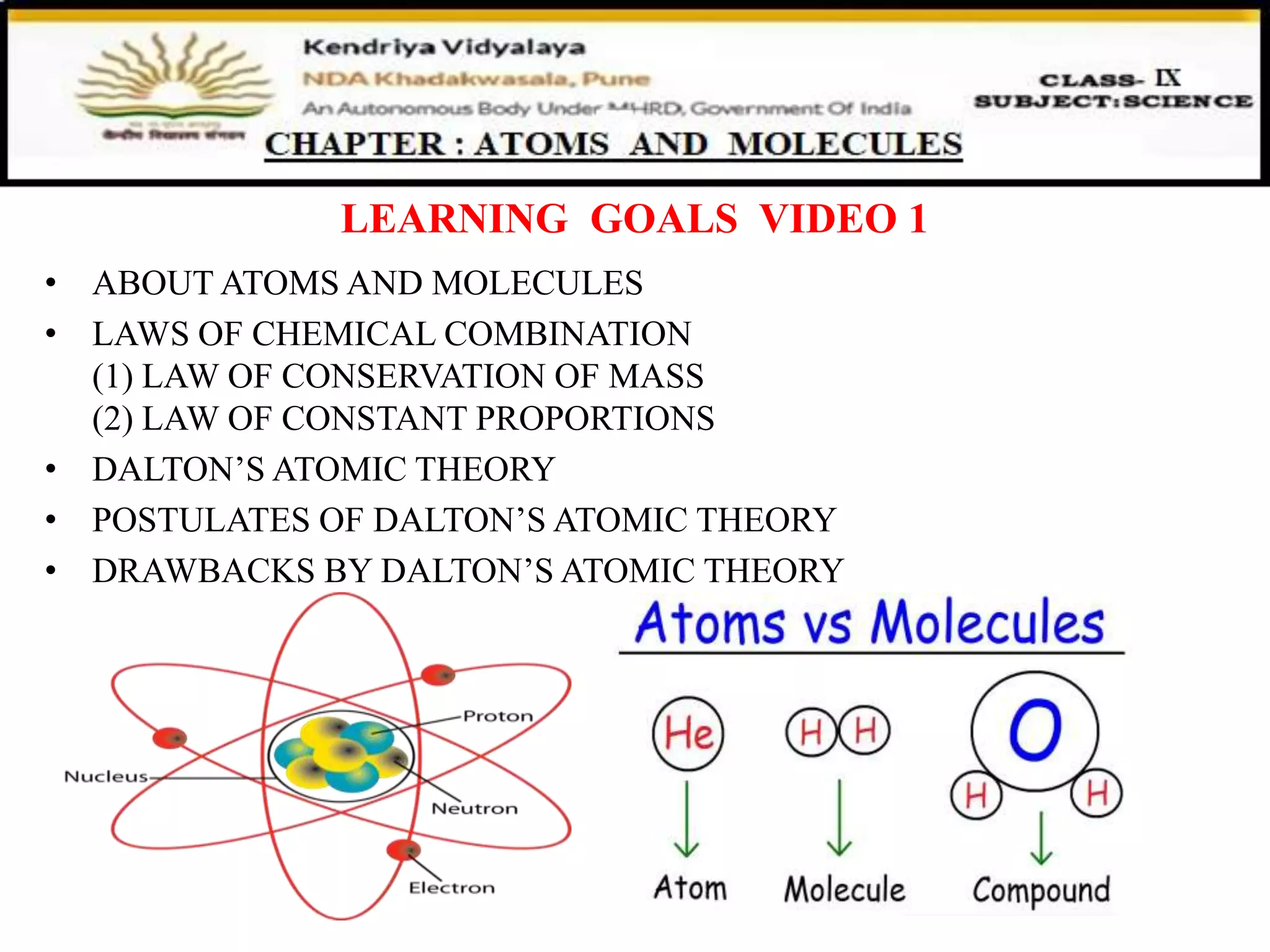
The document discusses fundamental concepts in chemistry, focusing on atoms, molecules, and laws of chemical combination, including the law of conservation of mass and the law of constant proportions. It also outlines Dalton's atomic theory, its postulates, and historical contributions from various philosophers on the nature of matter. Additionally, it provides examples and problems demonstrating these principles.