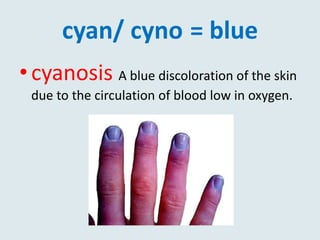
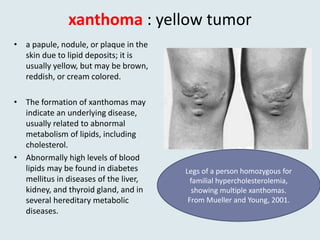
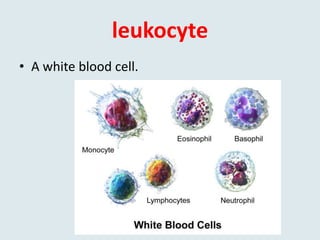
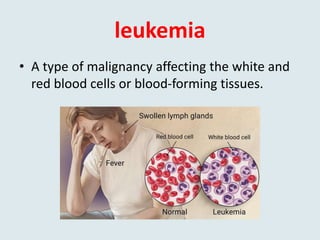
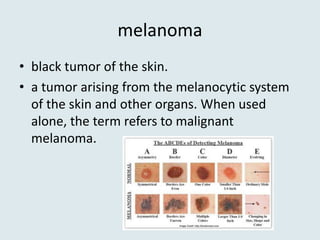
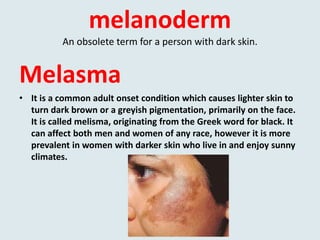
This document defines and provides examples of medical terms derived from Ancient Greek and Latin words referring to color. It discusses terms containing the roots "leuko" meaning white and used in words like leukocyte and leukemia, "melan/melano" meaning black and used in words like melanoma and melasma, "cyno/cyna" meaning blue and used in words like cyanosis and cyanide, and "xantho" meaning yellow and used in words like xanthoma and xanthodermic. Each term is defined and examples are given of diseases, skin conditions, or other medical contexts where the color-related root is used.



![melanoleukoderma
• mottled appearance of
the skin of the neck and
adjacent regions, a rare
manifestation of
syphilis.
• [melano- + leukos,
white, + derma, skin]
• Mottled skin](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/medicaltermscolors-160418133924/85/Medical-terms-colors-10-320.jpg)
![melanophore
• A dermal pigment cell that does not secrete its pigment granules but
participates in rapid color changes by intracellular aggregation and
dispersal of melanosomes; it is well developed in fish, amphibians, and
reptiles, but absent in humans.
• [melano- + . phoros, bearing]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/medicaltermscolors-160418133924/85/Medical-terms-colors-11-320.jpg)