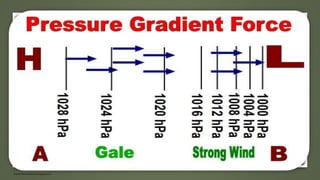
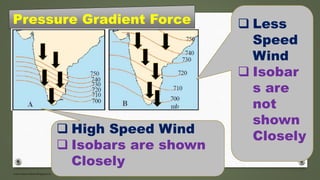
The document discusses various types of winds including planetary winds, periodic winds, and local winds. It provides details on factors influencing atmospheric pressure and wind speed and direction. Some key points summarized:
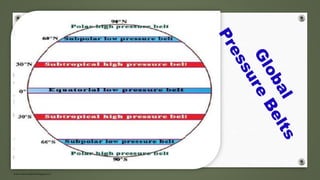
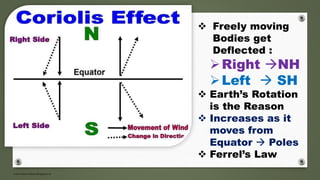
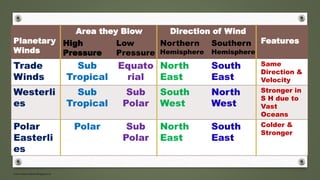
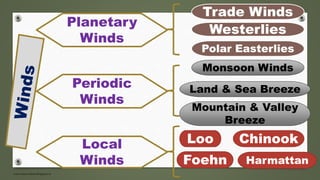
- Planetary winds include trade winds, westerlies, and polar easterlies which are formed between global pressure belts.
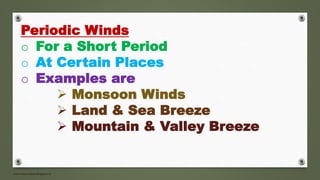
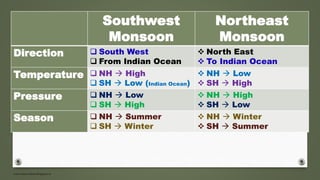
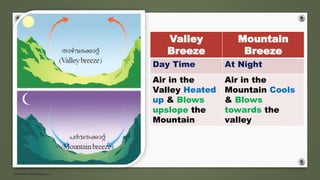
- Periodic winds include monsoon winds and land/sea breezes which occur for short periods in certain places. Monsoons are caused by seasonal pressure and temperature changes.
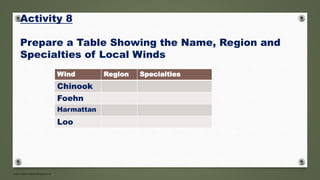
- Local winds arise from local pressure differences and include winds like loo, chinook, foehn and harmattan.
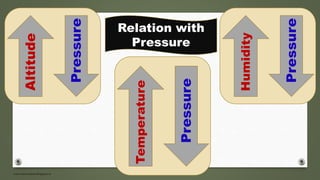
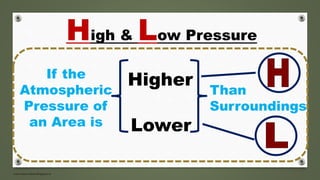
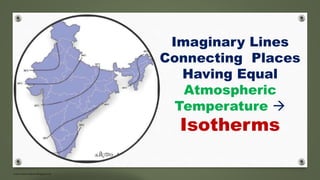
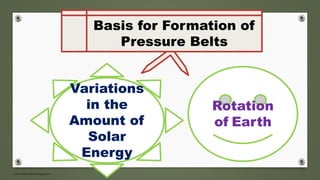
The document examines formation of pressure belts and influence of factors like altitude, temperature