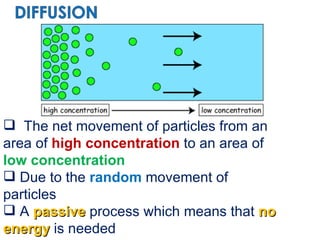
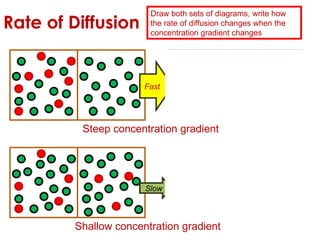
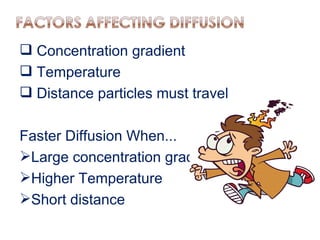
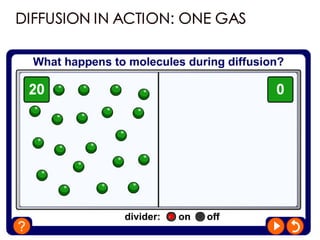
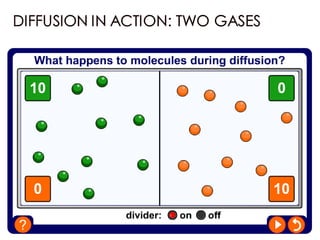
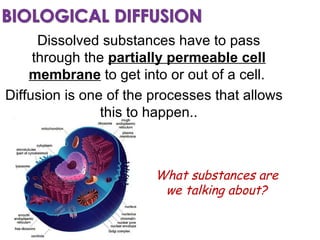
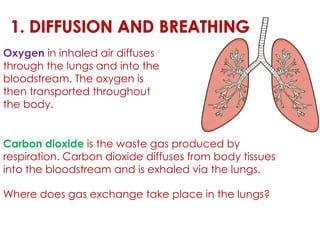
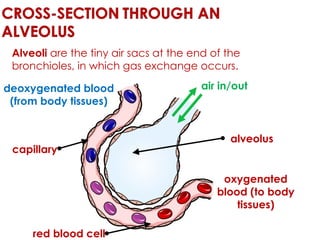
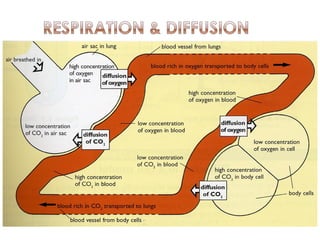
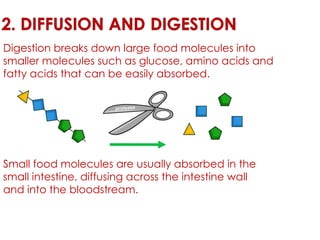
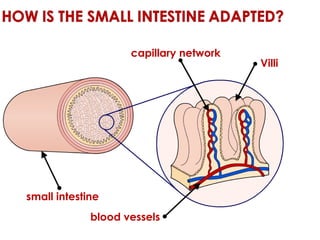
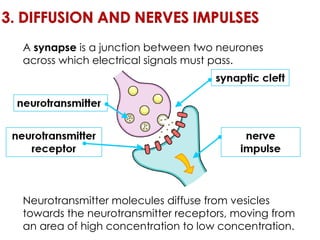
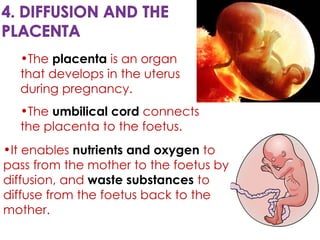
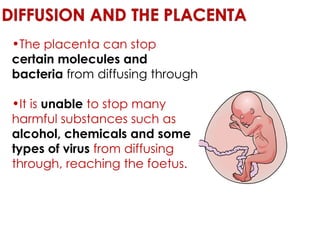
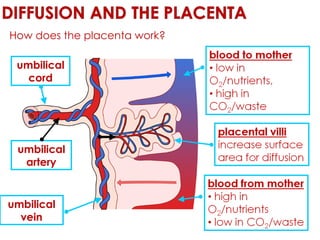
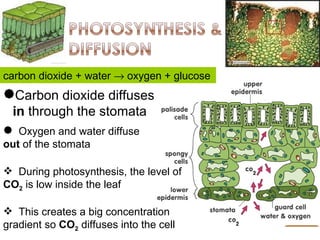
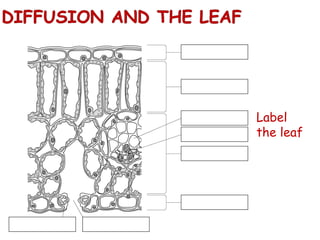
Diffusion is the net movement of particles from an area of high concentration to low concentration due to random particle motion. It is a passive process that does not require energy. The rate of diffusion increases with larger concentration gradients and higher temperatures. Diffusion allows for the exchange of gases and other substances across membranes in cells, organs, and between a mother and unborn child.