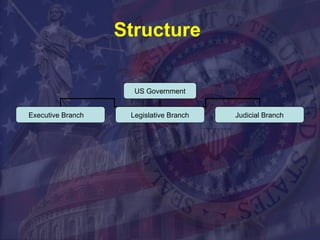
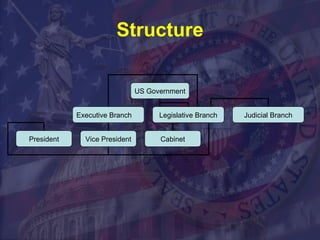
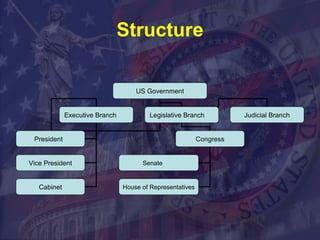
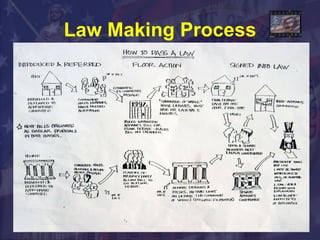
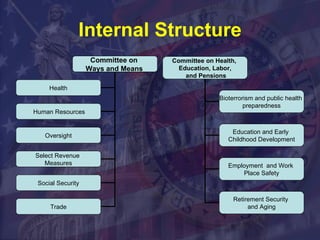
The legislative branch comprises Congress, which is made up of the Senate and House of Representatives. Congress has the responsibility of making laws, overseeing the executive branch, and preserving democracy through checks and balances on the president and judicial branch. Most of the legislative work is done in committees and subcommittees before bills reach the floor for debate and votes.