The document shows the steps to calculate the variance and standard deviation of a probability distribution. It involves creating columns for the random variable x, the probability P(x), the products x*P(x) and x^2*P(x). The mean is calculated as the sum of x*P(x). The variance is calculated as the sum of x^2*P(x) - the mean squared.



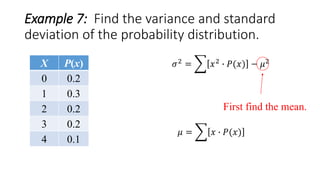
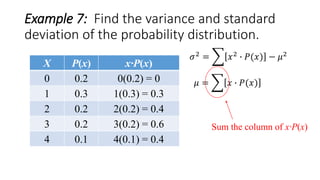
![Example 7: Find the variance and standard
deviation of the probability distribution.
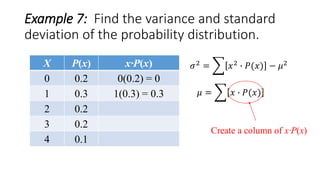
X P(x) x∙P(x)
0 0.2 0(0.2) = 0
1 0.3 1(0.3) = 0.3
2 0.2 2(0.2) = 0.4
3 0.2 3(0.2) = 0.6
4 0.1 4(0.1) = 0.4
𝜇 = 𝑥 ∙ 𝑃(𝑥)
Sum the column of x∙P(x)
Σ[x∙P(x)]=1.7
𝜎2 = 𝑥2 ∙ 𝑃(𝑥) − 𝜇2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/varianceandstandarddeviationofadiscreterandomvariable-160626135719/85/Variance-and-standard-deviation-of-a-discrete-random-variable-13-320.jpg)
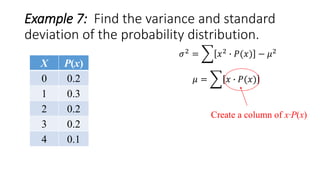
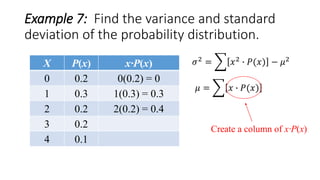
![Example 7: Find the variance and standard
deviation of the probability distribution.
X P(x) x∙P(x)
0 0.2 0(0.2) = 0
1 0.3 1(0.3) = 0.3
2 0.2 2(0.2) = 0.4
3 0.2 3(0.2) = 0.6
4 0.1 4(0.1) = 0.4
𝜇 = 𝑥 ∙ 𝑃(𝑥) = 1.7
Σ[x∙P(x)]=1.7
𝜎2 = 𝑥2 ∙ 𝑃(𝑥) − 𝜇2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/varianceandstandarddeviationofadiscreterandomvariable-160626135719/85/Variance-and-standard-deviation-of-a-discrete-random-variable-14-320.jpg)
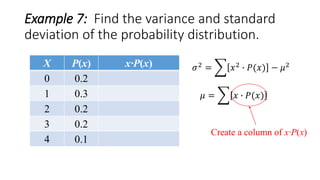
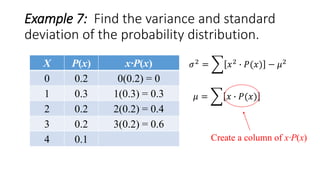
![Example 7: Find the variance and standard
deviation of the probability distribution.
X P(x) x∙P(x)
0 0.2 0(0.2) = 0
1 0.3 1(0.3) = 0.3
2 0.2 2(0.2) = 0.4
3 0.2 3(0.2) = 0.6
4 0.1 4(0.1) = 0.4
𝜇 = 𝑥 ∙ 𝑃(𝑥) = 1.7
Σ[x∙P(x)]=1.7
𝜎2
= 𝑥2
∙ 𝑃(𝑥) − 𝜇2
Create a column of x2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/varianceandstandarddeviationofadiscreterandomvariable-160626135719/85/Variance-and-standard-deviation-of-a-discrete-random-variable-15-320.jpg)
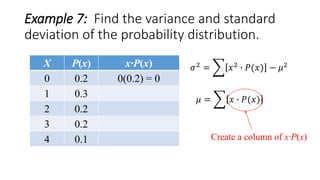
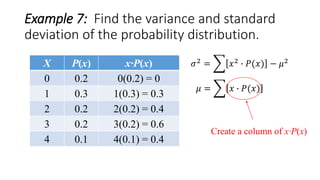
![Example 7: Find the variance and standard
deviation of the probability distribution.
