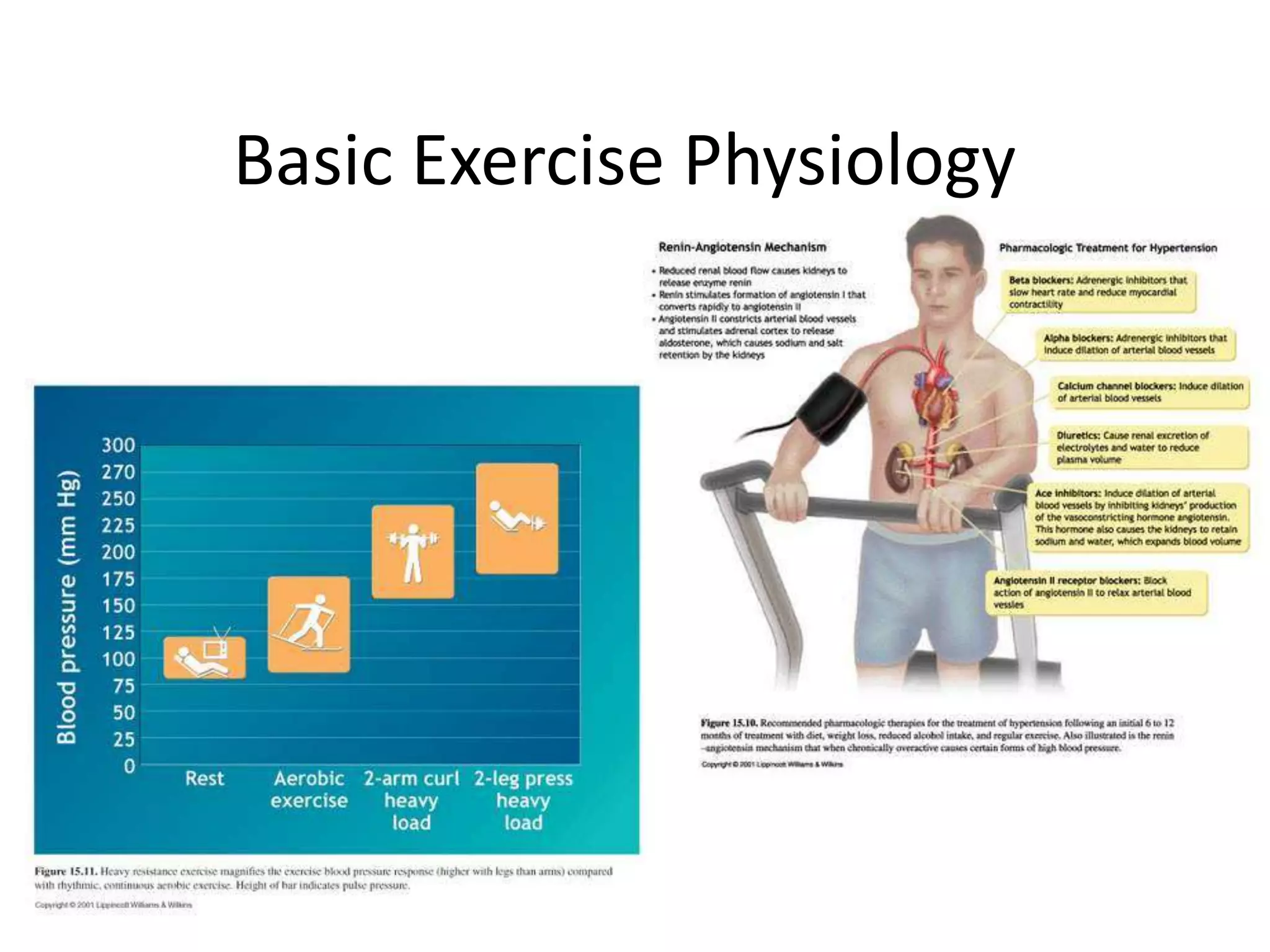
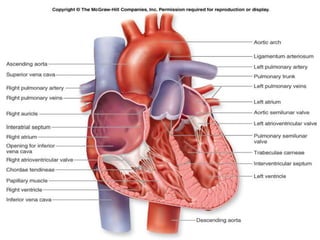
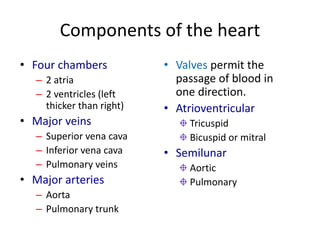
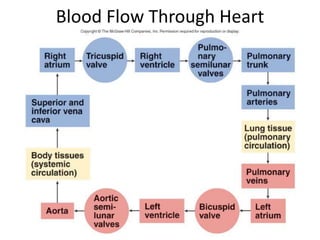
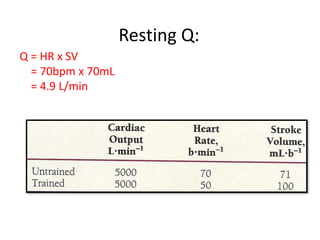
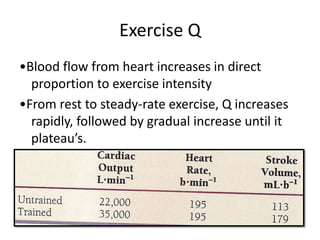
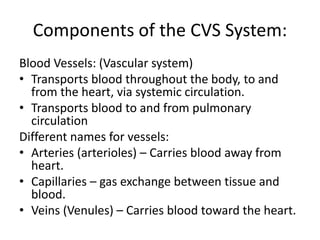
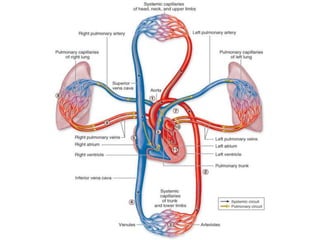
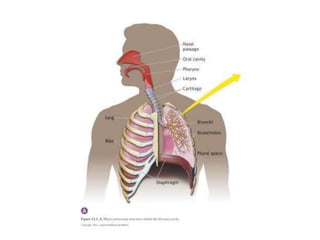
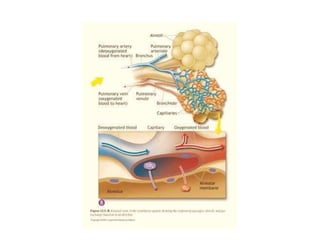
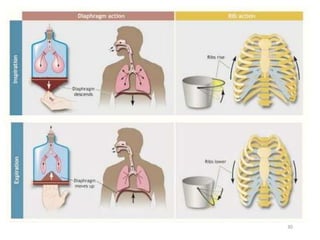
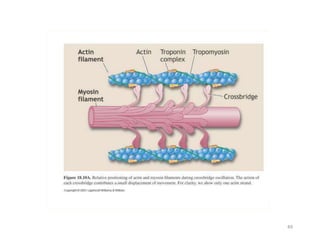
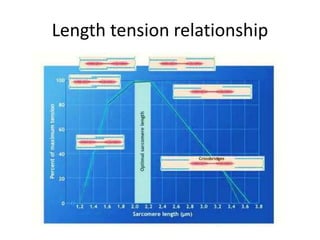
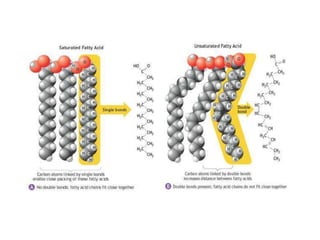
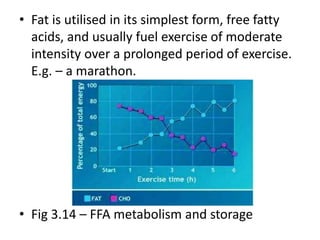
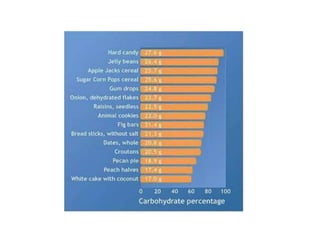
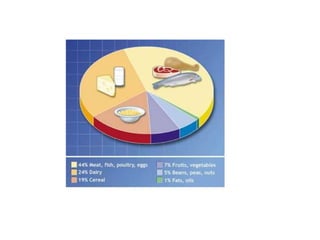
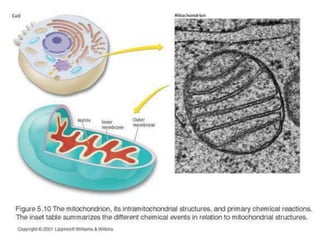
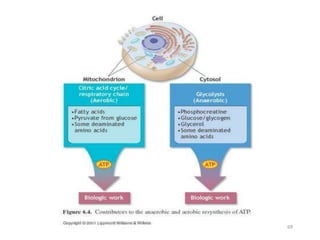
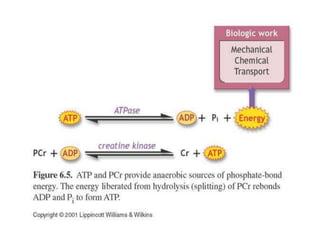
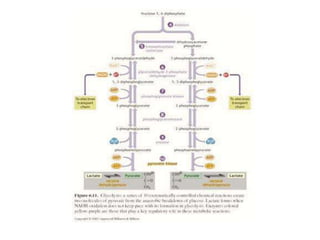
