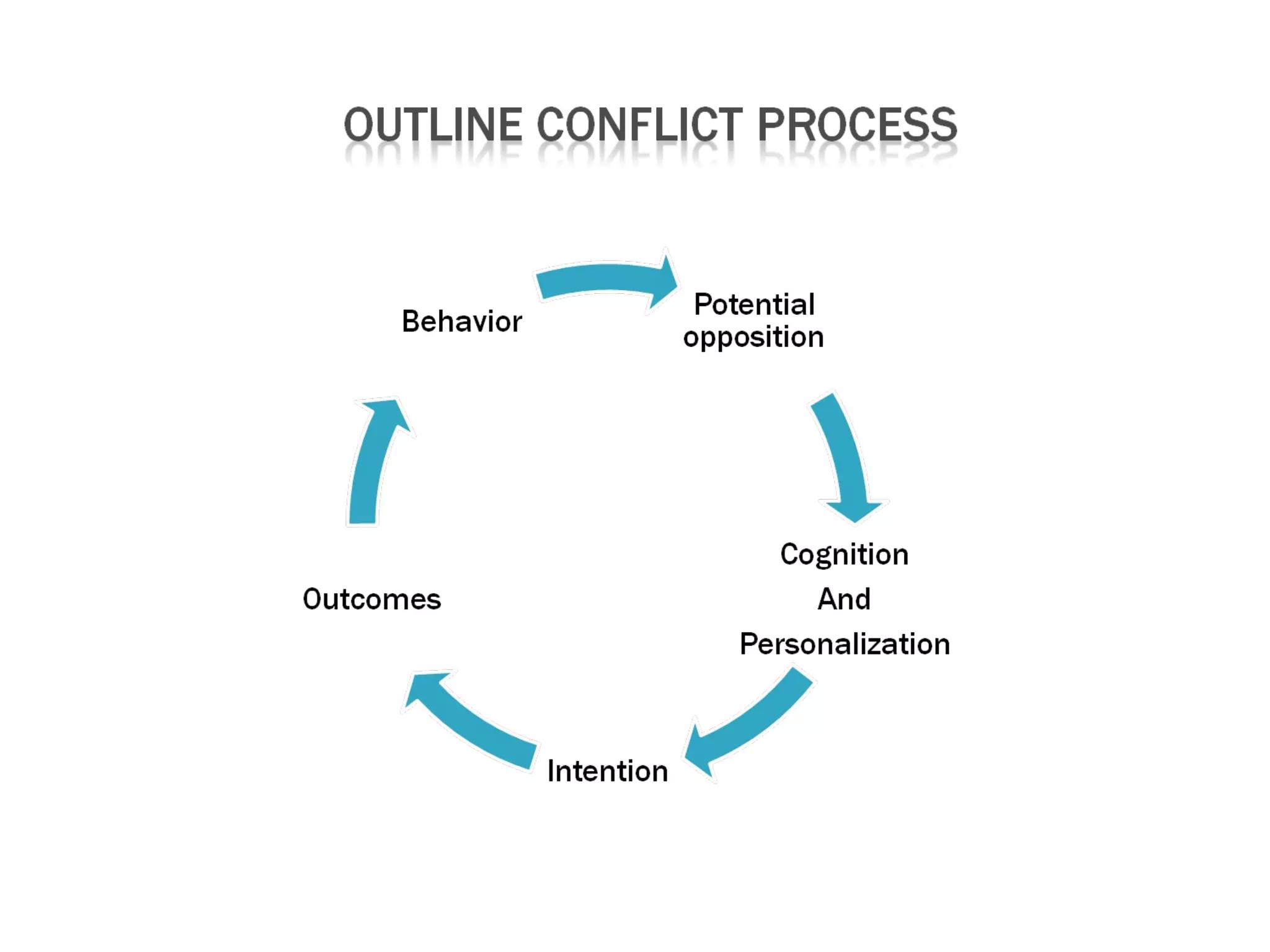
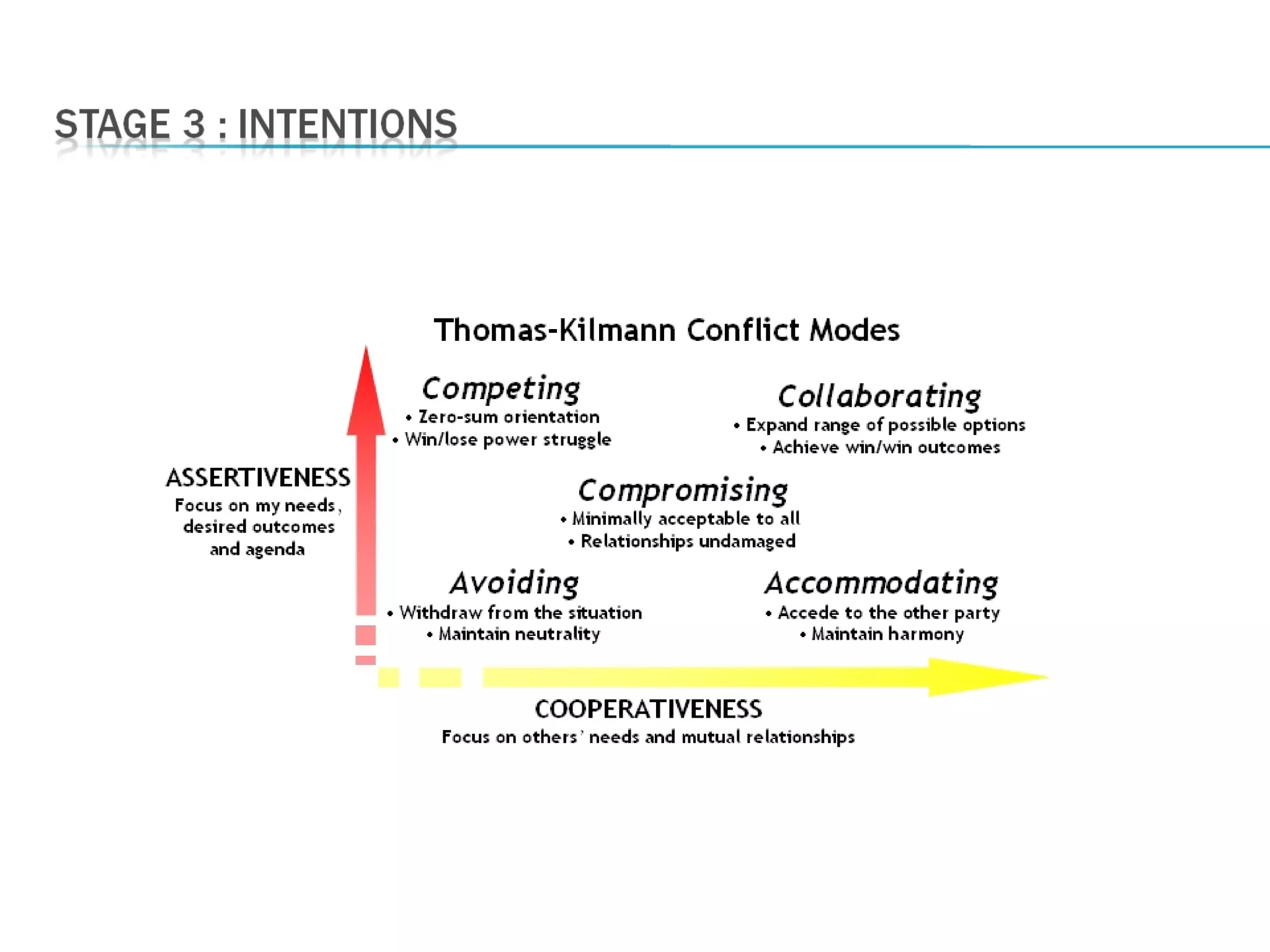
There are three main views of conflict: the traditional view sees it as something to avoid; the human relations view sees it as natural and inevitable; the interactionist view sees some conflict as necessary for group performance. Conflict arises from differences and incompatibilities between parties and can be task-related, relationship-related, or process-related. Negotiation is the process of resolving conflict where parties determine how to allocate scarce resources through bargaining strategies like distributive or integrative bargaining. Personality traits, moods, emotions, and gender can influence negotiation effectiveness. Third parties can take on roles like mediator, arbitrator, conciliator, or consultant to help facilitate conflict resolution.