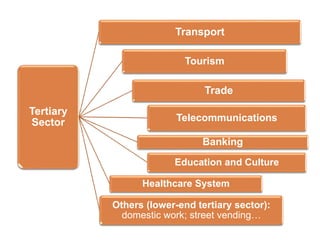
The document outlines the tertiary sector and its various components, including transport, tourism, trade, telecommunications, banking, education, and healthcare. It distinguishes between upper-end and lower-end services, emphasizing the characteristics, classification, and importance of information and communication services. Additionally, it discusses disparities in access to education and healthcare between developed and less developed countries.