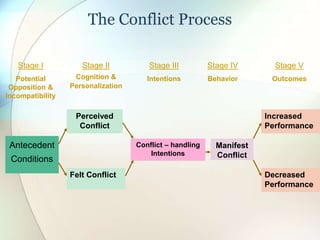
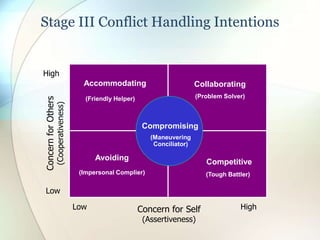
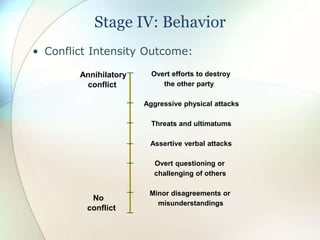
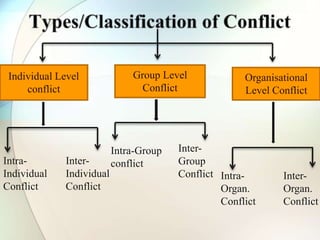
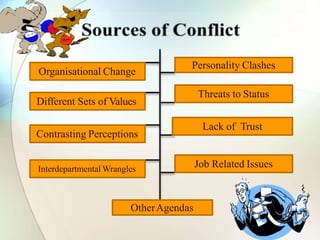
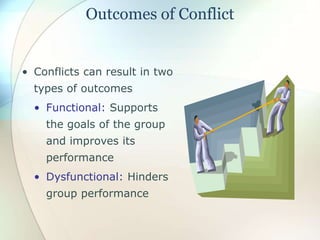
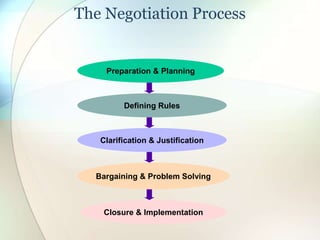
This document discusses conflict, negotiation, and collaboration. It defines conflict as disagreements that cause feelings of adversity. The conflict process involves five stages: potential opposition, cognition and personalization, intentions, behavior, and outcomes. Conflict can be functional and improve group performance or dysfunctional and hinder it. Negotiation is a process where parties try to reach agreement despite disagreement. It discusses distributive and integrative bargaining approaches. The document also outlines conflict resolution and stimulation techniques as well as the roles of third parties in negotiations.