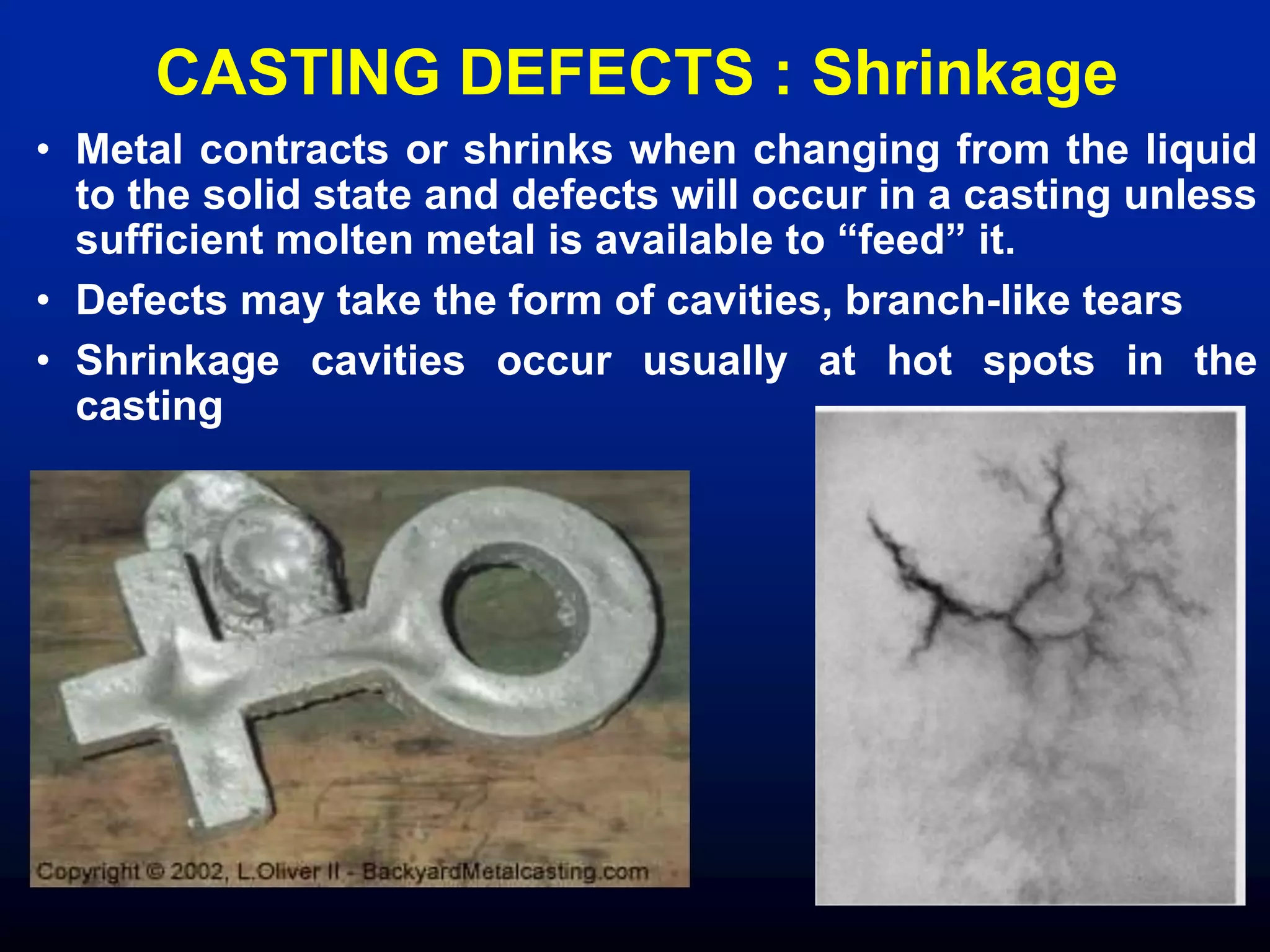
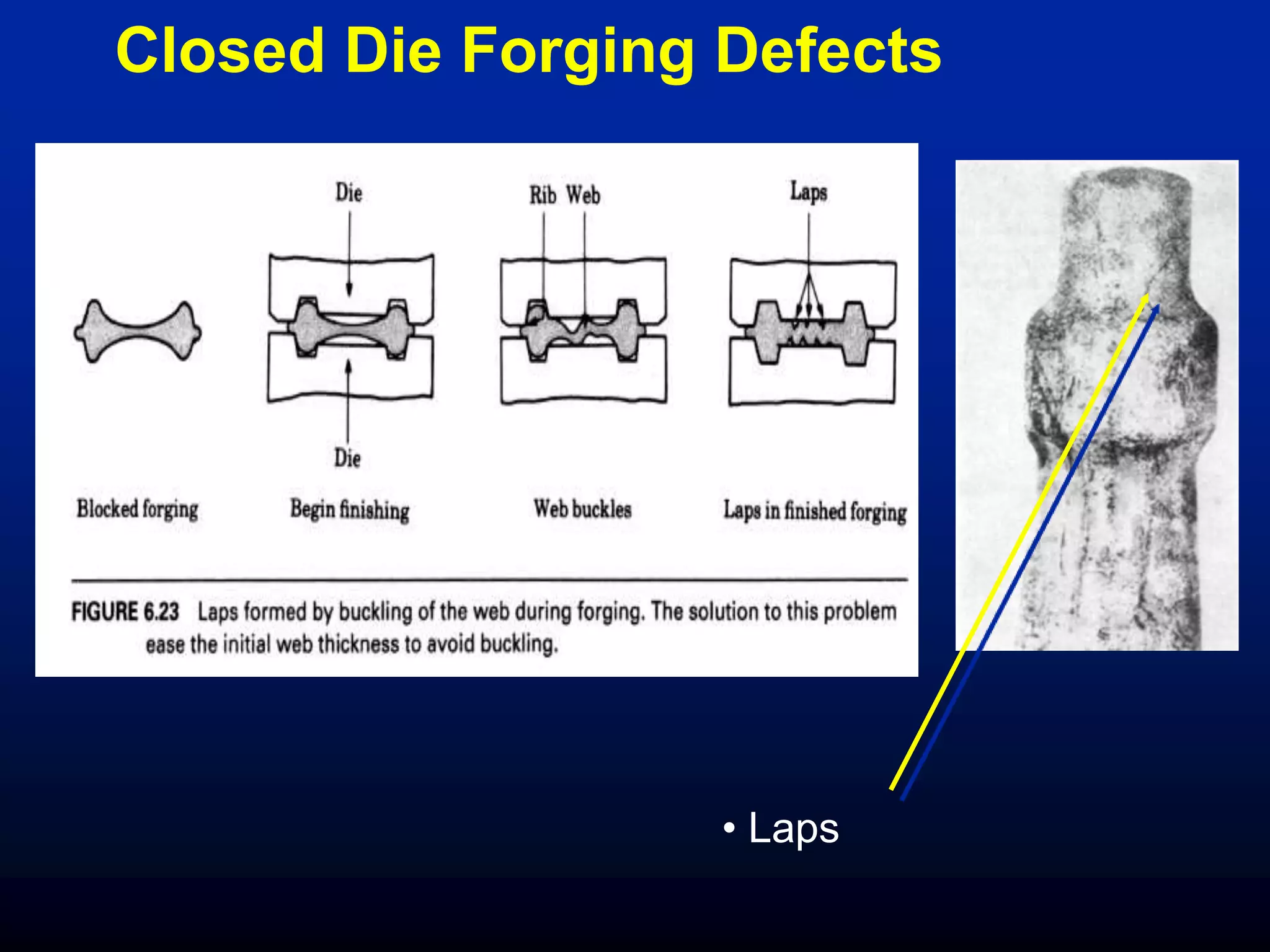
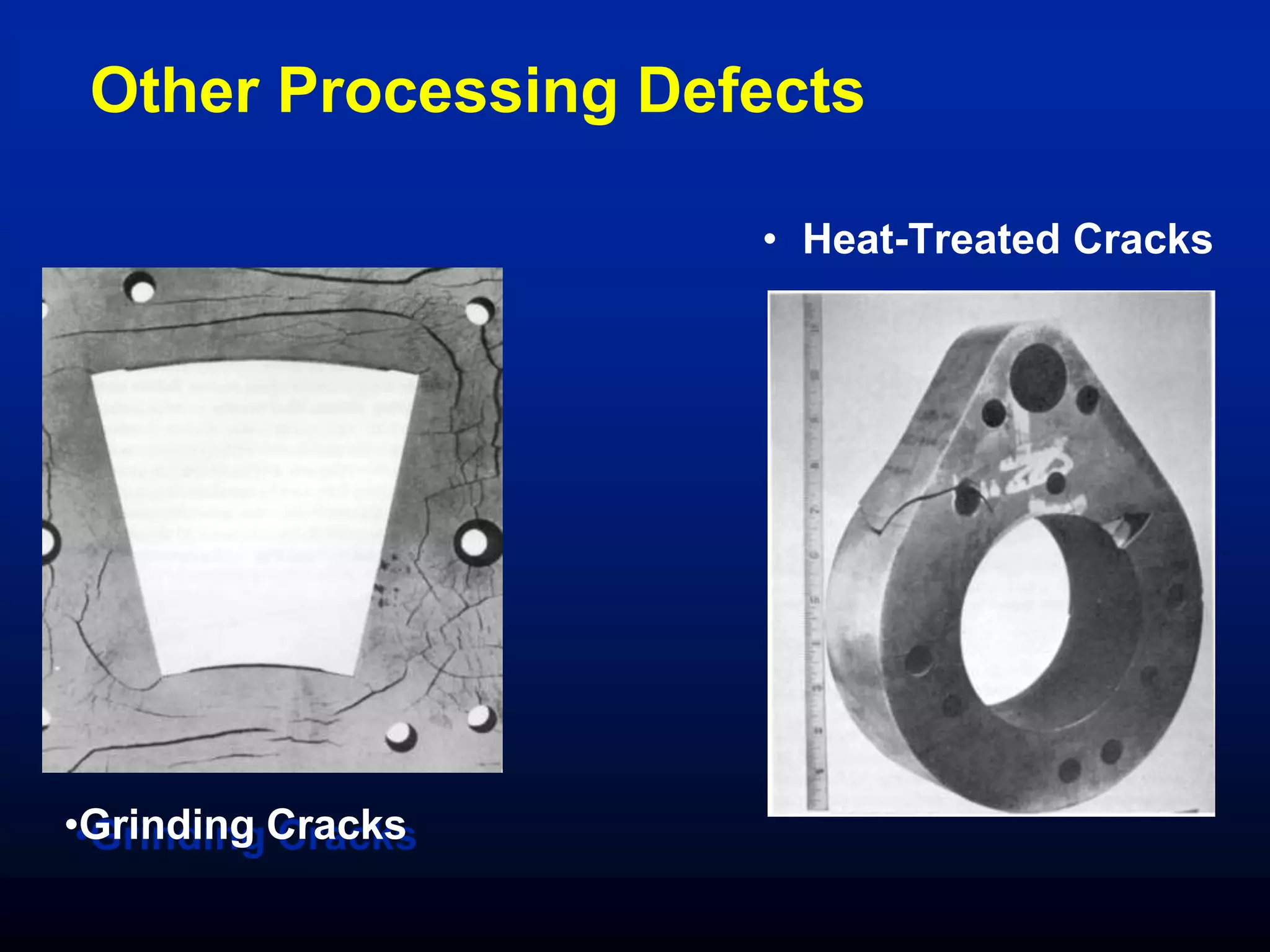
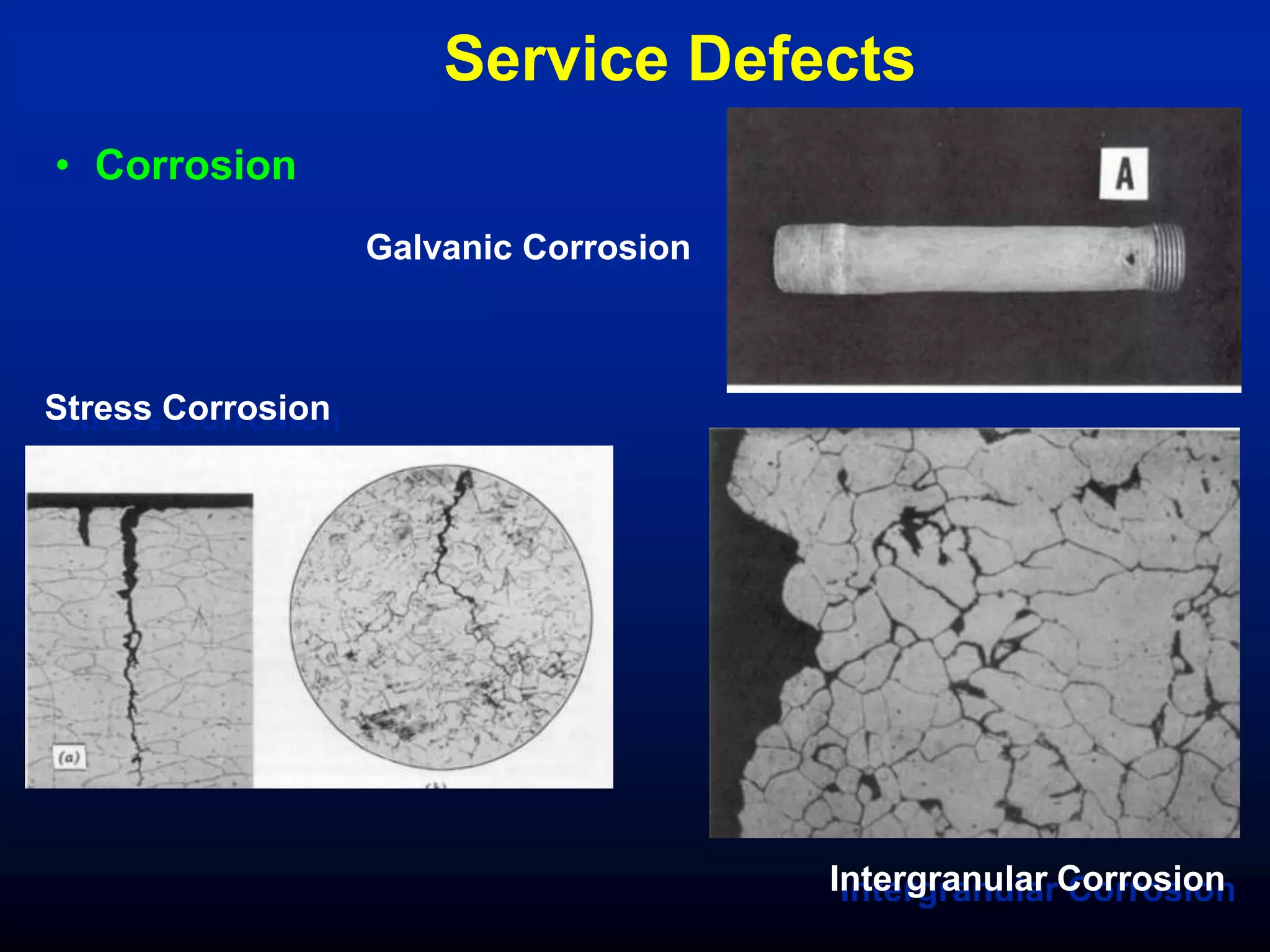
The document discusses various defects in materials, including microscopic and macroscopic defects caused by inherent, processing, and service-related factors, which negatively impact physical and mechanical properties. It outlines specific casting defects such as inclusions, porosity, shrinkage, and defects from bulk deformation processes like forging and rolling, as well as other processing defects and service-related issues including corrosion and fatigue failure. Methods for detecting defects are also covered, highlighting destructive and non-destructive testing approaches.