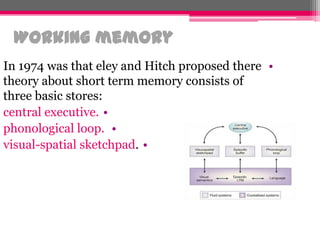
The document discusses the stages of memory formation and retrieval. It explains that memory involves encoding external information through the senses, storing it permanently, and later recalling it in response to cues. It describes the three main types of memory as sensory memory, short-term memory, and long-term memory. Sensory memory holds information for seconds, short-term for seconds to a minute, and long-term relies on neural connections for permanent storage. The document also mentions working memory involves a central executive, phonological loop, and visual-spatial sketchpad according to a 1974 theory.