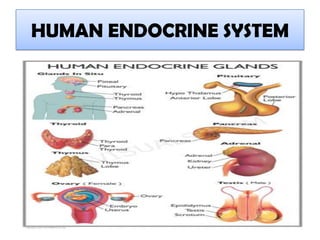
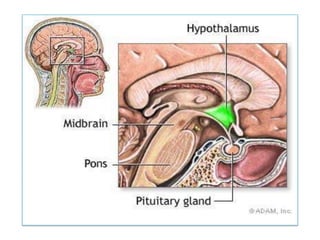
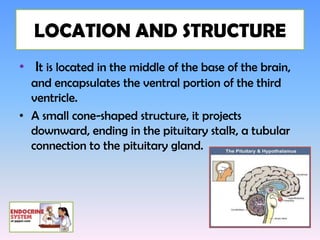
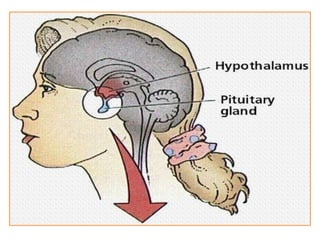
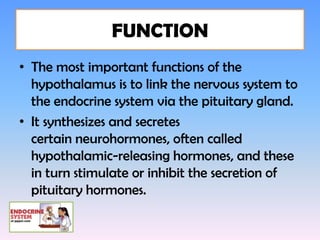
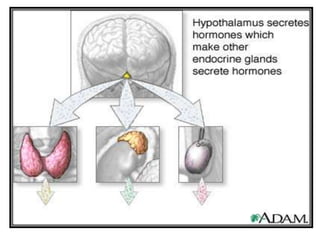
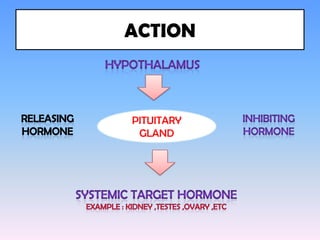
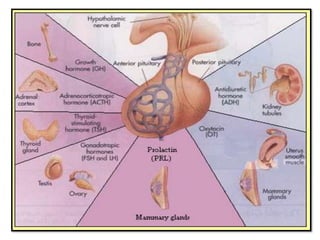
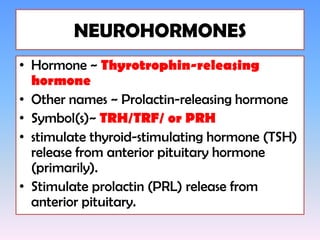
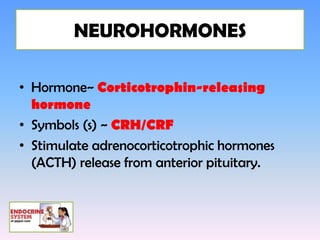
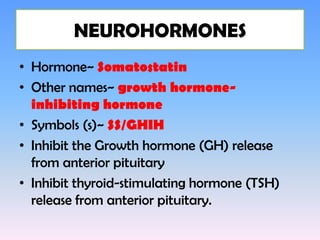
The hypothalamus is a small structure located at the base of the brain that connects the nervous system to the endocrine system. It produces neurohormones that stimulate or inhibit the secretion of hormones from the pituitary gland. Some key neurohormones produced by the hypothalamus include thyrotrophin-releasing hormone, corticotrophin-releasing hormone, gonadotropin-releasing hormone, growth hormone-releasing hormone, and antidiuretic hormone. These neurohormones help regulate important bodily functions.