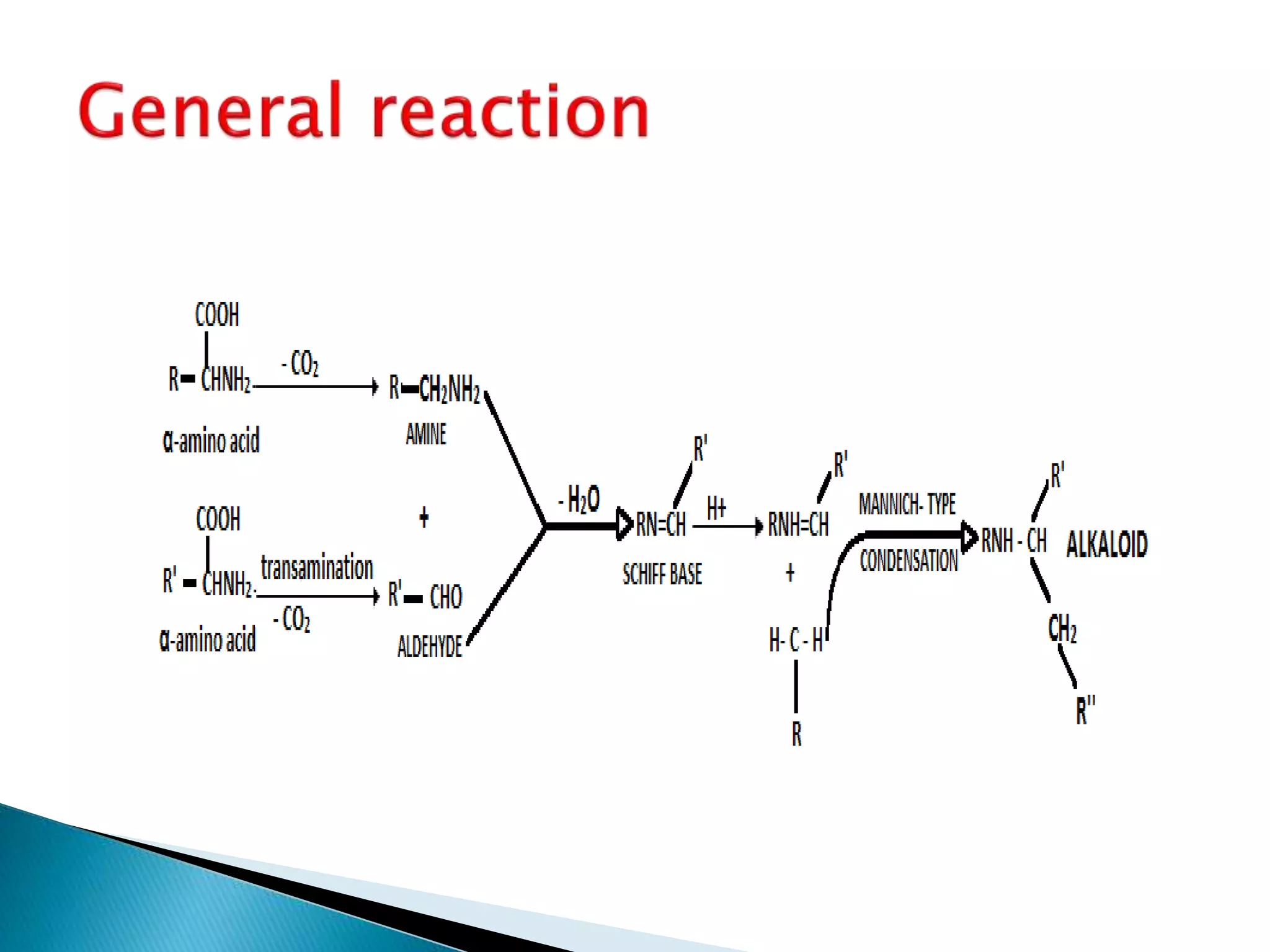
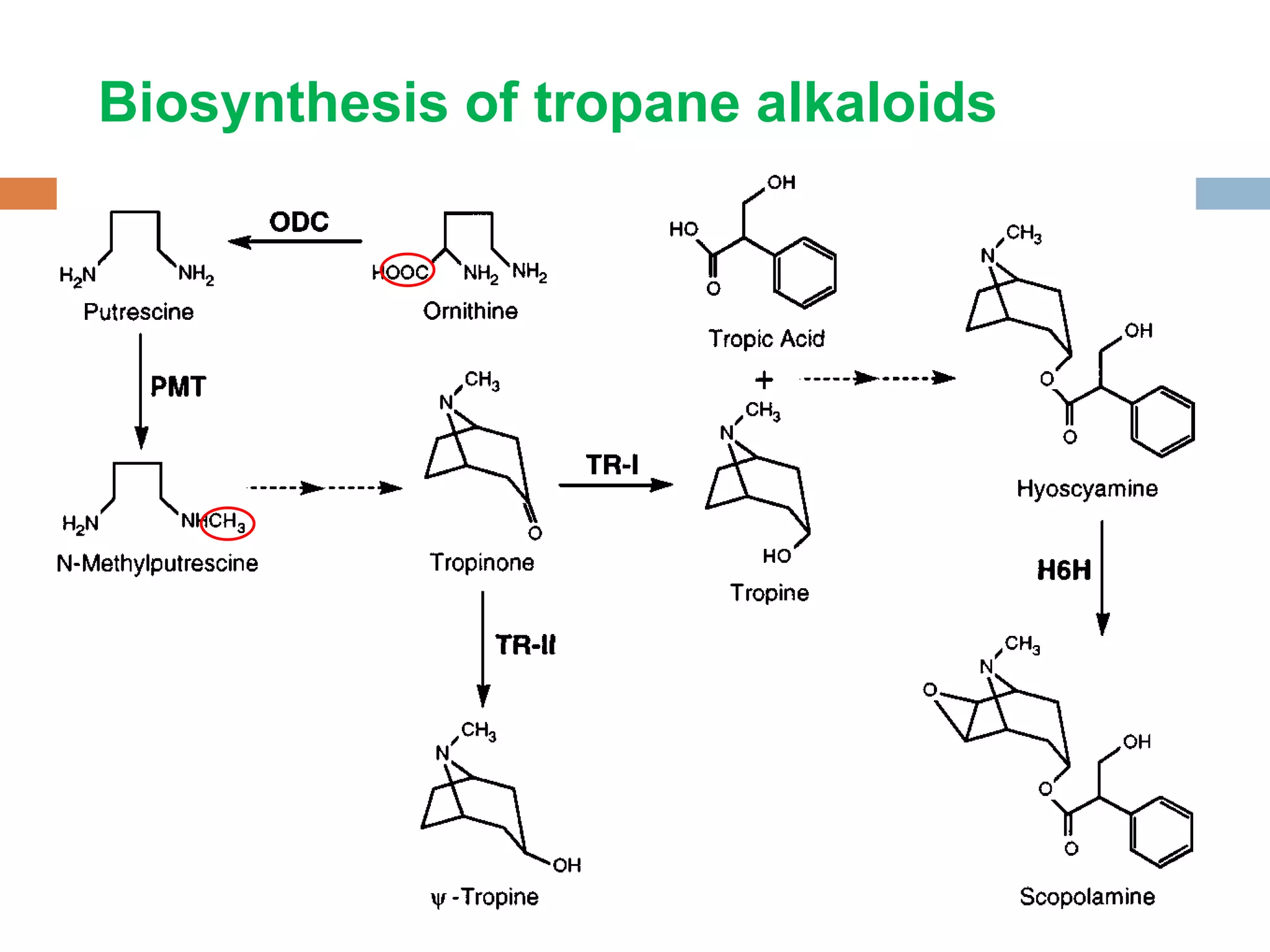
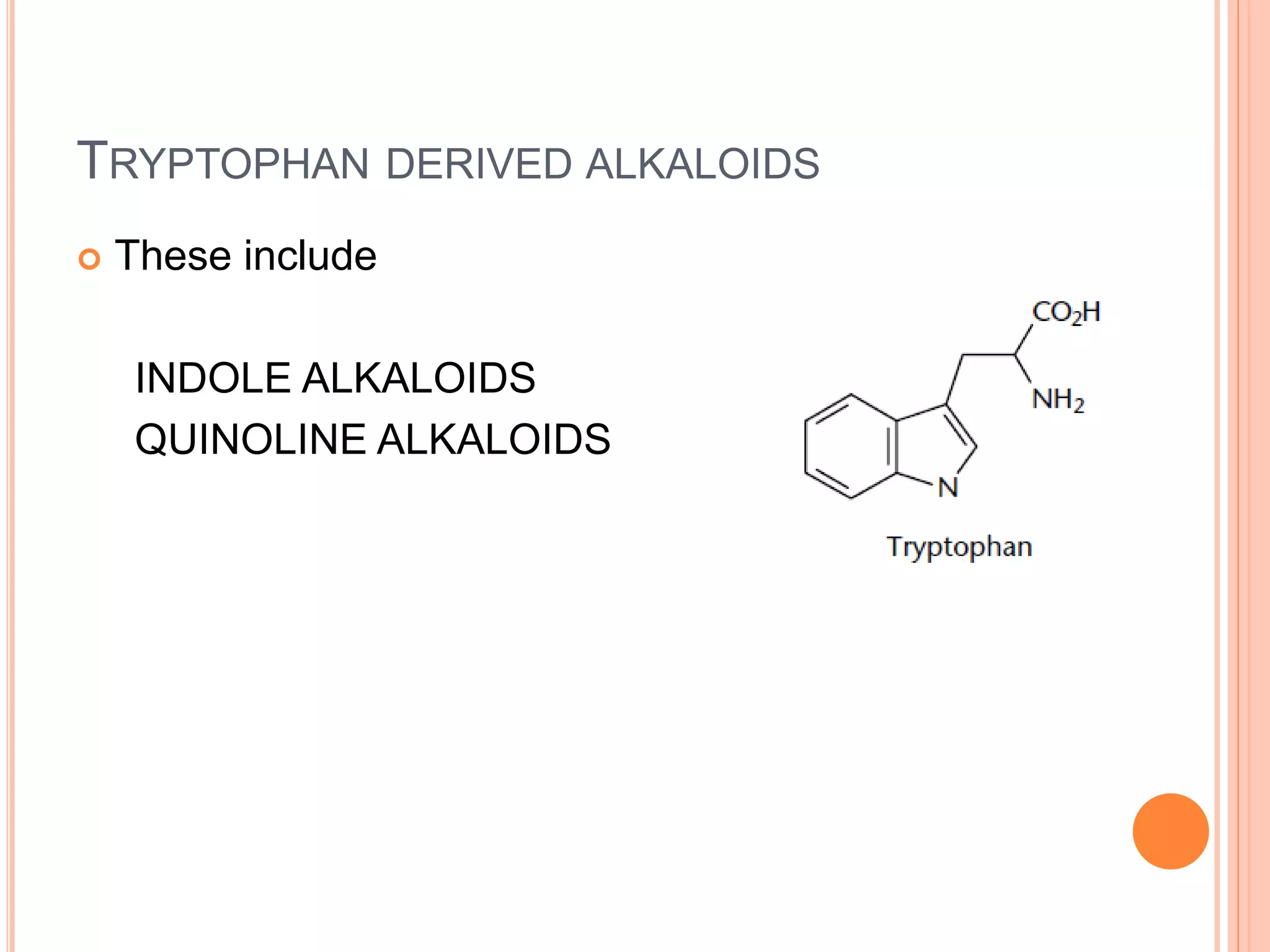
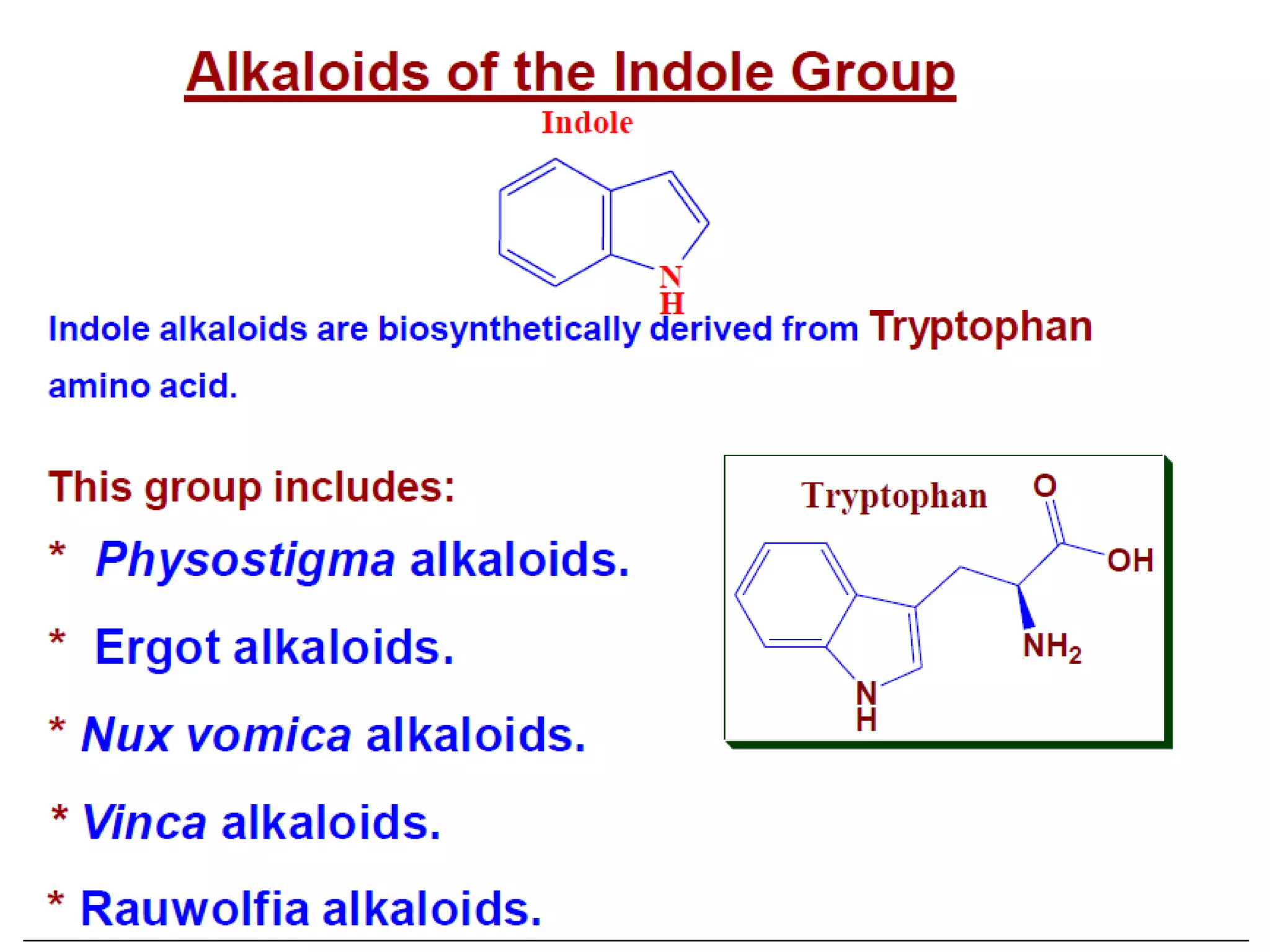
