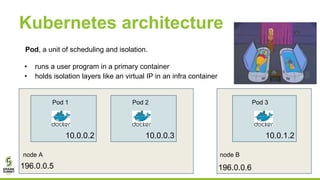
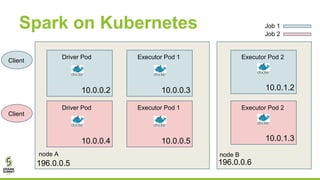
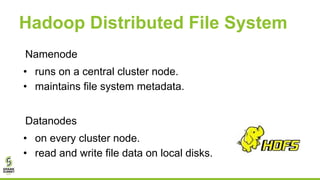
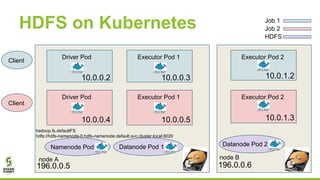
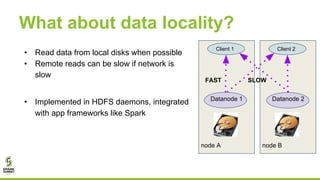
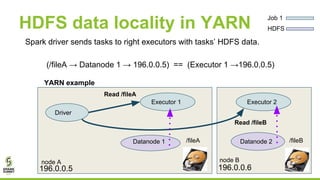
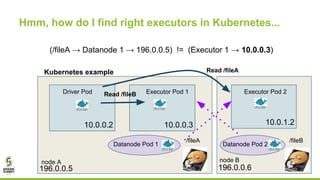
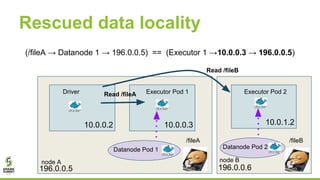
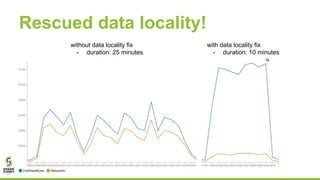
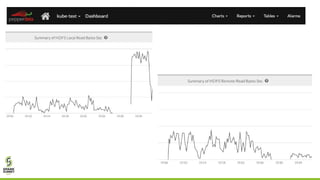
This document outlines lessons learned from running HDFS on Kubernetes, covering key topics such as Kubernetes architecture, integration with big data tools like Spark, and the importance of data locality in enhancing performance. It details the challenges faced, including data locality issues and the solutions implemented to improve task execution efficiency. The document also encourages collaboration and further inquiries, providing links to relevant resources and career opportunities.