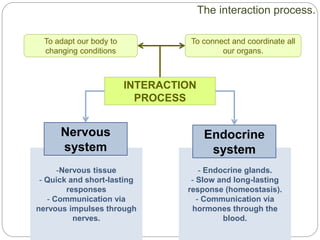
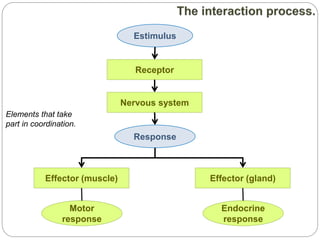
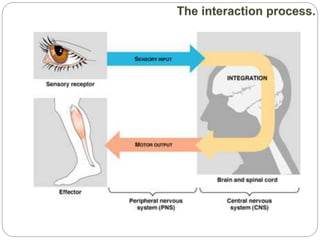
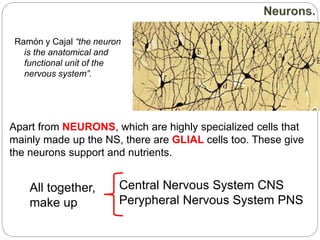
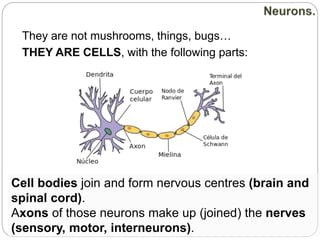
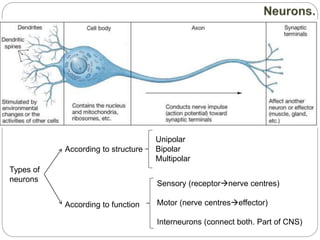
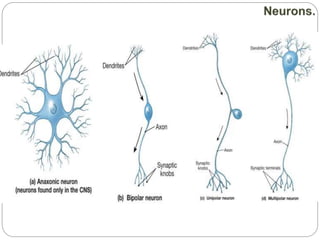
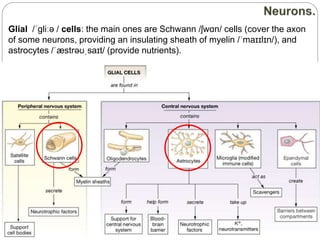
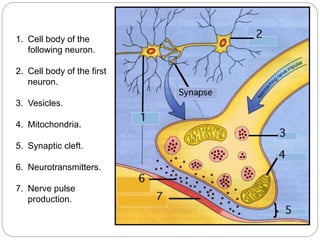
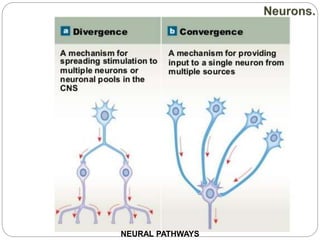
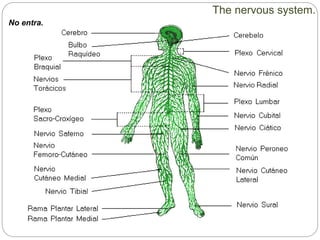
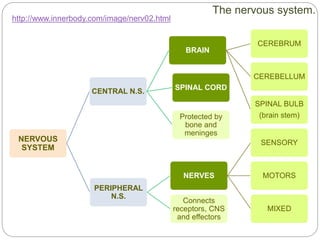
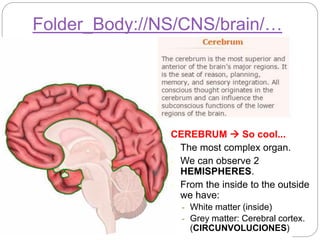
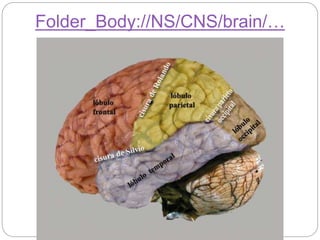
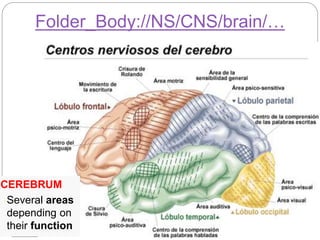
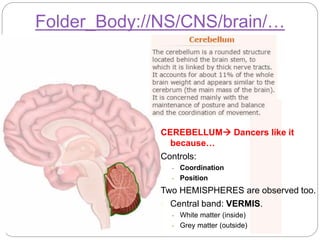
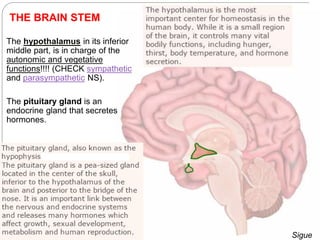
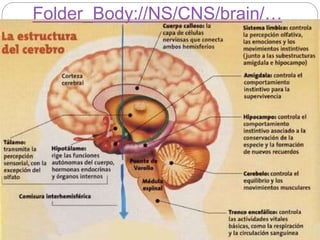
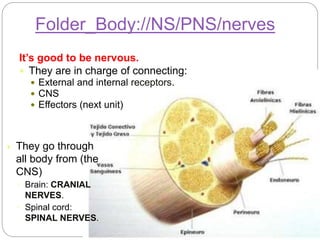
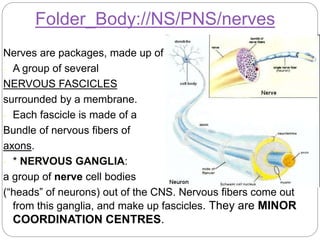
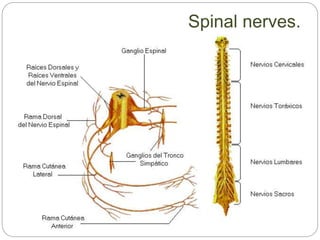
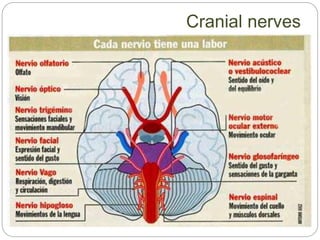