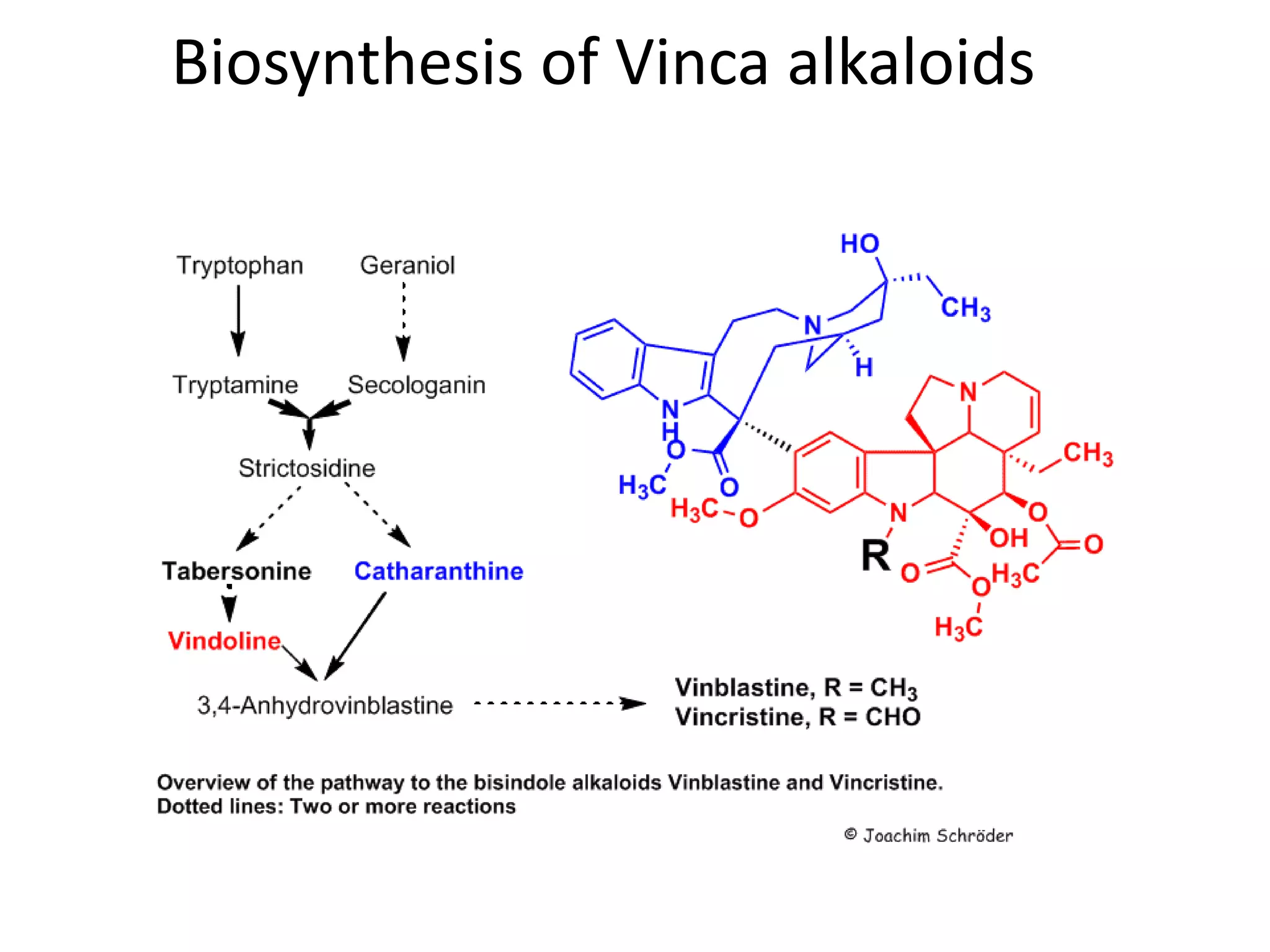
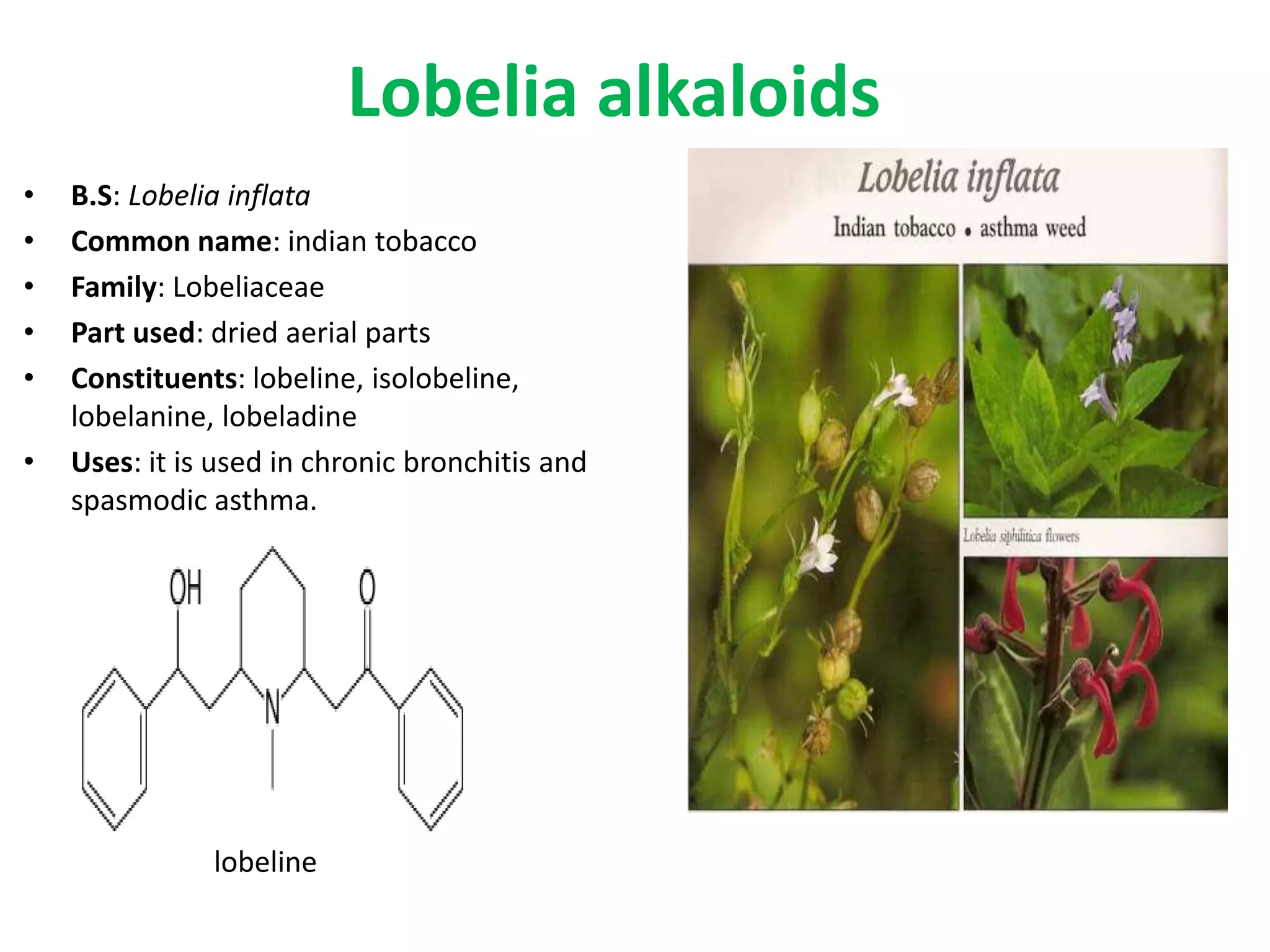
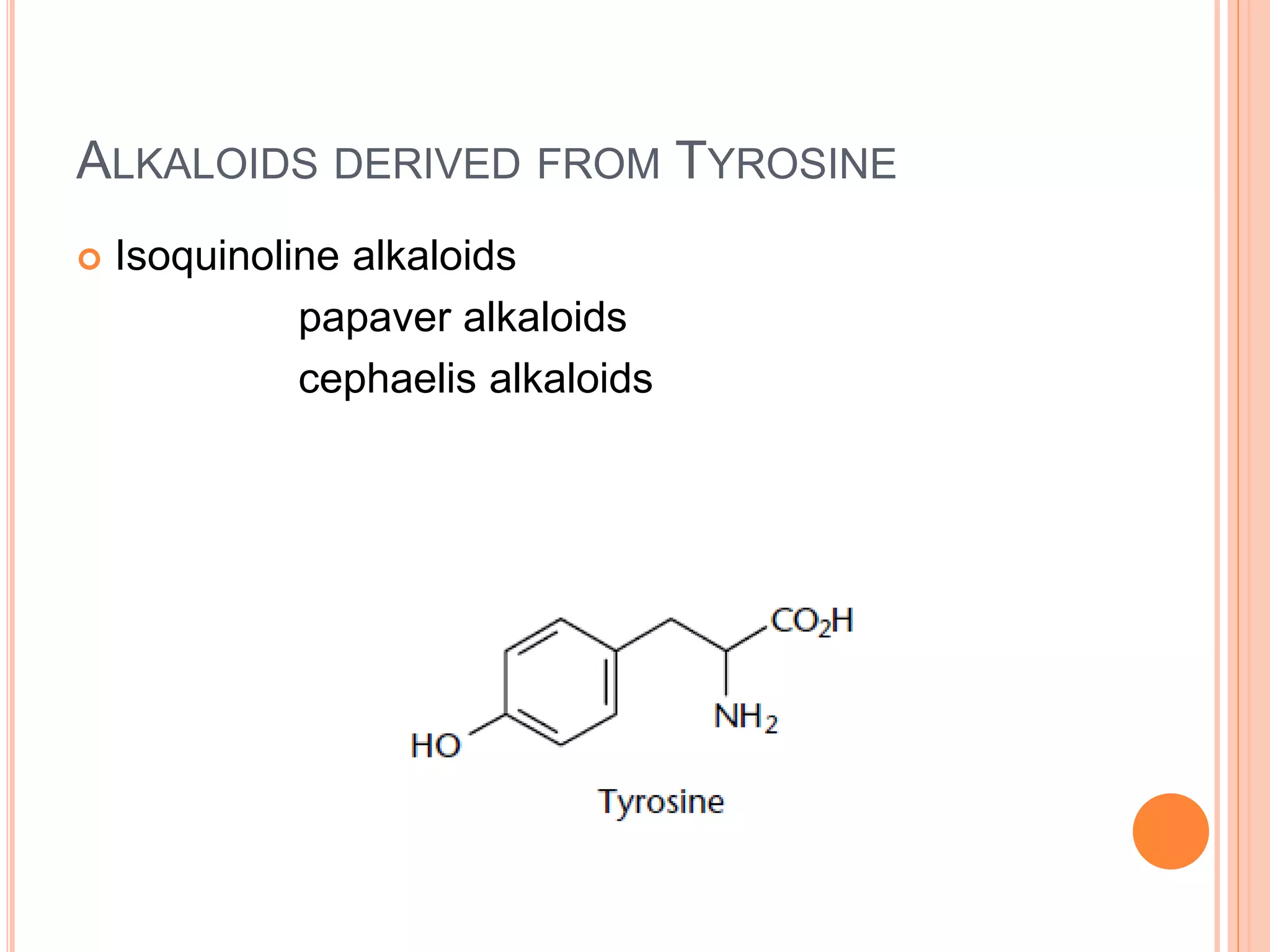
