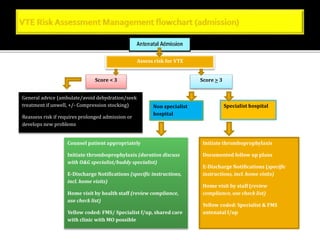
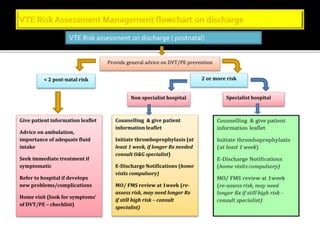
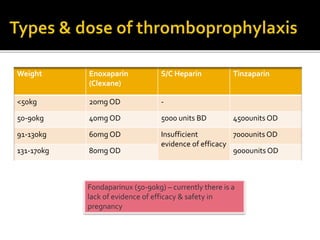
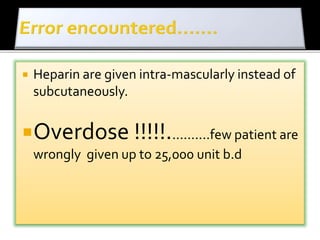
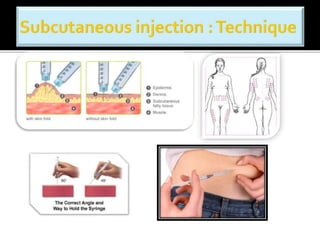
This document discusses strategies to reduce maternal mortality from venous thromboembolism (VTE) in Sarawak, Malaysia. Pulmonary embolism is a leading cause of maternal death in Malaysia and Sarawak. The document outlines a VTE risk assessment and management program for antenatal and postnatal patients. It provides a risk scoring system and recommends thromboprophylaxis for high-risk patients. LMWHs like enoxaparin and tinzaparin are preferred treatments but are porcine-derived, requiring discussion with Muslim patients. Unfractionated heparin and fondaparinux are alternatives but have limitations. The program aims to standardize VTE screening and protocols across health clinics and hospitals in Sar