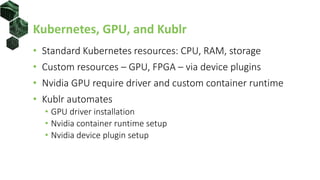
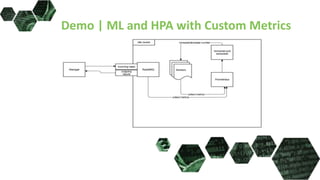
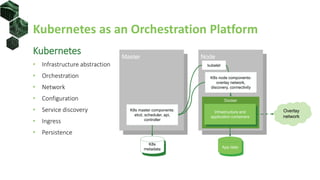
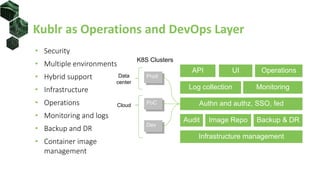
The document discusses the integration of Kubernetes with machine learning (ML) and data science, highlighting common challenges and approaches in ML, such as data preparation and model serving. It outlines the advantages of using Kubernetes for ML, including scalability, cloud compatibility, and resource management, and provides insights into various ML stacks compatible with Kubernetes. Additionally, it reviews operational layers, storage management with HDFS, and automates GPU resource handling in Kubernetes setups.









![Storage| Rook and Ceph
Rook = Ceph operator
Cloud native Ceph
Custom resources:
• Cluster
• Replica pool
• File system
Supported storage types:
• Block (rdb)
• Filesystem
• Object (S3, OpenStack
API)
[1] https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=iwVAvV_lI_Q](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/kubernetesdatascienceandmachinelearning-180607161038/85/Kubernetes-data-science-and-machine-learning-13-320.jpg)