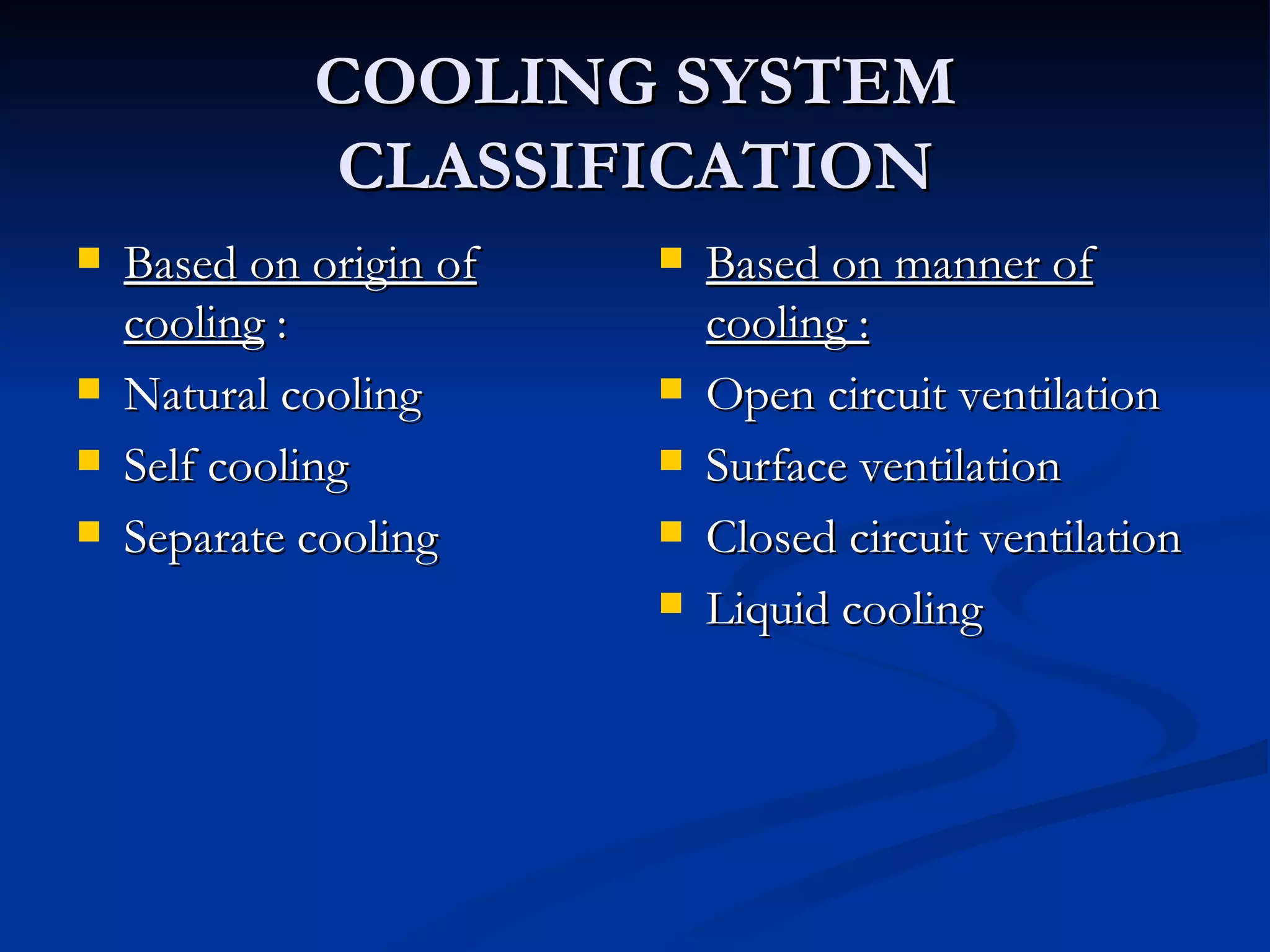
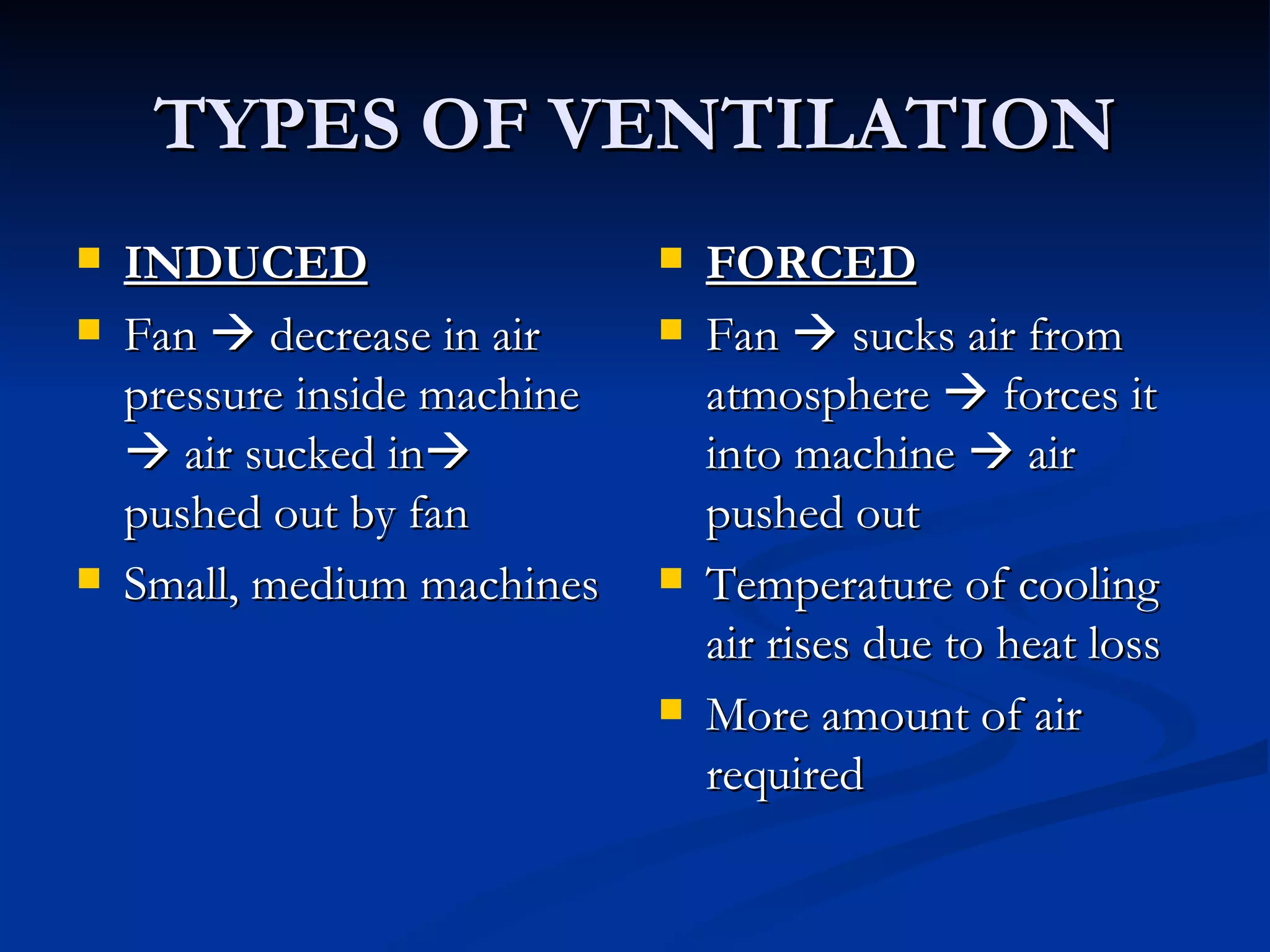
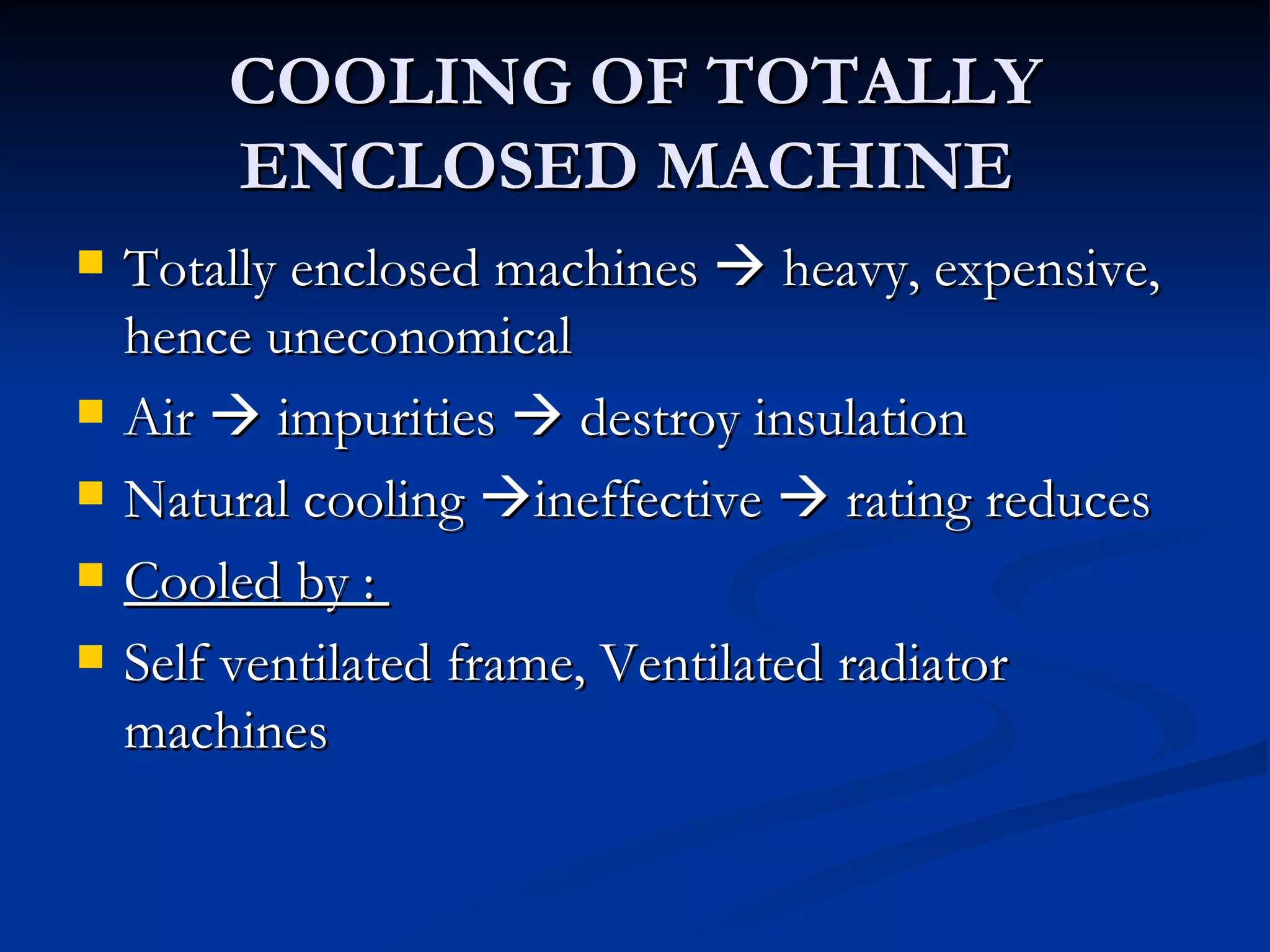
The document outlines the methods of cooling for rotating electrical machines, emphasizing the necessity of cooling due to heat losses that occur during energy transfer and conversion. Various cooling methods are categorized based on their origin and mechanisms, including natural and forced ventilation, liquid cooling, and specialized systems for specific machine types like turbo-alternators. It also discusses the advantages and disadvantages of different cooling strategies, such as air, hydrogen, and water cooling, and their impact on machine efficiency and longevity.