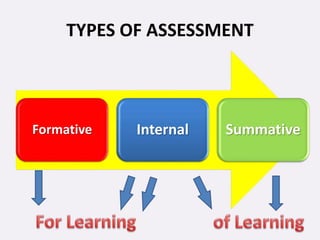
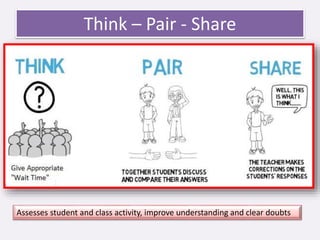
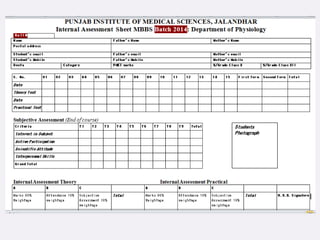
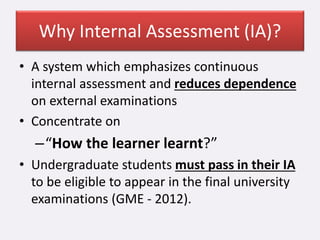
This document discusses internal and formative assessment in medical education. It notes that assessment in medical education requires both quantitative and qualitative information from different sources as well as professional judgment. Summative exams have pitfalls like being subject to chance and not identifying regular versus irregular students. Formative assessment identifies student strengths and weaknesses, guides teaching and learning, and supports self-motivated learning over assessment-driven motives. The document discusses various formative assessment tools and emphasizes that assessment should promote an evolving learning process rather than just grading.