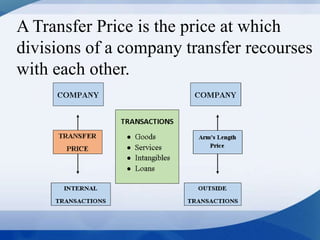
The document discusses the concept of transfer pricing, which is the price at which company divisions trade resources. It outlines various methods of transfer pricing, such as cost-based, market-based, and negotiated pricing, along with their advantages and disadvantages. The objectives of transfer pricing include minimizing tax liability, maintaining divisional autonomy, and enhancing competitive positioning.