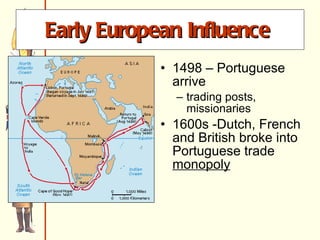
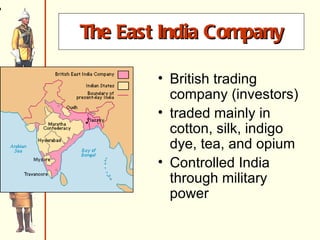
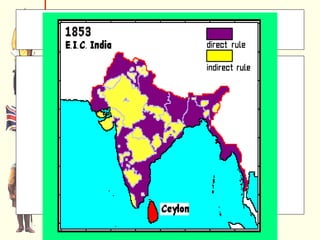
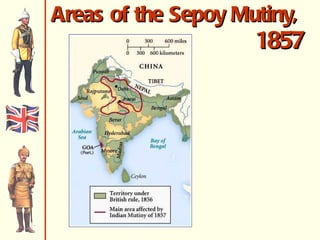
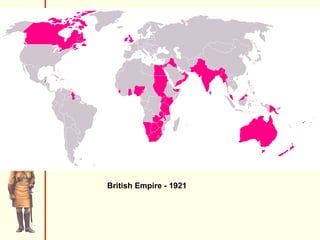
The document discusses Rudyard Kipling's poem "The White Man's Burden" and provides context about European imperialism in India. It describes how the British East India Company gained control of India in the 17th-18th centuries through trade and military power. This led to unrest among Indian troops and the Sepoy Rebellion of 1857, after which Britain took direct control of India. The effects of British rule included new economic and social changes as well as the growth of Indian nationalism seeking independence in the late 19th/early 20th centuries.