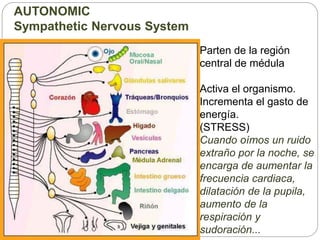
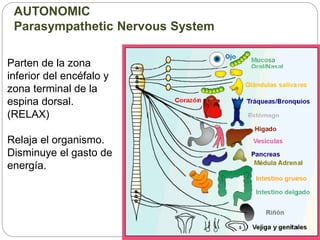
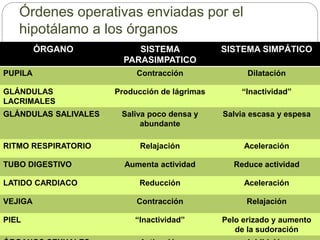
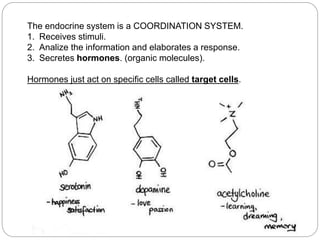
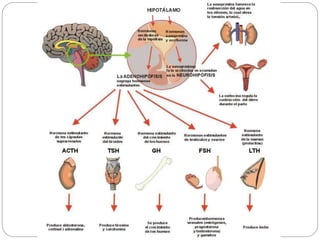
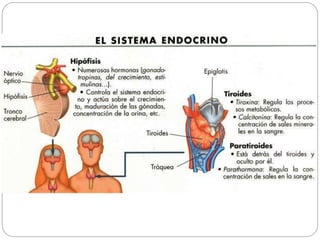
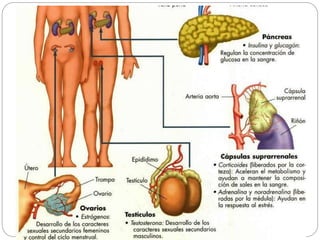
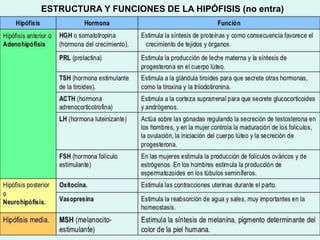
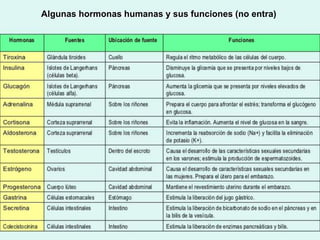
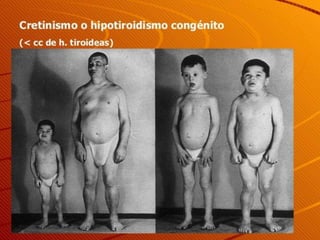
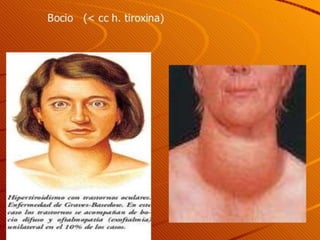
The document describes the interaction between the nervous and endocrine systems in coordinating and regulating bodily functions. The nervous system provides quick responses via electrical signals transmitted along nerves, while the endocrine system provides slower but longer-lasting responses via chemical hormones released into the bloodstream. Together they work to maintain homeostasis and allow the body to adapt to changing internal and external conditions.