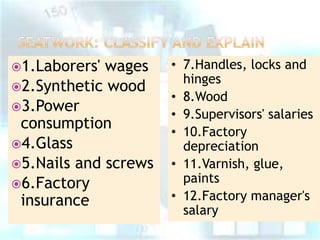
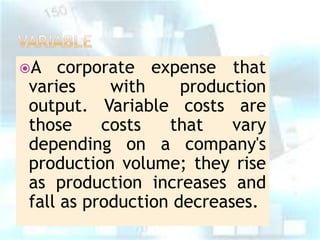
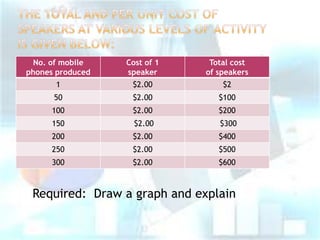
This document provides an overview of classifying different types of costs in management accounting. It discusses direct and indirect costs, classifying materials and labor as direct or indirect, and defining fixed, variable, and semi-variable costs. Examples are given for each type of cost classification. The document also briefly introduces different costing methods like job costing, batch costing, process costing, contract costing, and service costing.