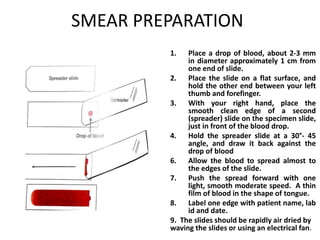
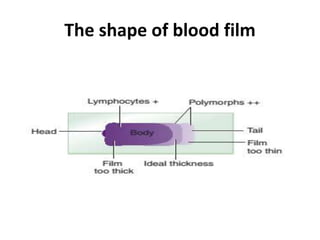
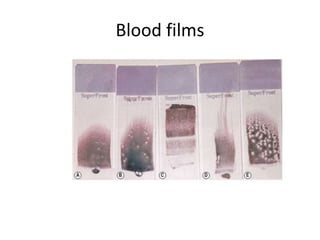
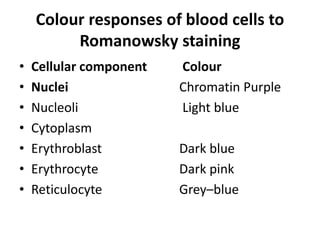
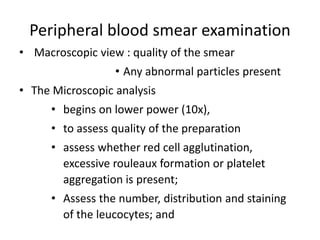
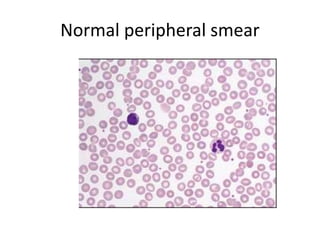
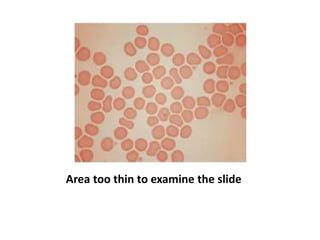
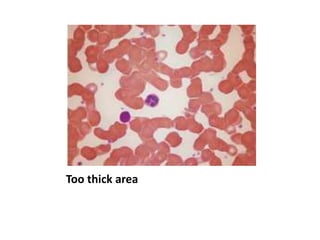
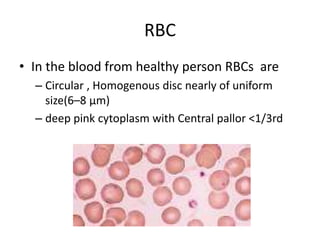
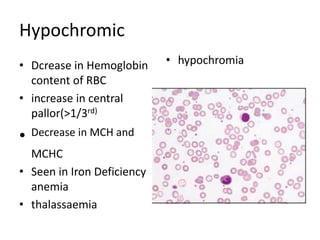
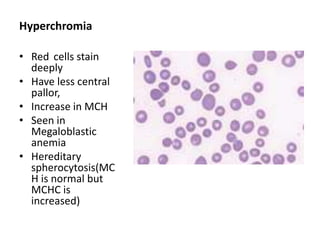
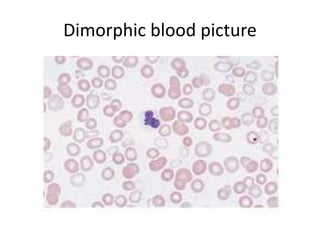
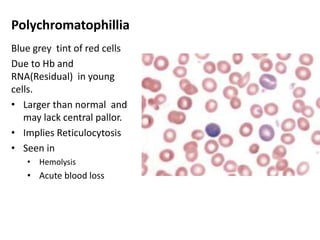
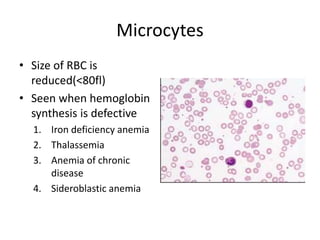
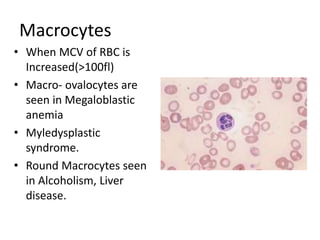
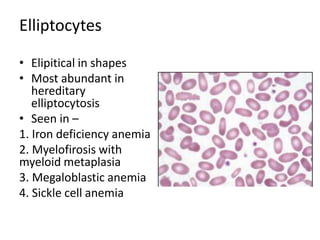
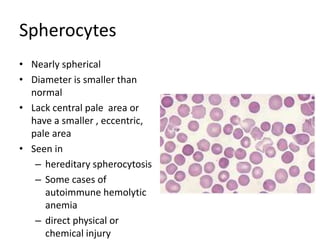
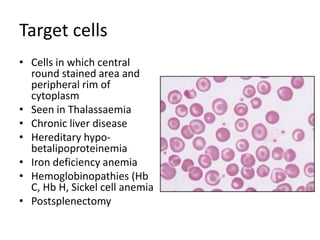
