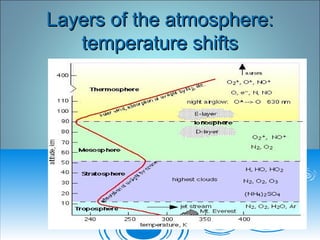
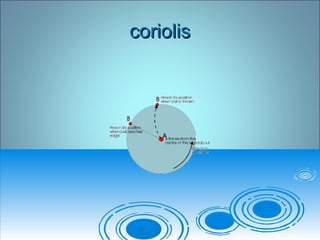
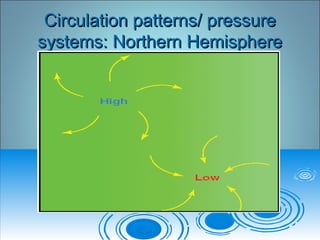
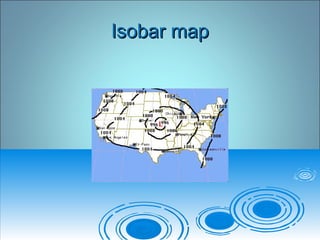
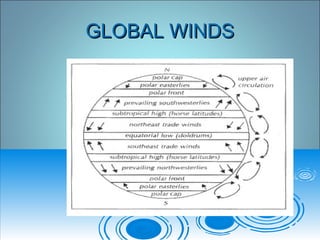
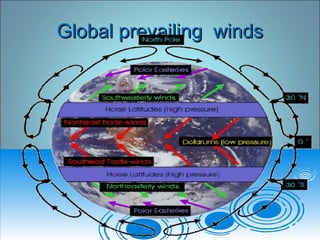
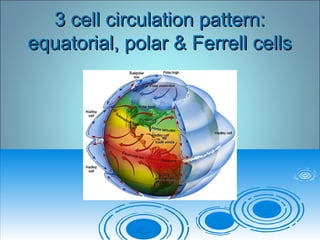
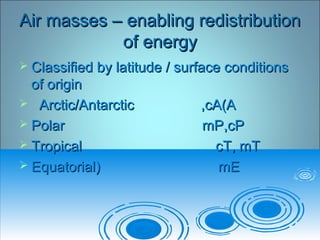
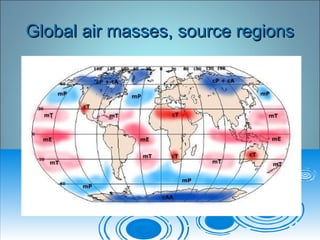
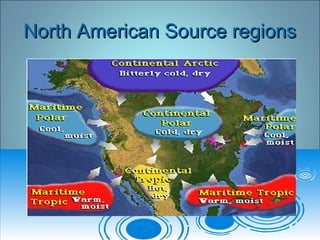
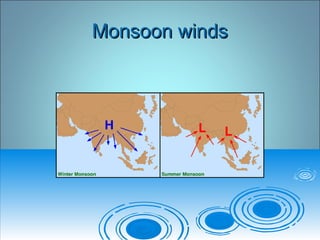
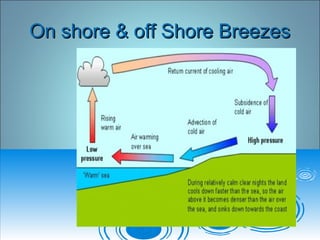
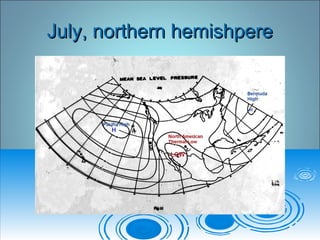
Air pressure and circulation are driven by global patterns of heating and cooling. Warm air rises at the equator and sinks at 30-60° latitude, driving circulation in three main cells. Additional regional patterns arise from pressure gradients, the Coriolis effect, and surface friction. These global and regional wind systems interact with air mass origins to redistribute heat worldwide. Seasonal shifts in insolation cause pressure belts to migrate, altering prevailing winds and weather. Local winds further modify conditions through convection, mountain valleys, and coastal interactions.