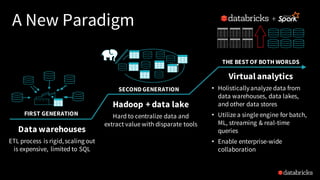
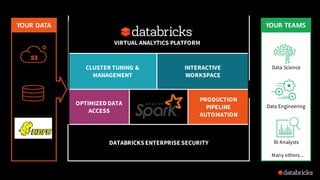
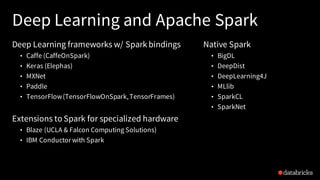
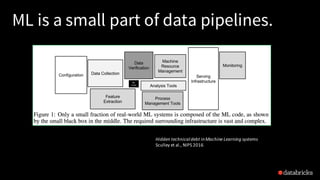
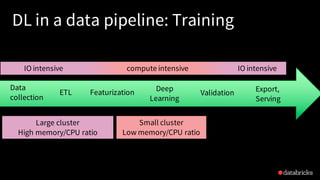
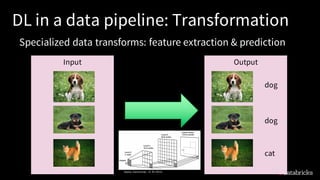
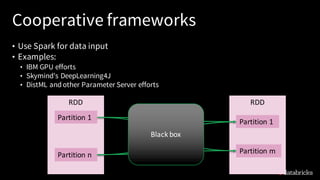
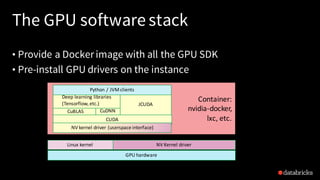
The document discusses deep learning integration with Apache Spark, emphasizing workflows and best practices. It highlights the various deep learning frameworks supported by Spark, including TensorFlow and Keras, and provides insights into data pipeline patterns, monitoring, and the use of GPUs. The talk aims to guide users in optimizing their deep learning applications within the Spark ecosystem.