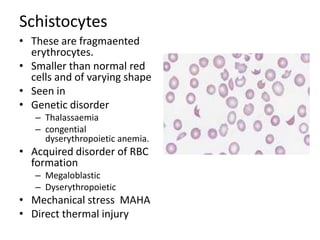
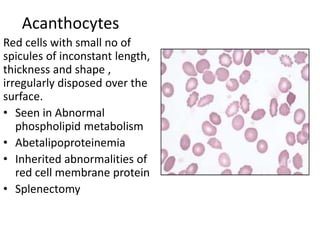
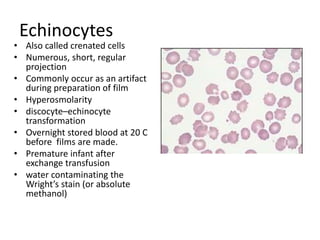
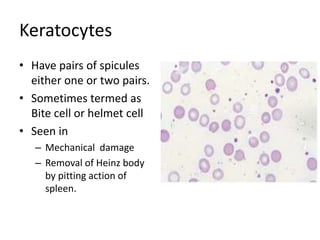
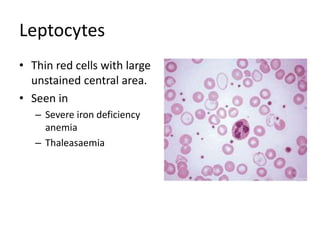
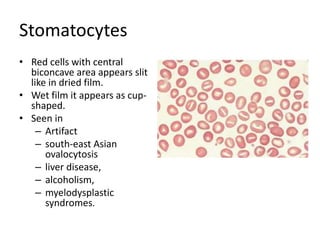
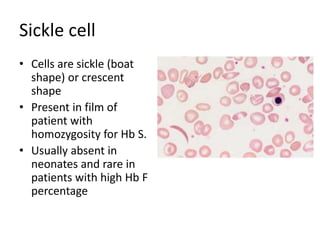
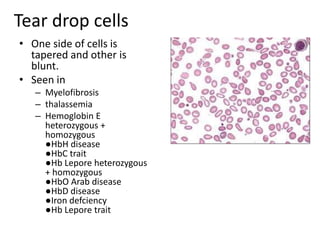
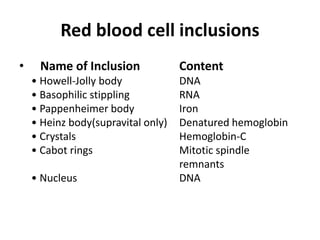
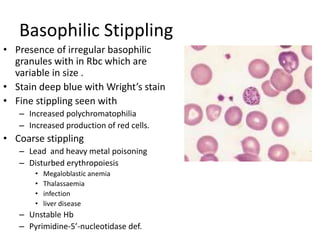
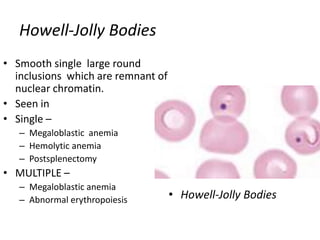
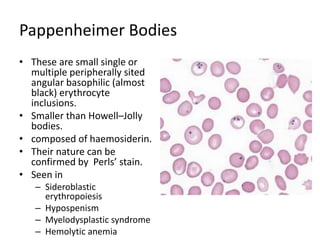
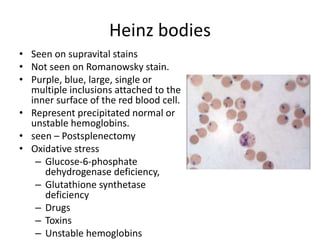
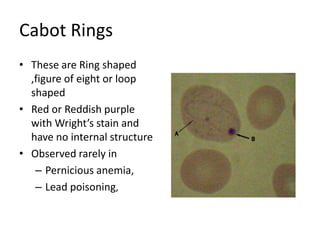
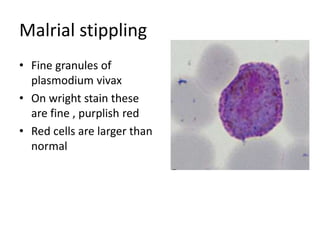
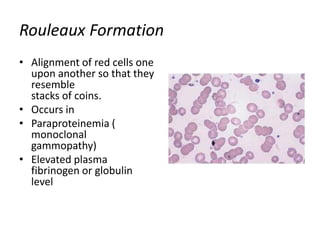
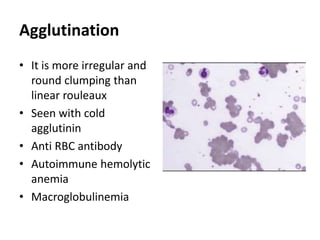
