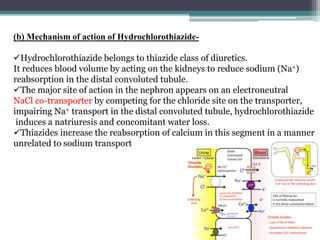
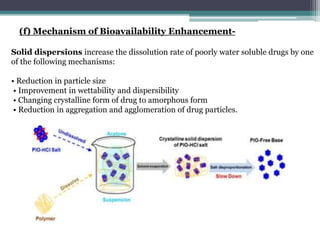
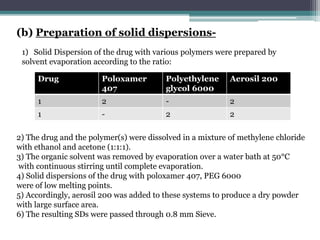
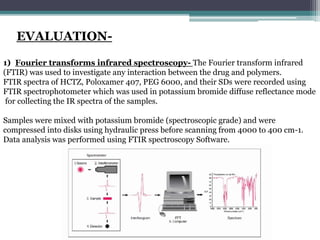
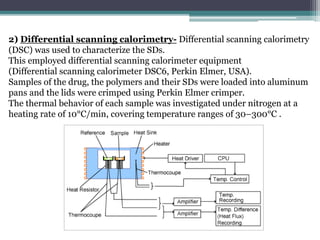
The document details an experiment aimed at improving the dissolution characteristics of the slightly soluble drug hydrochlorothiazide through solid dispersion techniques. It discusses the theoretical background of hydrochlorothiazide and the polymer excipients poloxamer 407 and polyethylene glycol 6000, as well as the procedures for preparing solid dispersions and evaluating their effectiveness. The conclusion emphasizes the significant enhancement in drug dissolution rates due to the formation of binary solid dispersions and changes in the drug's crystalline structure.