X P(x) x∙P(x) x2
0 0.2 0(0.2) = 0
1 0.3 1(0.3) = 0.3
2 0.2 2(0.2) = 0.4
3 0.2 3(0.2) = 0.6
4 0.1 4(0.1) = 0.4
𝜇 = 𝑥 ∙ 𝑃(𝑥) = 1.7
Σ[x∙P(x)]=1.7
𝜎2
= 𝑥2
∙ 𝑃(𝑥) − 𝜇2
Create a column of x2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/varianceandstandarddeviationofadiscreterandomvariable-160626135719/85/Variance-and-standard-deviation-of-a-discrete-random-variable-16-320.jpg)
![Example 7: Find the variance and standard
deviation of the probability distribution.
X P(x) x∙P(x) x2
0 0.2 0(0.2) = 0 02 = 0
1 0.3 1(0.3) = 0.3
2 0.2 2(0.2) = 0.4
3 0.2 3(0.2) = 0.6
4 0.1 4(0.1) = 0.4
𝜇 = 𝑥 ∙ 𝑃(𝑥) = 1.7
Σ[x∙P(x)]=1.7
𝜎2
= 𝑥2
∙ 𝑃(𝑥) − 𝜇2
Create a column of x2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/varianceandstandarddeviationofadiscreterandomvariable-160626135719/85/Variance-and-standard-deviation-of-a-discrete-random-variable-17-320.jpg)
![Example 7: Find the variance and standard
deviation of the probability distribution.
X P(x) x∙P(x) x2
0 0.2 0(0.2) = 0 02 = 0
1 0.3 1(0.3) = 0.3 12 = 1
2 0.2 2(0.2) = 0.4
3 0.2 3(0.2) = 0.6
4 0.1 4(0.1) = 0.4
𝜇 = 𝑥 ∙ 𝑃(𝑥) = 1.7
Σ[x∙P(x)]=1.7
𝜎2
= 𝑥2
∙ 𝑃(𝑥) − 𝜇2
Create a column of x2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/varianceandstandarddeviationofadiscreterandomvariable-160626135719/85/Variance-and-standard-deviation-of-a-discrete-random-variable-18-320.jpg)
![Example 7: Find the variance and standard
deviation of the probability distribution.
X P(x) x∙P(x) x2
0 0.2 0(0.2) = 0 02 = 0
1 0.3 1(0.3) = 0.3 12 = 1
2 0.2 2(0.2) = 0.4 22 = 4
3 0.2 3(0.2) = 0.6
4 0.1 4(0.1) = 0.4
𝜇 = 𝑥 ∙ 𝑃(𝑥) = 1.7
Σ[x∙P(x)]=1.7
𝜎2
= 𝑥2
∙ 𝑃(𝑥) − 𝜇2
Create a column of x2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/varianceandstandarddeviationofadiscreterandomvariable-160626135719/85/Variance-and-standard-deviation-of-a-discrete-random-variable-19-320.jpg)
![Example 7: Find the variance and standard
deviation of the probability distribution.
X P(x) x∙P(x) x2
0 0.2 0(0.2) = 0 02 = 0
1 0.3 1(0.3) = 0.3 12 = 1
2 0.2 2(0.2) = 0.4 22 = 4
3 0.2 3(0.2) = 0.6 32 = 9
4 0.1 4(0.1) = 0.4
𝜇 = 𝑥 ∙ 𝑃(𝑥) = 1.7
Σ[x∙P(x)]=1.7
𝜎2
= 𝑥2
∙ 𝑃(𝑥) − 𝜇2
Create a column of x2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/varianceandstandarddeviationofadiscreterandomvariable-160626135719/85/Variance-and-standard-deviation-of-a-discrete-random-variable-20-320.jpg)
![Example 7: Find the variance and standard
deviation of the probability distribution.
