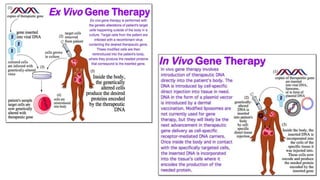
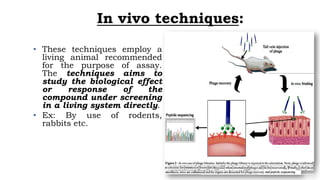
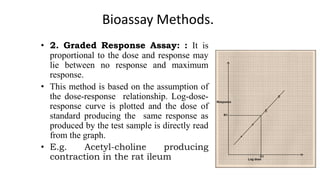
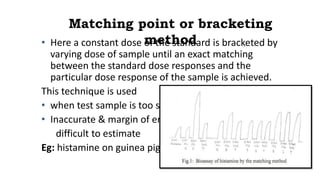
This document discusses various bioassay techniques used to estimate the concentration or potency of substances. It defines bioassay as the determination of a substance's concentration or potency by measuring the biological response it produces. There are three main types of bioassays - in vitro, in vivo, and ex vivo. In vitro uses cell cultures, in vivo uses live animals, and ex vivo uses isolated tissues or cells. Bioassays can be qualitative, assessing effects, or quantitative, estimating concentrations. Common quantitative bioassay methods described include endpoint, graded response, interpolation, and multi-point assays. Immunological assays like ELISA and techniques using radioisotopes like radioimmunoassay are also summarized.












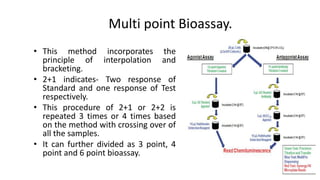
![Three point assay [2+1 dose assay]
• Fast & convenient:
– Log dose response [LDR] curve plotted with varying conc of std
drug solutions and given test solution
– Select two std doses s1& s2 [ in 2:3 dose ratio] from linear part
of LDR [ Let the corresponding response be S1, S2]
– Choose a test dose t with a response T between S1 & S2
– Record 4 sets data as follows
• s1 s2 t
• t s1 s2
• s2 t s1
• s1 s2 t
• Log Potency ratio [M] = [(T –S1) / (S2-S1)] X log (dose ratio)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bioassayubm-180518095805/85/Bioassay-Techniques-19-320.jpg)
![4 point assay [2 +2 dose assay]
• [E.g. Ach bioassay]
• Log dose response [LDR] curve plotted with varying conc of std Ach
solutions and given test solution
• Select two std doses s1& s2 from linear part of DRC [ Let the
corresponding response be S1, S2]
• Choose two test doses t1 & t2 with response T1 &T2 between S1 & S2 ;
• Also s2/s1 = t2/t1 = 2/3
Record 4 data sets
• s1 s2 t1 t2
• s2 t1 t2 s1
• t1 t2 s1 s2
• t2 s1 s2 t1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bioassayubm-180518095805/85/Bioassay-Techniques-20-320.jpg)





![Principle of radioimmunoassay
It uses an immune reaction [antigen-
antibody reaction] to estimate a ligand.
Ag+Ag*+Ab → [Ag -Ab+ Ag*Ab + Ag +
Ab*]
• - Unbound Ag* and Ag washed out
• - Radio activity of bound residue
measured.
• - Ligand concentration is inversely
related to
the radio activity.
• - [Ag: ligand to be measured;
Ag*:radiolabelled ligand].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bioassayubm-180518095805/85/Bioassay-Techniques-27-320.jpg)




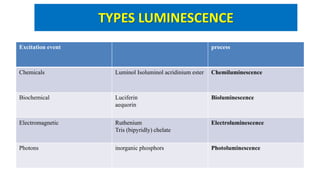
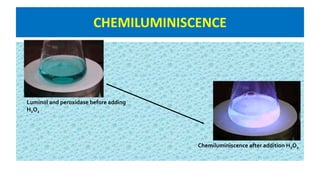
![CHEMILUMINESCENCE
Emission of light with limited emission of heat (luminescence), as
the result of a chemical reaction.
[A] + [B] → [◊] → [Products] + light
[A], [B]: reactants
[◊]: excited intermediate](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bioassayubm-180518095805/85/Bioassay-Techniques-34-320.jpg)