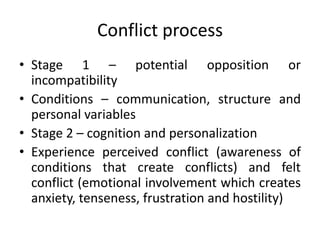
1. Conflict arises when one party feels another has negatively affected something they care about, such as incompatible goals or different interpretations of facts.
2. Views of conflict have transitioned from seeing it as purely harmful, to recognizing it as natural and sometimes necessary for group performance.
3. Negotiation is an exchange between parties to agree on terms, and can be distributive, seeking to divide a fixed amount, or integrative, creating a win-win solution.
4. Managing conflict effectively requires creating a win-win situation, defusing tensions immediately, and finding opportunities in disputes.