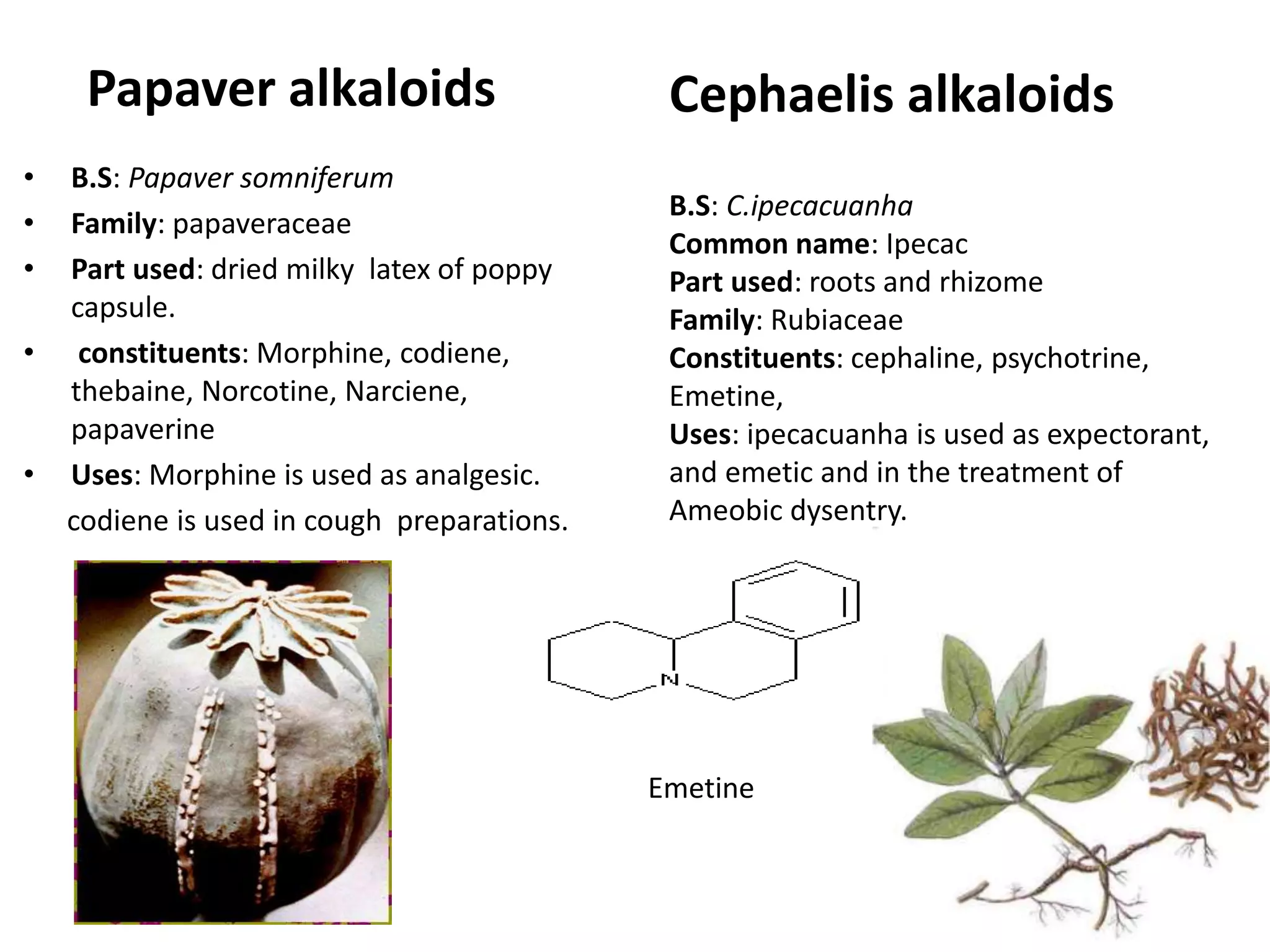
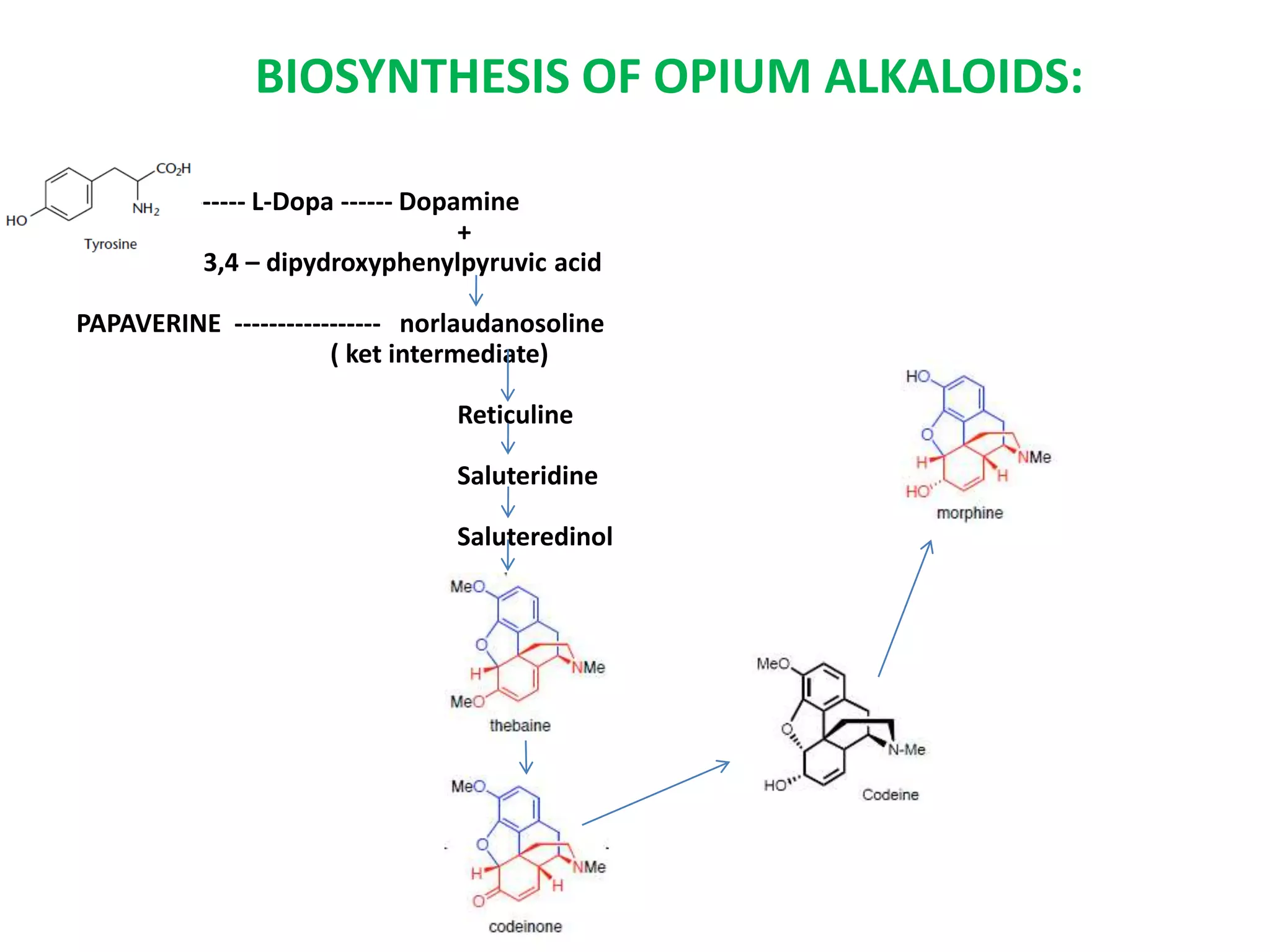
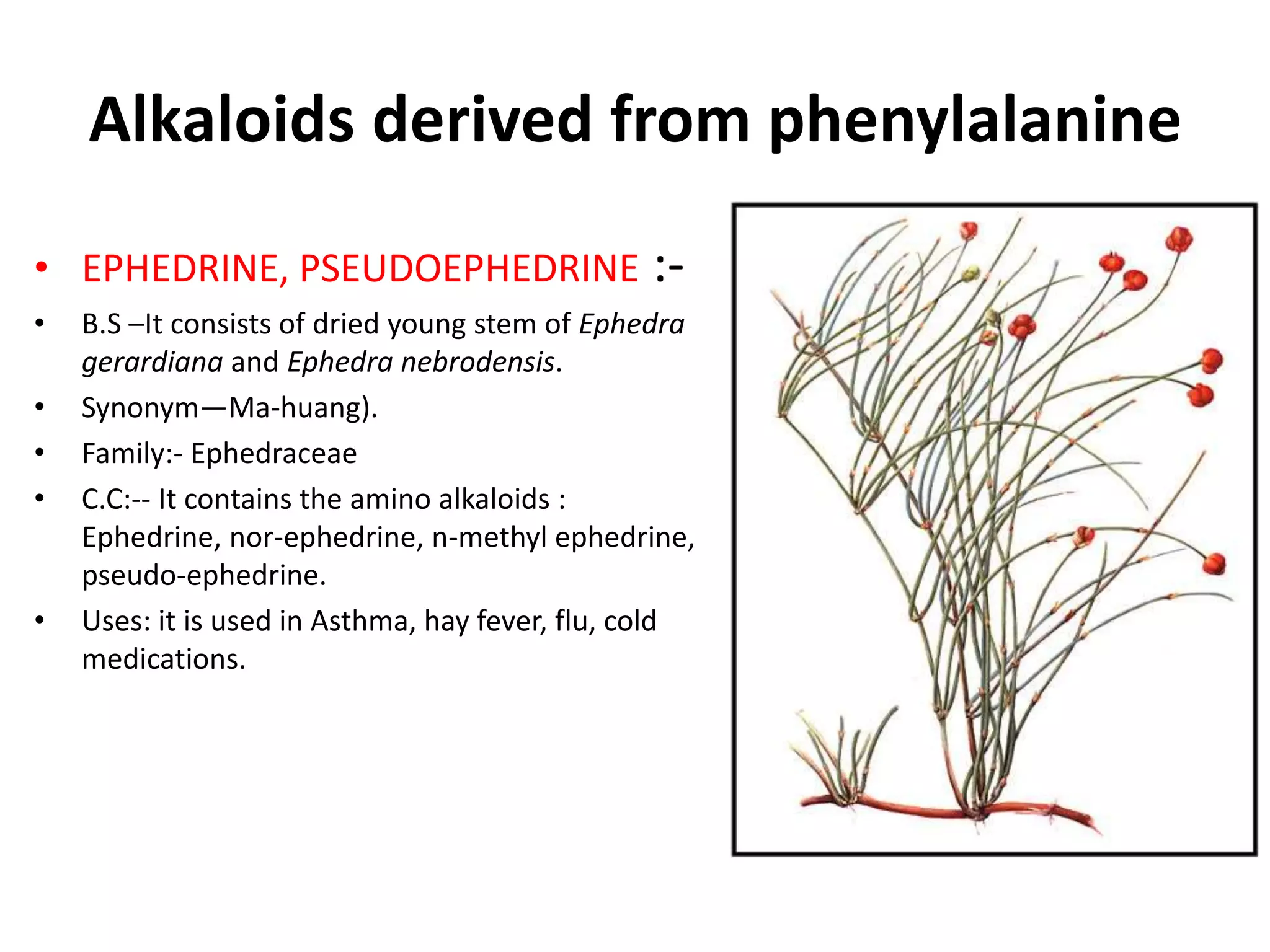
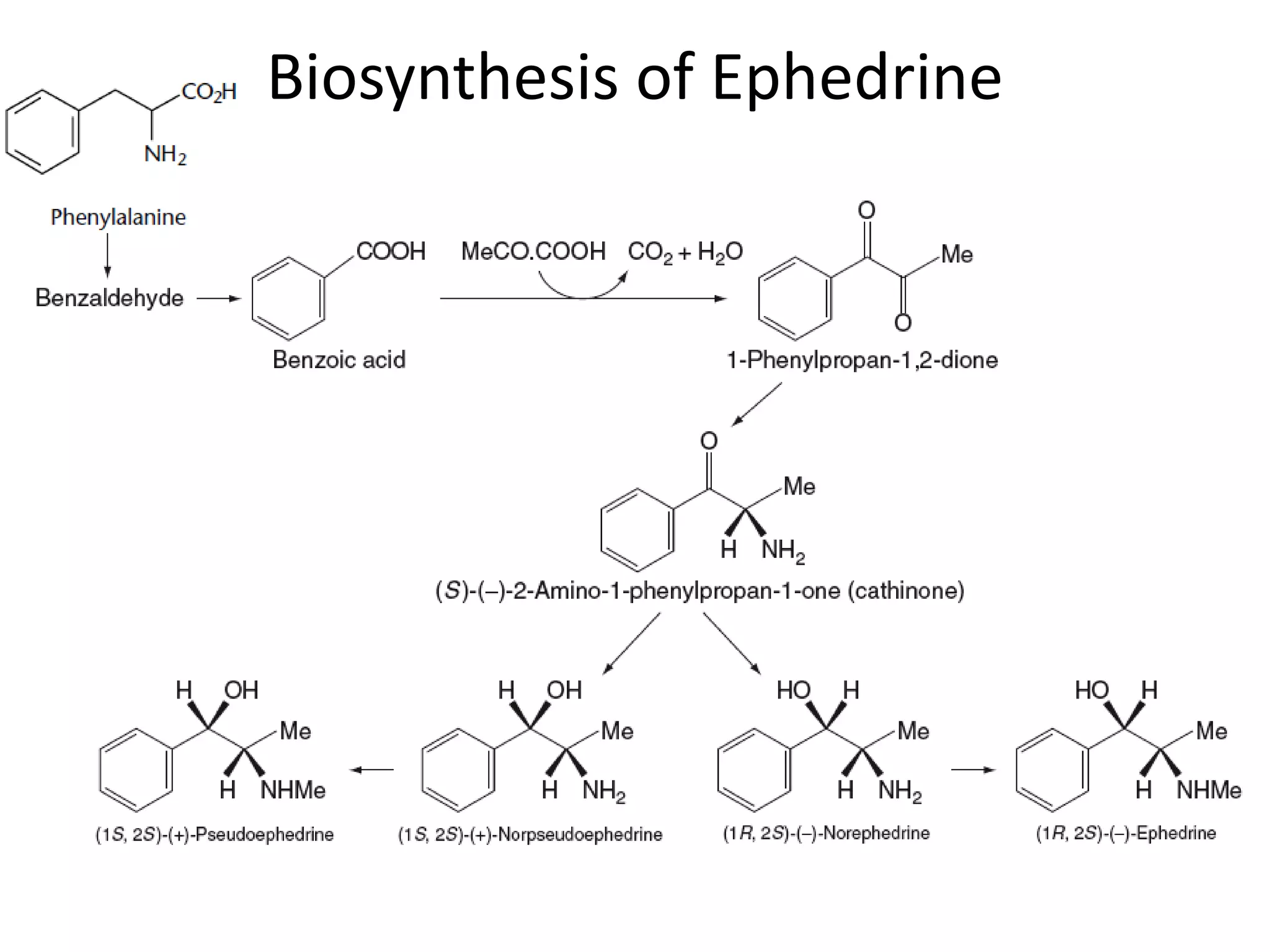
