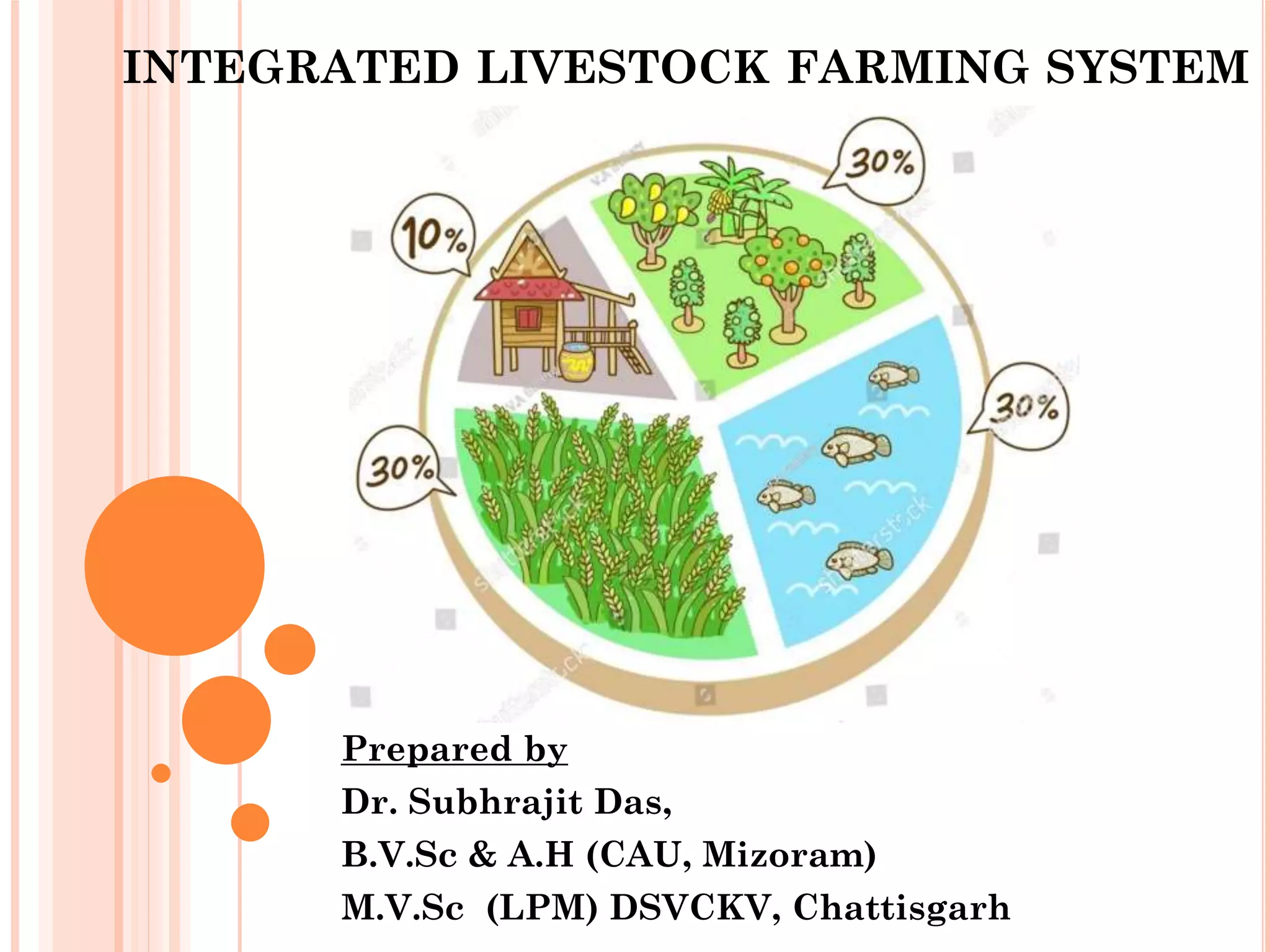
The document outlines various integrated livestock and fish farming systems, highlighting their advantages and types, such as duck-fish, poultry-fish, and pig-fish integration. It emphasizes the benefits of recycling waste for sustainable production and improved profitability, along with the importance of sustainable development in rural economies. The integration of fish with livestock and agriculture is presented as a viable strategy for enhancing returns on investment and promoting environmental protection.