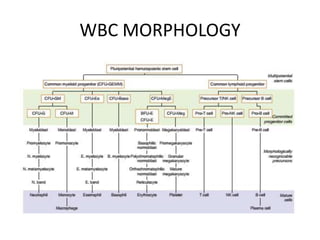
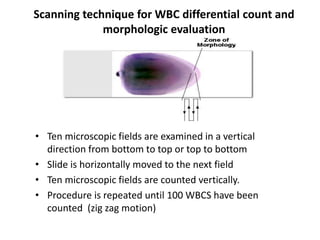
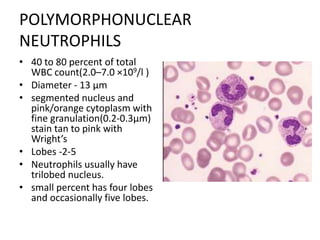
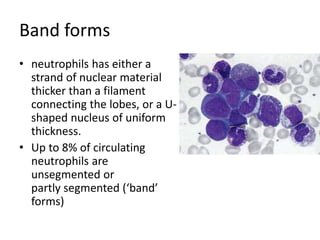
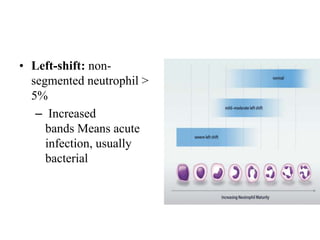
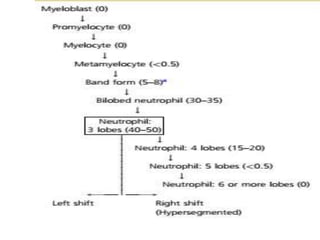
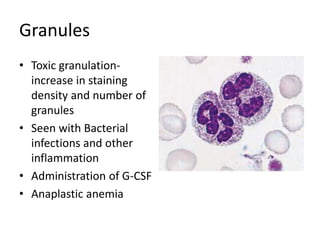
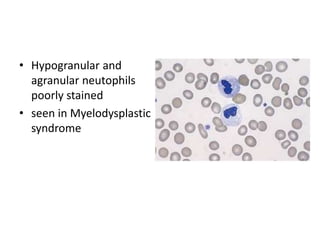
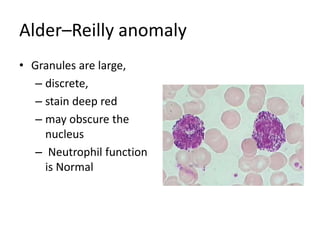
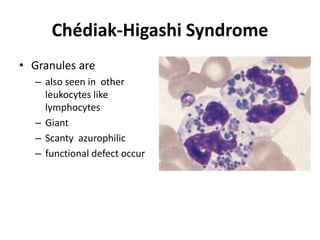
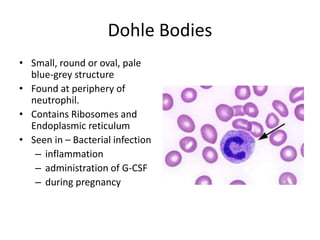
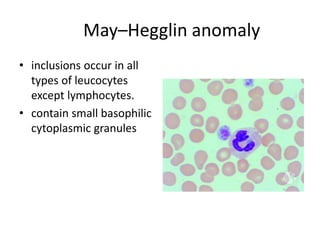
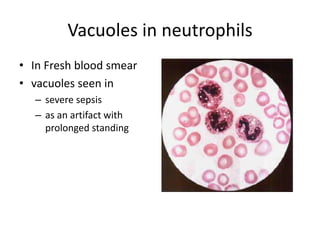
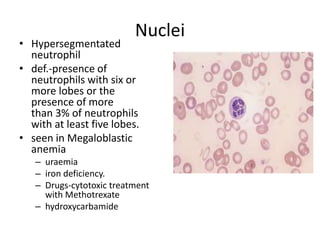
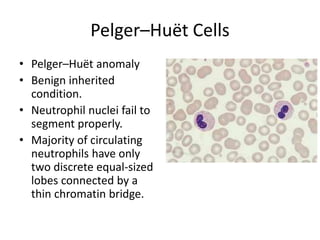
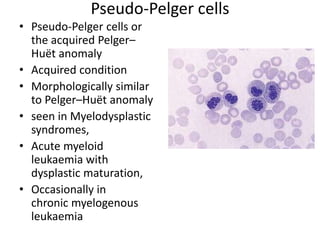
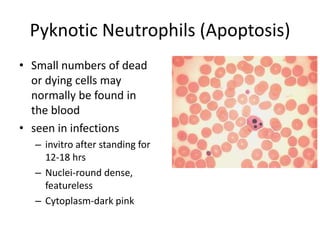
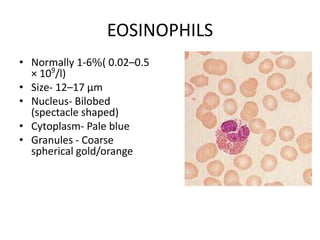
