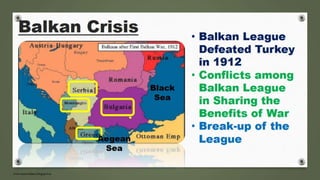
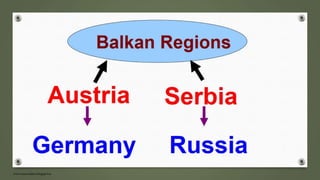
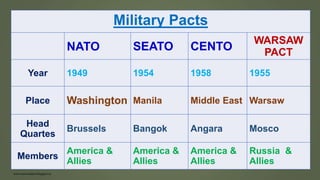
The document discusses the rise of fascism in Italy and Nazism in Germany. It describes the circumstances that allowed Mussolini and Hitler to rise to power, including economic destruction from World War 1, high inflation and unemployment. Both leaders capitalized on the peoples' frustrations by blaming minority groups and using aggressive paramilitary groups to intimidate opponents and seize control. Once in power, they established brutal dictatorships based on extreme nationalism, racism and militarism.