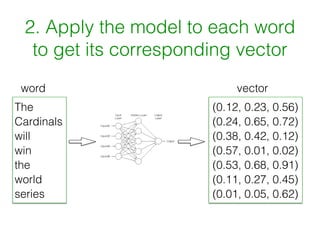
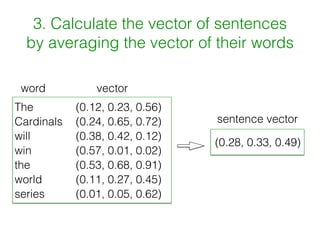
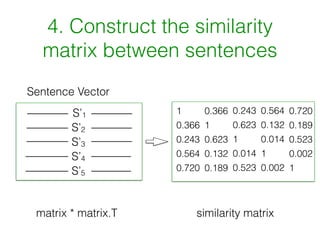
Word2vec works by using documents to train a neural network model to learn word vectors that encode the words' semantic meanings. It trains the model to predict a word's context by learning vector representations of words. It then represents sentences as the average of the word vectors, and constructs a similarity matrix between sentences to score them using PageRank to identify important summary sentences.