X P(x) x∙P(x) x2
0 0.2 0(0.2) = 0 02 = 0
1 0.3 1(0.3) = 0.3 12 = 1
2 0.2 2(0.2) = 0.4 22 = 4
3 0.2 3(0.2) = 0.6 32 = 9
4 0.1 4(0.1) = 0.4 42 = 16
𝜇 = 𝑥 ∙ 𝑃(𝑥) = 1.7
Σ[x∙P(x)]=1.7
𝜎2
= 𝑥2
∙ 𝑃(𝑥) − 𝜇2
Create a column of x2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/varianceandstandarddeviationofadiscreterandomvariable-160626135719/85/Variance-and-standard-deviation-of-a-discrete-random-variable-21-320.jpg)
![Example 7: Find the variance and standard
deviation of the probability distribution.
X P(x) x∙P(x) x2
0 0.2 0(0.2) = 0 02 = 0
1 0.3 1(0.3) = 0.3 12 = 1
2 0.2 2(0.2) = 0.4 22 = 4
3 0.2 3(0.2) = 0.6 32 = 9
4 0.1 4(0.1) = 0.4 42 = 16
𝜇 = 𝑥 ∙ 𝑃(𝑥) = 1.7
Σ[x∙P(x)]=1.7
𝜎2
= 𝑥2
∙ 𝑃(𝑥) − 𝜇2
Create a column of x2∙P(x)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/varianceandstandarddeviationofadiscreterandomvariable-160626135719/85/Variance-and-standard-deviation-of-a-discrete-random-variable-22-320.jpg)
![Example 7: Find the variance and standard
deviation of the probability distribution.
X P(x) x∙P(x) x2 x2∙P(x)
0 0.2 0(0.2) = 0 02 = 0
1 0.3 1(0.3) = 0.3 12 = 1
2 0.2 2(0.2) = 0.4 22 = 4
3 0.2 3(0.2) = 0.6 32 = 9
4 0.1 4(0.1) = 0.4 42 = 16
𝜇 = 𝑥 ∙ 𝑃(𝑥) = 1.7
Σ[x∙P(x)]=1.7
𝜎2
= 𝑥2
∙ 𝑃(𝑥) − 𝜇2
Create a column of x2∙P(x)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/varianceandstandarddeviationofadiscreterandomvariable-160626135719/85/Variance-and-standard-deviation-of-a-discrete-random-variable-23-320.jpg)
![Example 7: Find the variance and standard
deviation of the probability distribution.
X P(x) x∙P(x) x2 x2∙P(x)
0 0.2 0(0.2) = 0 02 = 0 0(0.2) = 0
1 0.3 1(0.3) = 0.3 12 = 1
2 0.2 2(0.2) = 0.4 22 = 4
3 0.2 3(0.2) = 0.6 32 = 9
4 0.1 4(0.1) = 0.4 42 = 16
𝜇 = 𝑥 ∙ 𝑃(𝑥) = 1.7
Σ[x∙P(x)]=1.7
𝜎2
= 𝑥2
∙ 𝑃(𝑥) − 𝜇2
Create a column of x2∙P(x)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/varianceandstandarddeviationofadiscreterandomvariable-160626135719/85/Variance-and-standard-deviation-of-a-discrete-random-variable-24-320.jpg)
![Example 7: Find the variance and standard
deviation of the probability distribution.
X P(x) x∙P(x) x2 x2∙P(x)
0 0.2 0(0.2) = 0 02 = 0 0(0.2) = 0
1 0.3 1(0.3) = 0.3 12 = 1 1(0.3) = 0.3
2 0.2 2(0.2) = 0.4 22 = 4
3 0.2 3(0.2) = 0.6 32 = 9
4 0.1 4(0.1) = 0.4 42 = 16
𝜇 = 𝑥 ∙ 𝑃(𝑥) = 1.7
Σ[x∙P(x)]=1.7
𝜎2
= 𝑥2
∙ 𝑃(𝑥) − 𝜇2
Create a column of x2∙P(x)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/varianceandstandarddeviationofadiscreterandomvariable-160626135719/85/Variance-and-standard-deviation-of-a-discrete-random-variable-25-320.jpg)
![Example 7: Find the variance and standard
deviation of the probability distribution.
