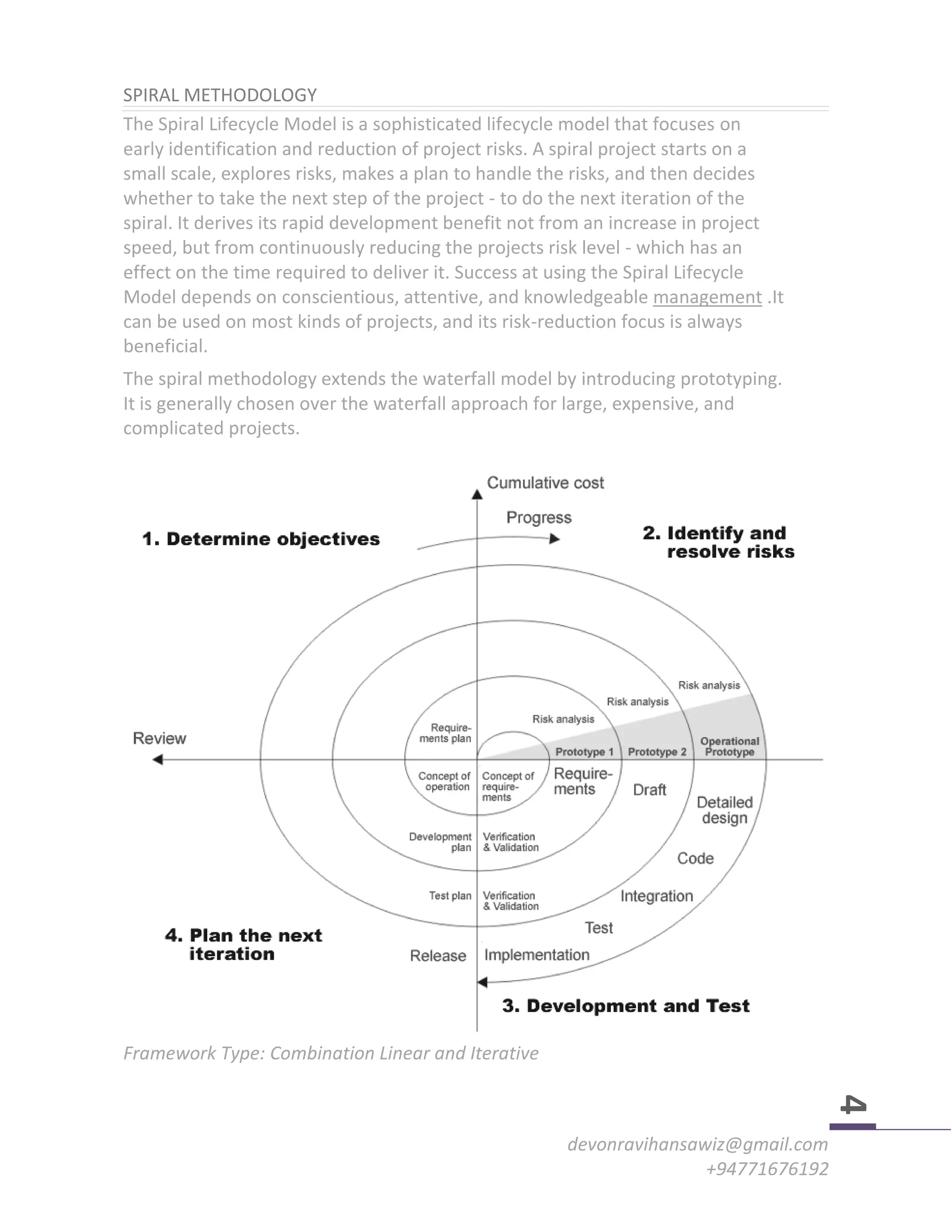
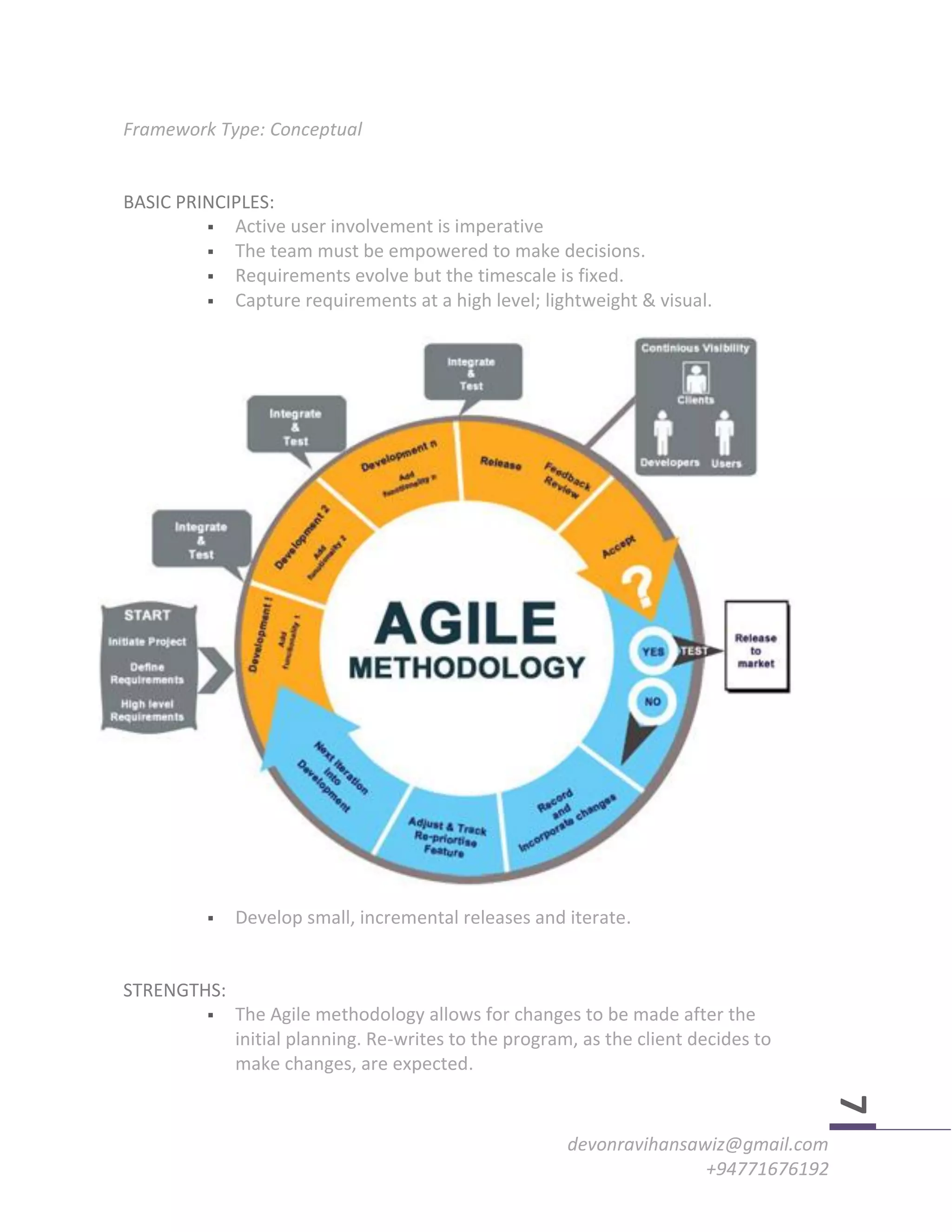
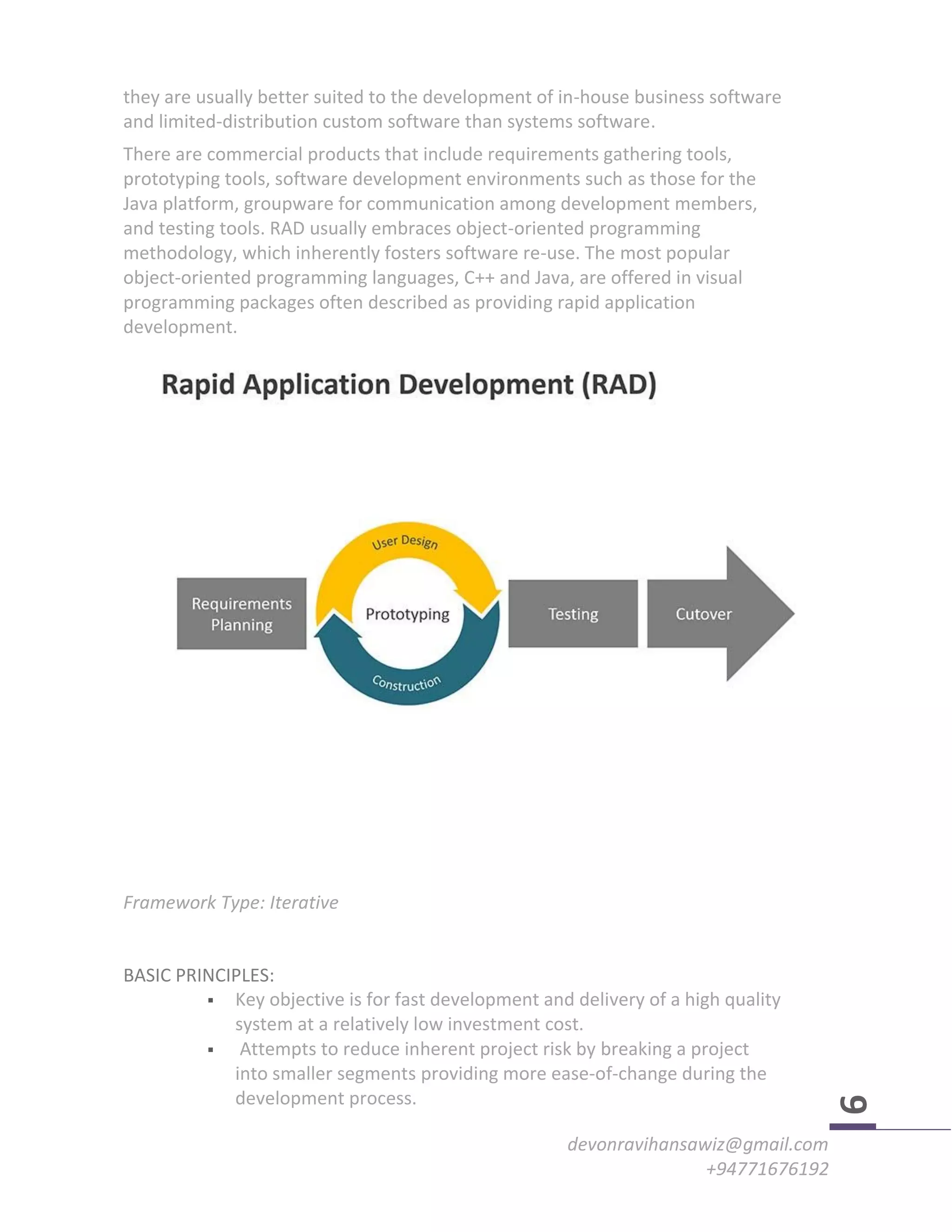
The document discusses various software development methodologies, including the Waterfall, Spiral, and Agile techniques, highlighting their principles, strengths, weaknesses, and appropriate application scenarios. Each methodology caters to different project needs, with Waterfall being linear and rigid, Spiral focusing on risk reduction through iterative development, and Agile promoting flexibility and user involvement. The choice of methodology is crucial and depends on project scale, complexity, and specific requirements.