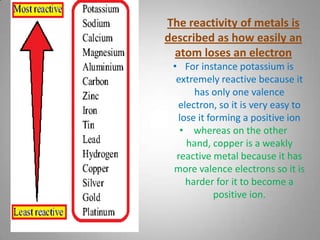
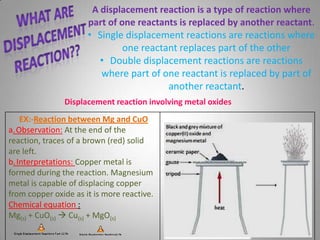
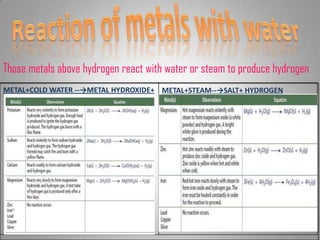
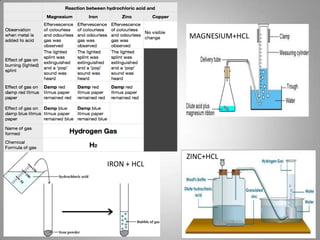
The document discusses the reactivity of metals, displacement reactions, and reactions of metals with acids and water. It explains that more reactive metals, like potassium, lose electrons more easily and form positive ions. Less reactive metals, like copper, have more valence electrons and are harder to oxidize. A displacement reaction occurs when one reactant replaces part of another. Single displacement reactions involve one reactant replacing part of the other, while double displacement reactions involve parts of two reactants being exchanged. The reactivity series can predict how vigorously a metal will react with acids based on its position on the series.