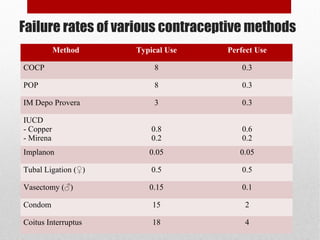
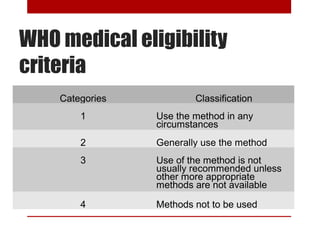
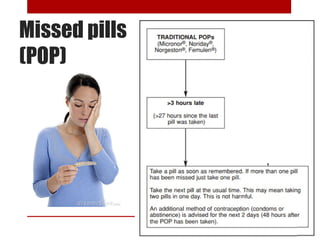
This document discusses various contraceptive methods including hormonal and barrier methods. It provides details on typical and perfect use failure rates. Combined oral contraceptives are discussed in depth, including examples available in Malaysia, when to start, missed pill rules, and side effects. Progestogen-only pills and injectable methods like Depo Provera are also summarized. Intrauterine devices including copper and hormonal options are covered as well as risks, contraindications and timing of insertion. The importance of counseling and tailoring the contraceptive choice to the individual's health needs is emphasized for effective prepregnancy care and contraceptive success.