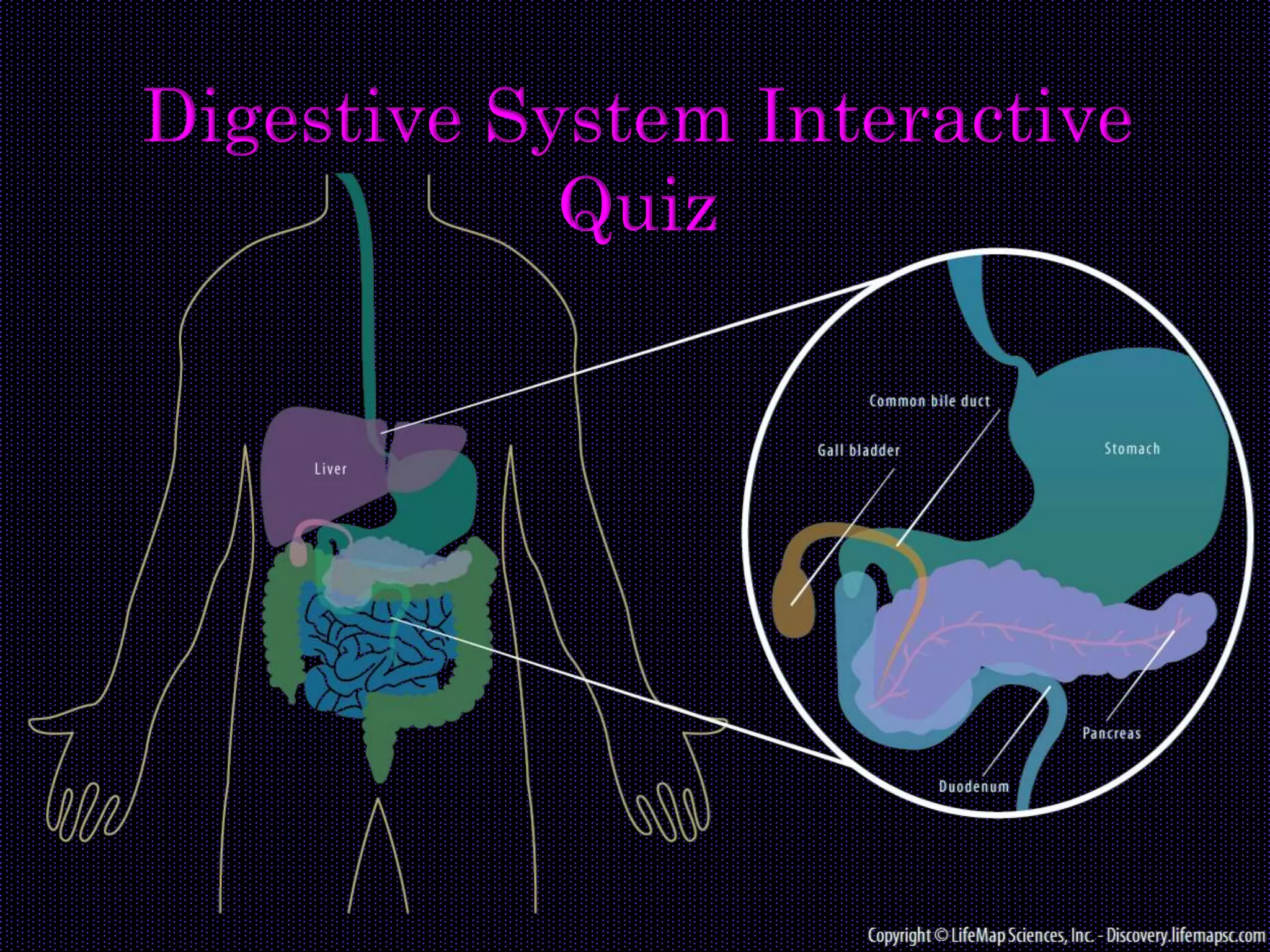
This document contains a quiz on the digestive system with three rounds of multiple choice questions: Easy, Average, and Difficult. The quiz covers topics like the major organs of the digestive system, their functions, enzymes, and processes like ingestion, digestion, absorption and more. It begins with basic identifying questions and progresses to more complex questions testing understanding of the structure and processes of the digestive system.