0-for-Infrastructure-as-Code-Remote-Plan-Apply-23-320.jpg)
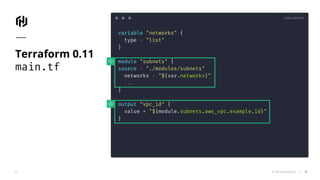
![CODE EDITOR
© 2018 HashiCorp
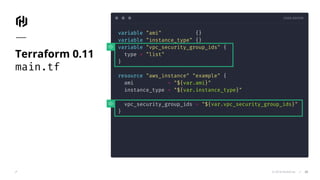
variable "ami" {}
variable "instance_type" {}
variable "vpc_security_group_ids" {
type = "string"
default = ""
}
resource "aws_instance" "example" {
ami = "${var.ami}"
instance_type = "${var.instance_type}"
vpc_security_group_ids =
"${var.vpc_security_group_id != "" ?
[var.vpc_security_group_id] : list("") }"
}
Terraform 0.11
main.tf
26](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/terraform0-181213185854/85/Terraform-0-12-Deep-Dive-HCL-2-0-for-Infrastructure-as-Code-Remote-Plan-Apply-26-320.jpg)
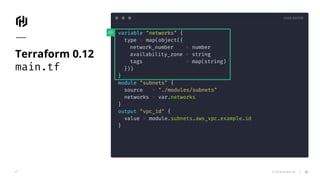
![CODE EDITOR
© 2018 HashiCorp
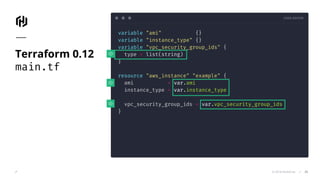
variable "ami" {}
variable "instance_type" {}
variable "vpc_security_group_ids" {
type = string
default = ""
}
resource "aws_instance" "example" {
ami = var.ami
instance_type = var.instance_type
vpc_security_group_ids =
var.vpc_security_group_id != "" ?
[var.vpc_security_group_id] : []
}
Terraform 0.12
main.tf
27](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/terraform0-181213185854/85/Terraform-0-12-Deep-Dive-HCL-2-0-for-Infrastructure-as-Code-Remote-Plan-Apply-27-320.jpg)