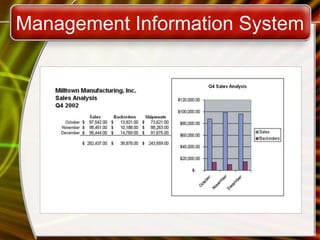
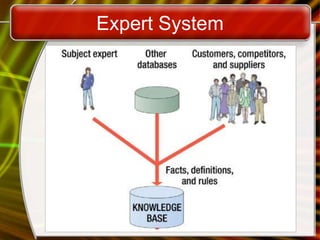
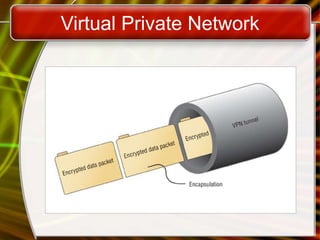
The document outlines the fundamentals of information systems, detailing their purposes and components, including data collection, organization, and retrieval. It categorizes various types of information systems such as office automation systems, transaction processing systems, and management information systems, along with technologies like intranets, extranets, and virtual private networks. Additionally, it emphasizes the role of information systems departments in maintaining technological infrastructure and supporting organizational operations.