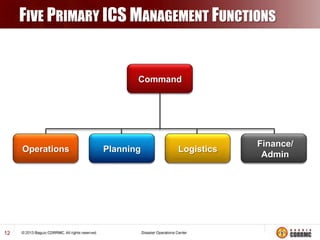
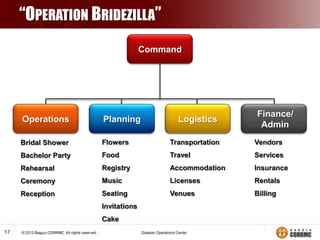
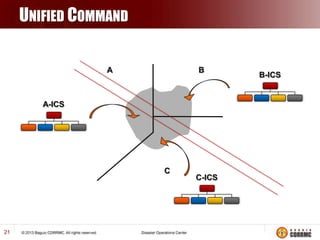
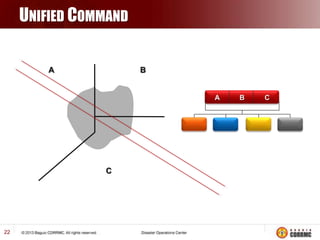
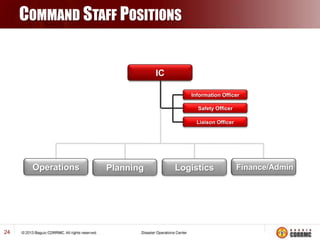
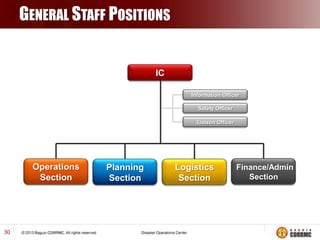
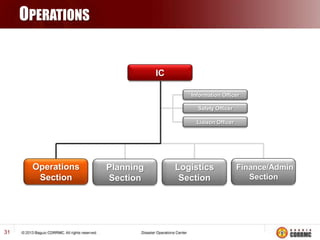
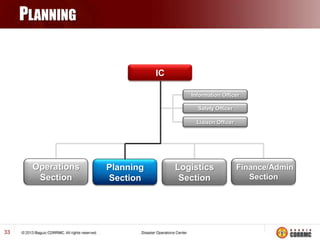
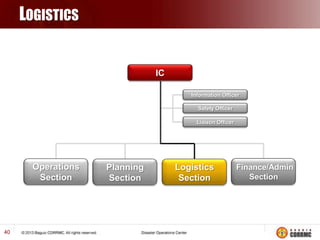
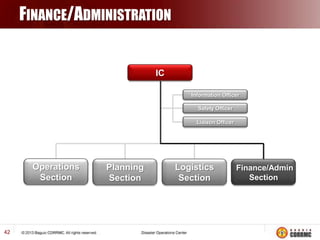
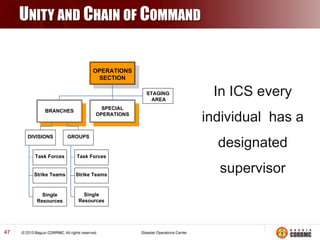
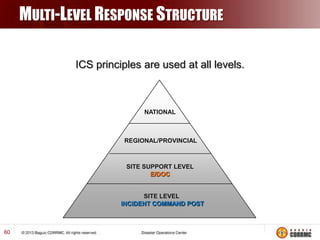
The Incident Command System (ICS) is a structured approach for managing emergency responses, ensuring effective command, control, and coordination at incident sites. The document outlines the need for ICS, its principles, functions, and the roles of various agencies involved in emergency management. It also highlights historical lessons, problem areas, and practical applications of ICS across different scenarios, emphasizing its importance in enhancing emergency response efficiency.