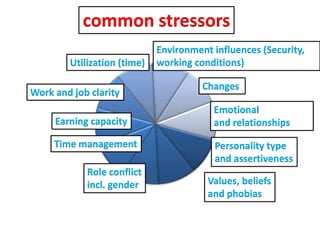
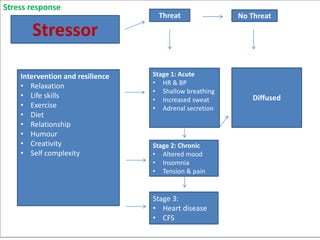
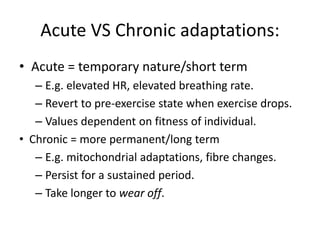
This document provides an overview of basic exercise physiology, covering the cardiovascular, respiratory, neuromuscular, and endocrine systems as well as energy systems. It describes the structure and function of each system at rest and in response to exercise. The cardiovascular system increases cardiac output to meet oxygen demands during exercise. The respiratory system increases ventilation to supply more oxygen to working muscles. The neuromuscular system controls voluntary movement through motor neurons. Hormones released by the endocrine system prepare and regulate the body's response to exercise. There are three energy systems - phosphogen, anaerobic and aerobic - that provide ATP for muscle contraction depending on exercise intensity and duration.