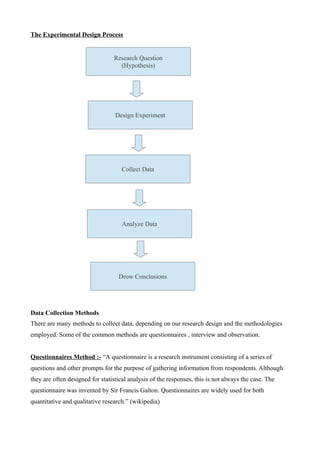
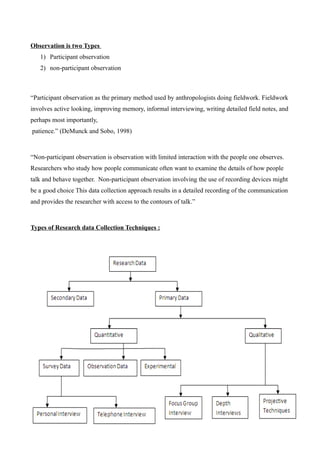
This document outlines different methods for collecting experimental data in research. It discusses quantitative and qualitative data types, as well as primary and secondary sources of data. Three common data collection methods are described: questionnaires, interviews, and observation. Questionnaires can be structured or unstructured, closed or open-ended. Interviews may be conducted in-person, by telephone, in focus groups, or using depth or projective techniques. Both questionnaires and interviews are effective ways to gather information for descriptive or analytical research. The document emphasizes the importance of planning, designing, and critically examining different data collection methods in research.