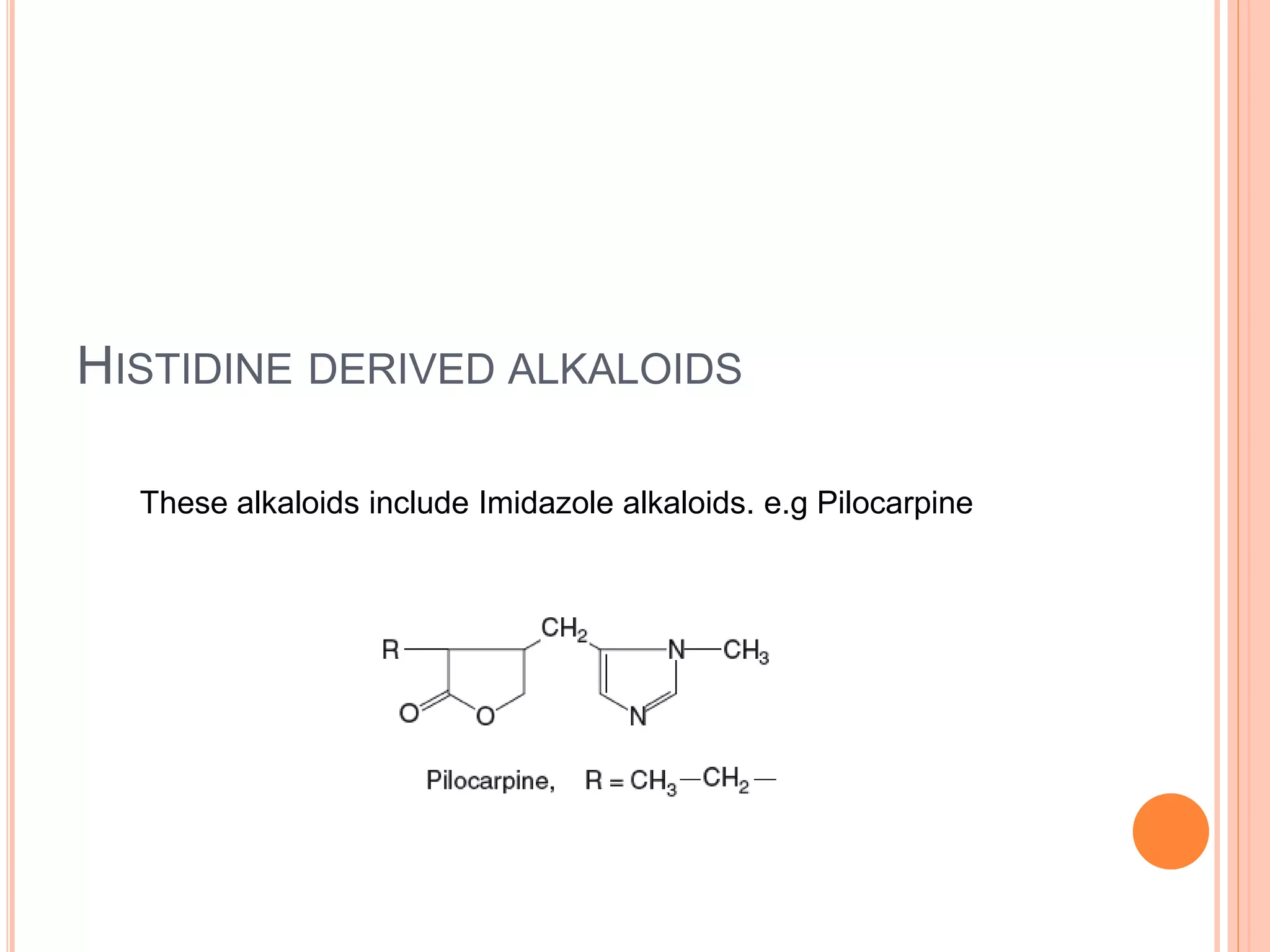
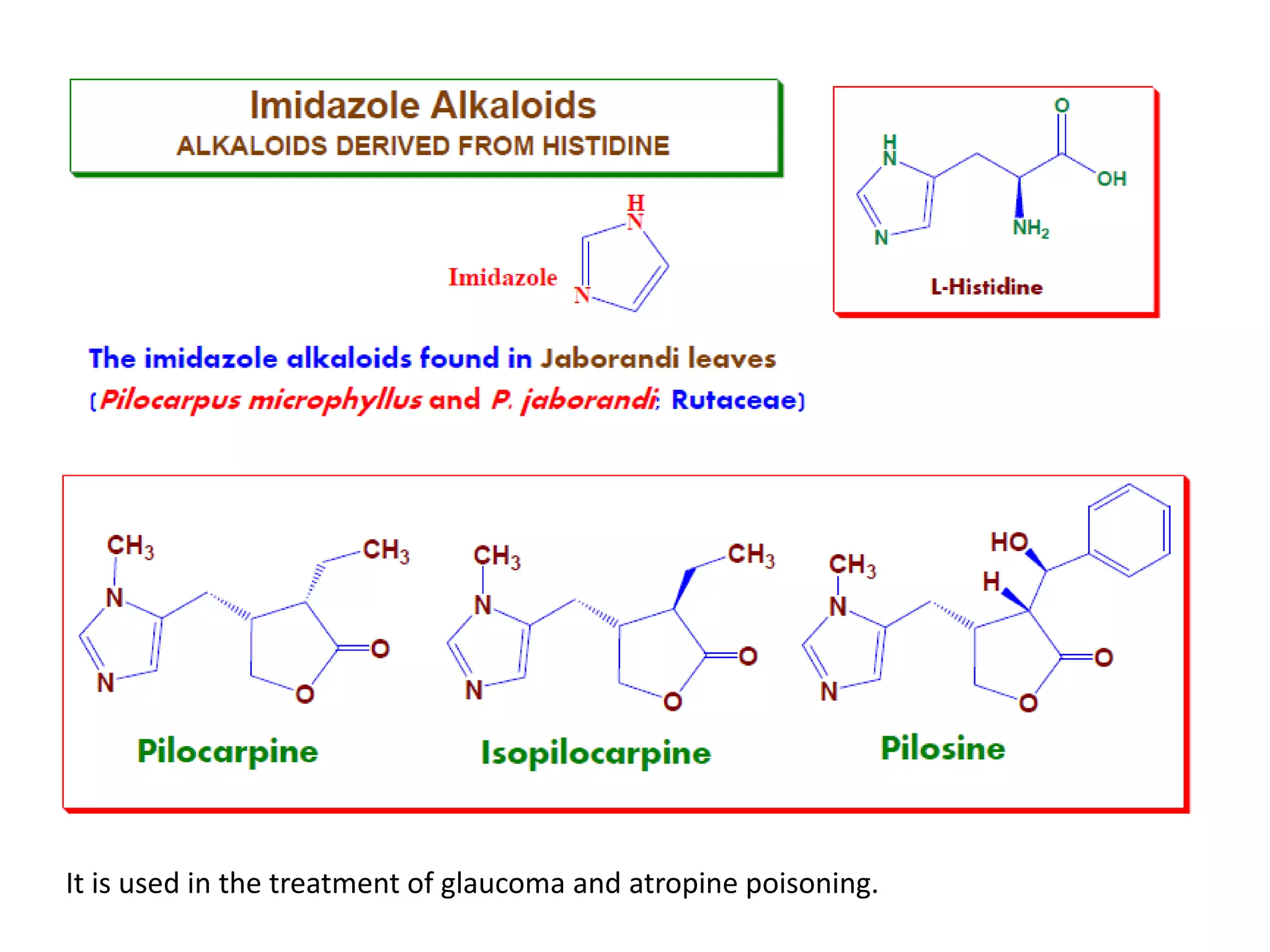
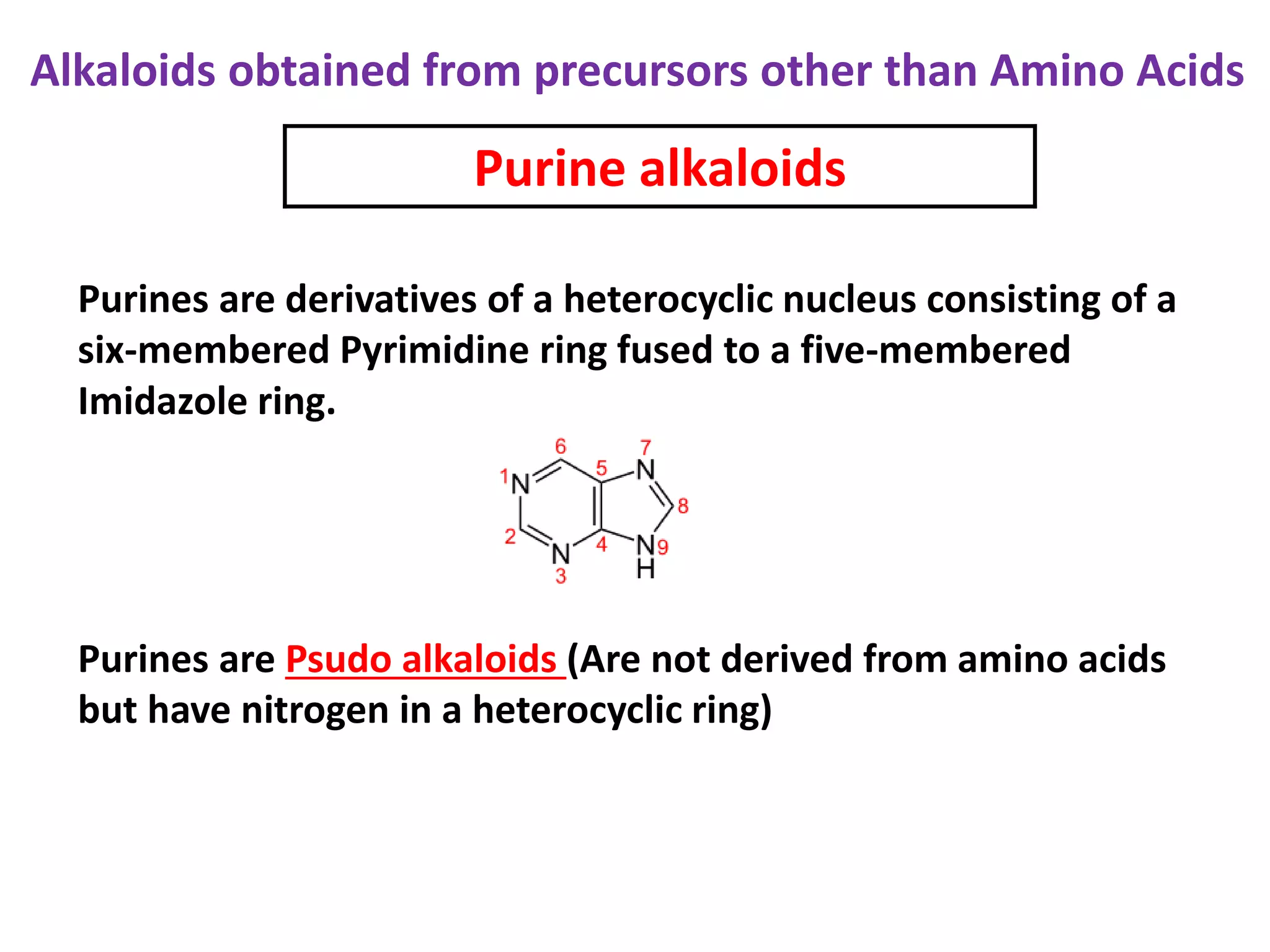
