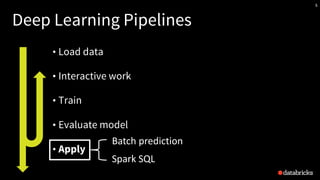
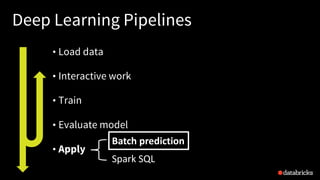
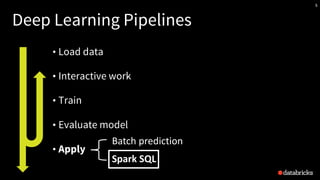
The presentation by Tim Hunter at the Databricks Spark Meetup discusses deep learning at scale using Apache Spark, highlighting its potential and current limitations in industry adoption. It introduces Deep Learning Pipelines, an open-source library designed for ease of use and integration with Spark, catering primarily to Python users while aiming to simplify the deep learning workflow from data loading to model evaluation. Future developments include support for more backends and improved functionalities such as distributed training and text featurization.


















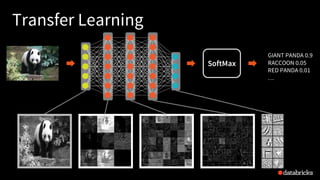
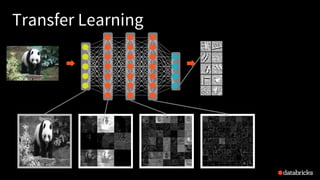
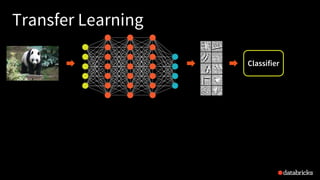
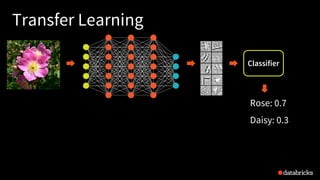

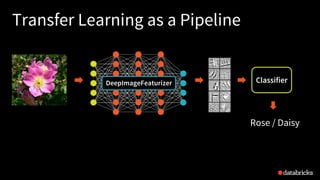
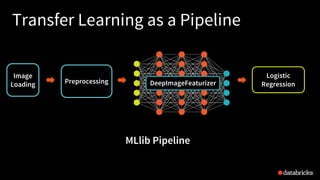
![Transfer Learning as a Pipeline
31put your #assignedhashtag here by setting the
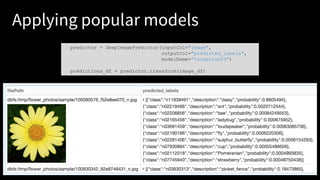
featurizer = DeepImageFeaturizer(inputCol="image",
outputCol="features",
modelName="InceptionV3")
lr = LogisticRegression(labelCol="label")
p = Pipeline(stages=[featurizer, lr])
p_model = p.fit(train_df)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/18-03-14meetupdeeplearningpipelines-180316185245/85/Build-Scale-and-Deploy-Deep-Learning-Pipelines-Using-Apache-Spark-31-320.jpg)


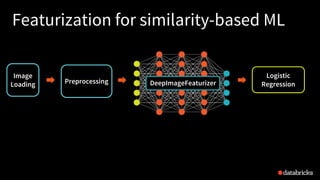
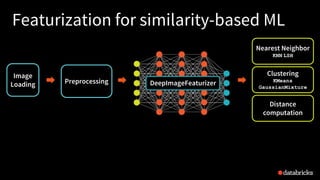
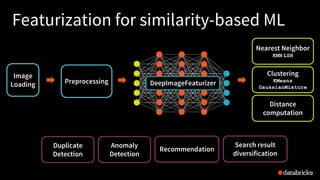

![39
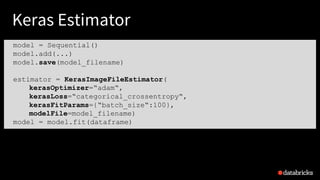
Keras Estimator in Model Selection
estimator = KerasImageFileEstimator(
kerasOptimizer=“adam“,
kerasLoss=“categorical_crossentropy“)
paramGrid = ( ParamGridBuilder()
.addGrid(kerasFitParams=[{“batch_size“:100}, {“batch_size“:200}])
.addGrid(modelFile=[model1, model2]) )
cv = CrossValidator(estimator=estimator,
estimatorParamMaps=paramGrid,
evaluator=BinaryClassificationEvaluator(),
numFolds=3)
best_model = cv.fit(train_df)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/18-03-14meetupdeeplearningpipelines-180316185245/85/Build-Scale-and-Deploy-Deep-Learning-Pipelines-Using-Apache-Spark-39-320.jpg)