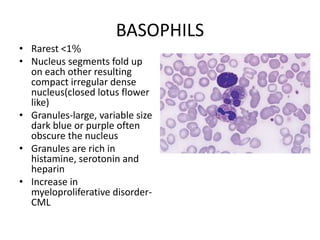
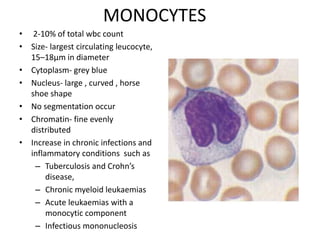
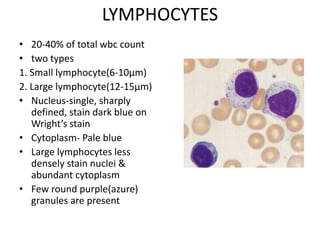
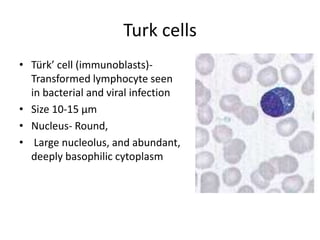
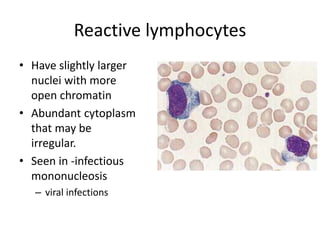
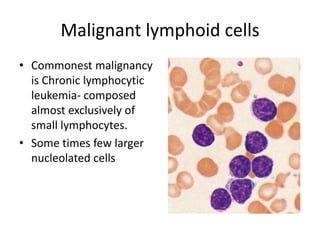
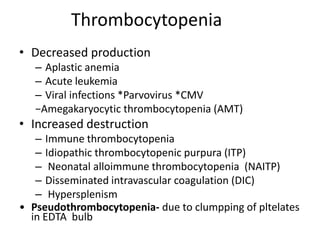
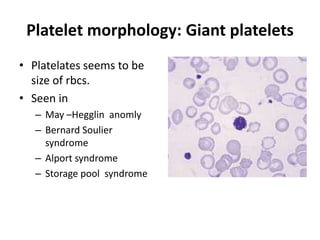
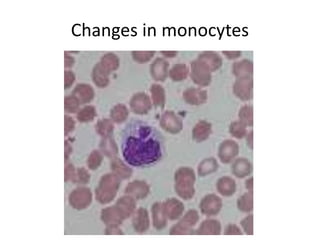
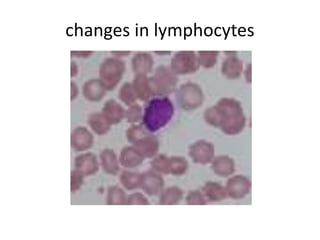
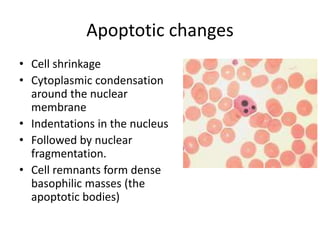
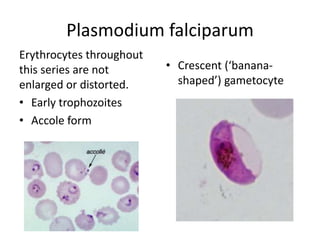
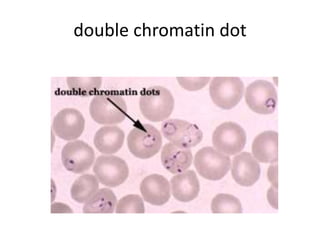
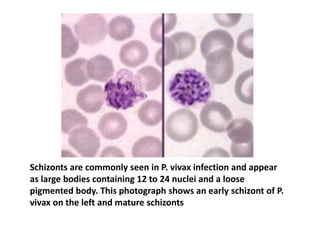
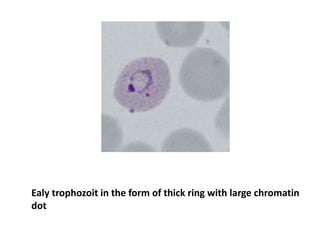
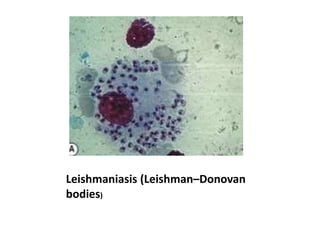
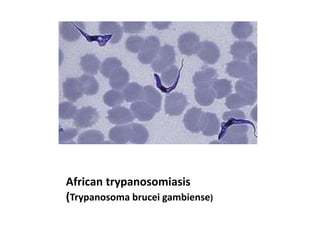
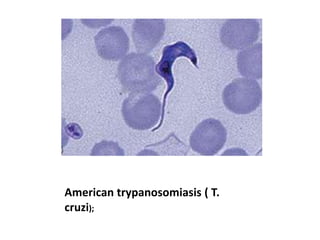
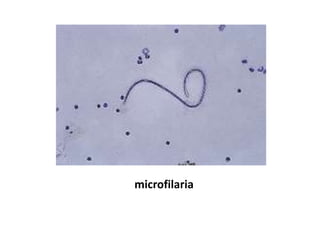
Peripheral blood smear examination plays an important role in the evaluation of various blood disorders. A good peripheral smear should be prepared using the wedge or coverslip technique to obtain an even distribution of red blood cells. The smear is then stained using the Romanowsky method which involves fixing the cells using methanol followed by staining with Giemsa stain. During examination, red blood cells, white blood cells, platelets and any abnormal cells or inclusions are evaluated under the microscope. Changes in the size, shape, color and structural features of red blood cells can provide clues to underlying hematological conditions.