X P(x) x∙P(x) x2 x2∙P(x)
0 0.2 0(0.2) = 0 02 = 0 0(0.2) = 0
1 0.3 1(0.3) = 0.3 12 = 1 1(0.3) = 0.3
2 0.2 2(0.2) = 0.4 22 = 4 4(0.2) = 0.8
3 0.2 3(0.2) = 0.6 32 = 9
4 0.1 4(0.1) = 0.4 42 = 16
𝜇 = 𝑥 ∙ 𝑃(𝑥) = 1.7
Σ[x∙P(x)]=1.7
𝜎2
= 𝑥2
∙ 𝑃(𝑥) − 𝜇2
Create a column of x2∙P(x)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/varianceandstandarddeviationofadiscreterandomvariable-160626135719/85/Variance-and-standard-deviation-of-a-discrete-random-variable-26-320.jpg)
![Example 7: Find the variance and standard
deviation of the probability distribution.
X P(x) x∙P(x) x2 x2∙P(x)
0 0.2 0(0.2) = 0 02 = 0 0(0.2) = 0
1 0.3 1(0.3) = 0.3 12 = 1 1(0.3) = 0.3
2 0.2 2(0.2) = 0.4 22 = 4 4(0.2) = 0.8
3 0.2 3(0.2) = 0.6 32 = 9 9(0.2) = 1.8
4 0.1 4(0.1) = 0.4 42 = 16
𝜇 = 𝑥 ∙ 𝑃(𝑥) = 1.7
Σ[x∙P(x)]=1.7
𝜎2
= 𝑥2
∙ 𝑃(𝑥) − 𝜇2
Create a column of x2∙P(x)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/varianceandstandarddeviationofadiscreterandomvariable-160626135719/85/Variance-and-standard-deviation-of-a-discrete-random-variable-27-320.jpg)
![Example 7: Find the variance and standard
deviation of the probability distribution.
X P(x) x∙P(x) x2 x2∙P(x)
0 0.2 0(0.2) = 0 02 = 0 0(0.2) = 0
1 0.3 1(0.3) = 0.3 12 = 1 1(0.3) = 0.3
2 0.2 2(0.2) = 0.4 22 = 4 4(0.2) = 0.8
3 0.2 3(0.2) = 0.6 32 = 9 9(0.2) = 1.8
4 0.1 4(0.1) = 0.4 42 = 16 16(0.1) = 1.6
𝜇 = 𝑥 ∙ 𝑃(𝑥) = 1.7
Σ[x∙P(x)]=1.7
𝜎2
= 𝑥2
∙ 𝑃(𝑥) − 𝜇2
Create a column of x2∙P(x)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/varianceandstandarddeviationofadiscreterandomvariable-160626135719/85/Variance-and-standard-deviation-of-a-discrete-random-variable-28-320.jpg)
![Example 7: Find the variance and standard
deviation of the probability distribution.
X P(x) x∙P(x) x2 x2∙P(x)
0 0.2 0(0.2) = 0 02 = 0 0(0.2) = 0
1 0.3 1(0.3) = 0.3 12 = 1 1(0.3) = 0.3
2 0.2 2(0.2) = 0.4 22 = 4 4(0.2) = 0.8
3 0.2 3(0.2) = 0.6 32 = 9 9(0.2) = 1.8
4 0.1 4(0.1) = 0.4 42 = 16 16(0.1) = 1.6
𝜇 = 𝑥 ∙ 𝑃(𝑥) = 1.7
Σ[x∙P(x)]=1.7
𝜎2
= 𝑥2
∙ 𝑃(𝑥) − 𝜇2
Sum the column of x2∙P(x)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/varianceandstandarddeviationofadiscreterandomvariable-160626135719/85/Variance-and-standard-deviation-of-a-discrete-random-variable-29-320.jpg)
![Example 7: Find the variance and standard
deviation of the probability distribution.