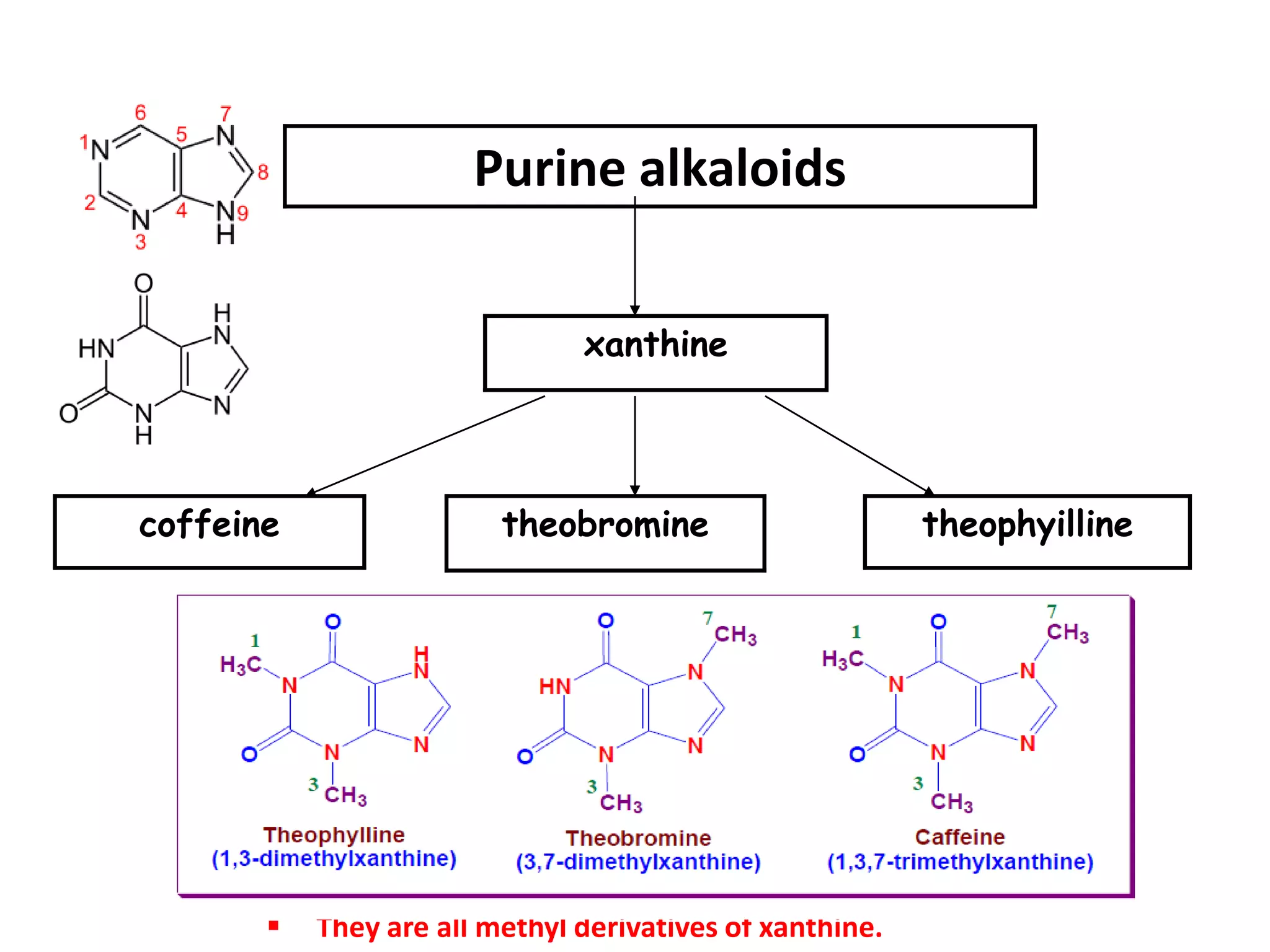
Alkaloids are classified based on their biosynthetic precursors, which include amino acids like ornithine, tryptophan, lysine, phenylalanine, tyrosine, and histidine. Other precursors include purines. Major classes include tropane alkaloids from ornithine, indole alkaloids from tryptophan, quinoline alkaloids from tryptophan, papaver alkaloids from tyrosine, and purine alkaloids like caffeine, theobromine, and theophylline not derived from amino acids. Biosynthesis involves reactions like decarboxylation and transamination of amino acid precursors.