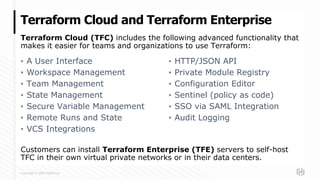
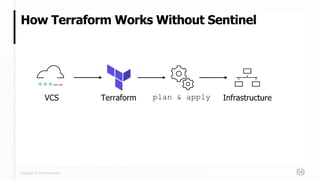
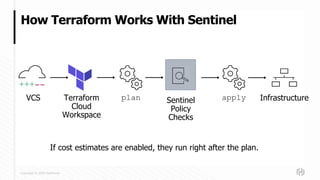
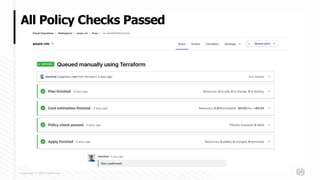
This document discusses new features in HashiCorp's Sentinel policy as code framework used with Terraform Cloud and Terraform Enterprise. It introduces Sentinel modules and new Terraform Sentinel v2 imports, and describes the evolution of Sentinel policies from first to third generation. It provides examples of prototypical third generation policies and discusses common functions, testing policies with the Sentinel CLI, and deploying policies.