X P(x) x∙P(x) x2 x2∙P(x)
0 0.2 0(0.2) = 0 02 = 0 0(0.2) = 0
1 0.3 1(0.3) = 0.3 12 = 1 1(0.3) = 0.3
2 0.2 2(0.2) = 0.4 22 = 4 4(0.2) = 0.8
3 0.2 3(0.2) = 0.6 32 = 9 9(0.2) = 1.8
4 0.1 4(0.1) = 0.4 42 = 16 16(0.1) = 1.6
𝜇 = 𝑥 ∙ 𝑃(𝑥) = 1.7
Σ[x∙P(x)]=1.7
𝜎2
= 𝑥2
∙ 𝑃(𝑥) − 𝜇2
Sum the column of x2∙P(x)
Σ[x2∙P(x)]=4.5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/varianceandstandarddeviationofadiscreterandomvariable-160626135719/85/Variance-and-standard-deviation-of-a-discrete-random-variable-30-320.jpg)
![Example 7: Find the variance and standard
deviation of the probability distribution.
X P(x) x∙P(x) x2 x2∙P(x)
0 0.2 0(0.2) = 0 02 = 0 0(0.2) = 0
1 0.3 1(0.3) = 0.3 12 = 1 1(0.3) = 0.3
2 0.2 2(0.2) = 0.4 22 = 4 4(0.2) = 0.8
3 0.2 3(0.2) = 0.6 32 = 9 9(0.2) = 1.8
4 0.1 4(0.1) = 0.4 42 = 16 16(0.1) = 1.6
𝜇 = 𝑥 ∙ 𝑃(𝑥) = 1.7
Σ[x∙P(x)]=1.7
𝜎2
= 𝑥2
∙ 𝑃(𝑥) − 𝜇2
= 4.5 – 1.72
= 1.61
Σ[x2∙P(x)]=4.5
Variance](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/varianceandstandarddeviationofadiscreterandomvariable-160626135719/85/Variance-and-standard-deviation-of-a-discrete-random-variable-31-320.jpg)
![Example 7: Find the variance and standard
deviation of the probability distribution.
X P(x) x∙P(x) x2 x2∙P(x)
0 0.2 0(0.2) = 0 02 = 0 0(0.2) = 0
1 0.3 1(0.3) = 0.3 12 = 1 1(0.3) = 0.3
2 0.2 2(0.2) = 0.4 22 = 4 4(0.2) = 0.8
3 0.2 3(0.2) = 0.6 32 = 9 9(0.2) = 1.8
4 0.1 4(0.1) = 0.4 42 = 16 16(0.1) = 1.6
𝜇 = 𝑥 ∙ 𝑃(𝑥) = 1.7
Σ[x∙P(x)]=1.7
𝜎2
= 𝑥2
∙ 𝑃(𝑥) − 𝜇2
= 4.5 – 1.72
= 1.61
Σ[x2∙P(x)]=4.5
Variance
𝜎 = 𝜎2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/varianceandstandarddeviationofadiscreterandomvariable-160626135719/85/Variance-and-standard-deviation-of-a-discrete-random-variable-32-320.jpg)
![Example 7: Find the variance and standard
deviation of the probability distribution.
X P(x) x∙P(x) x2 x2∙P(x)
0 0.2 0(0.2) = 0 02 = 0 0(0.2) = 0
1 0.3 1(0.3) = 0.3 12 = 1 1(0.3) = 0.3
2 0.2 2(0.2) = 0.4 22 = 4 4(0.2) = 0.8
3 0.2 3(0.2) = 0.6 32 = 9 9(0.2) = 1.8
4 0.1 4(0.1) = 0.4 42 = 16 16(0.1) = 1.6
𝜇 = 𝑥 ∙ 𝑃(𝑥) = 1.7
Σ[x∙P(x)]=1.7
𝜎2
= 𝑥2
∙ 𝑃(𝑥) − 𝜇2
= 4.5 – 1.72
= 1.61
Σ[x2∙P(x)]=4.5
Variance
𝜎 = 𝜎2 = 1.61 ≈ 1.27
Standard Deviation](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/varianceandstandarddeviationofadiscreterandomvariable-160626135719/85/Variance-and-standard-deviation-of-a-discrete-random-variable-33-320.jpg)