Embed presentation
Downloaded 201 times



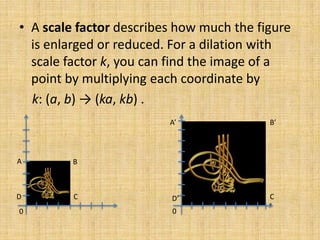


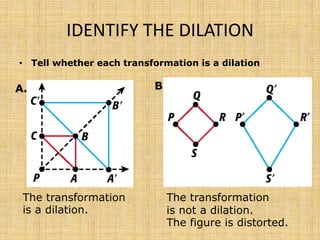
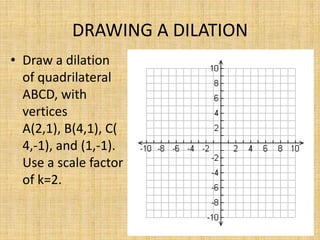

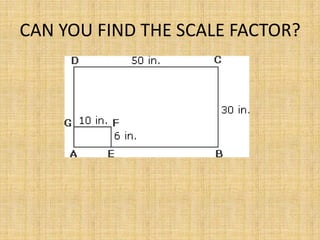
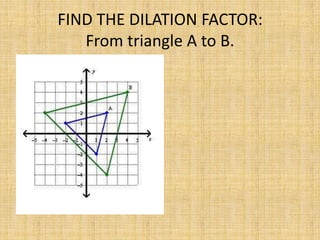
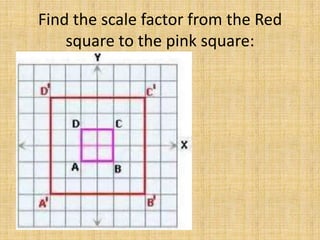
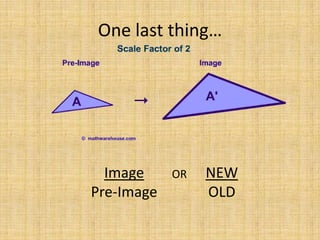


This document discusses dilations, which are transformations that change the size of a figure but not its shape. A dilation is identified by its scale factor, which describes how much the figure is enlarged or reduced. If the scale factor is greater than 1, it is an enlargement, and if it is less than 1, it is a reduction. The document provides examples of identifying dilations, drawing dilations of different figures using given scale factors, and finding the scale factor between two figures. Students are assigned independent practice and homework on dilations.














