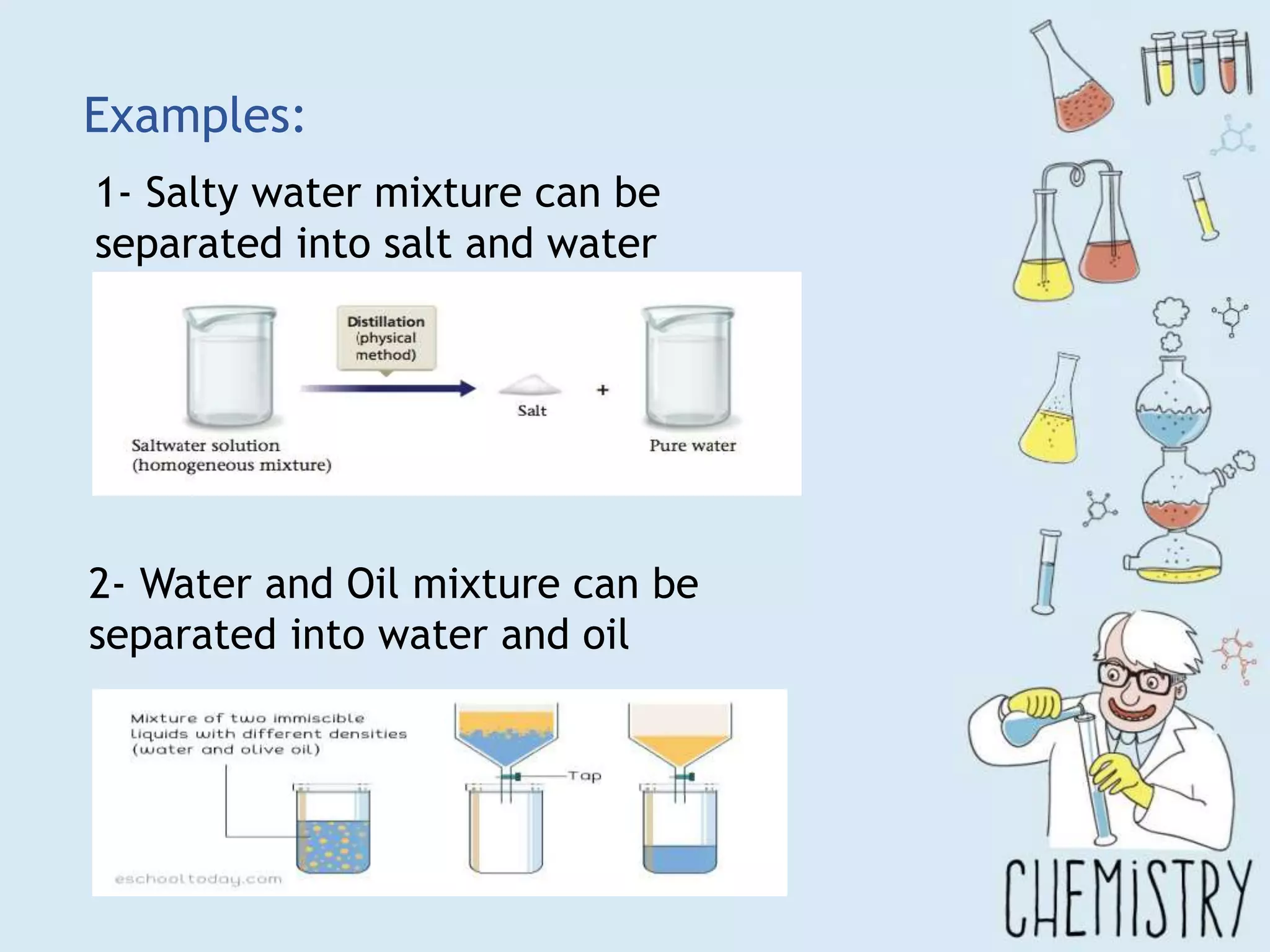
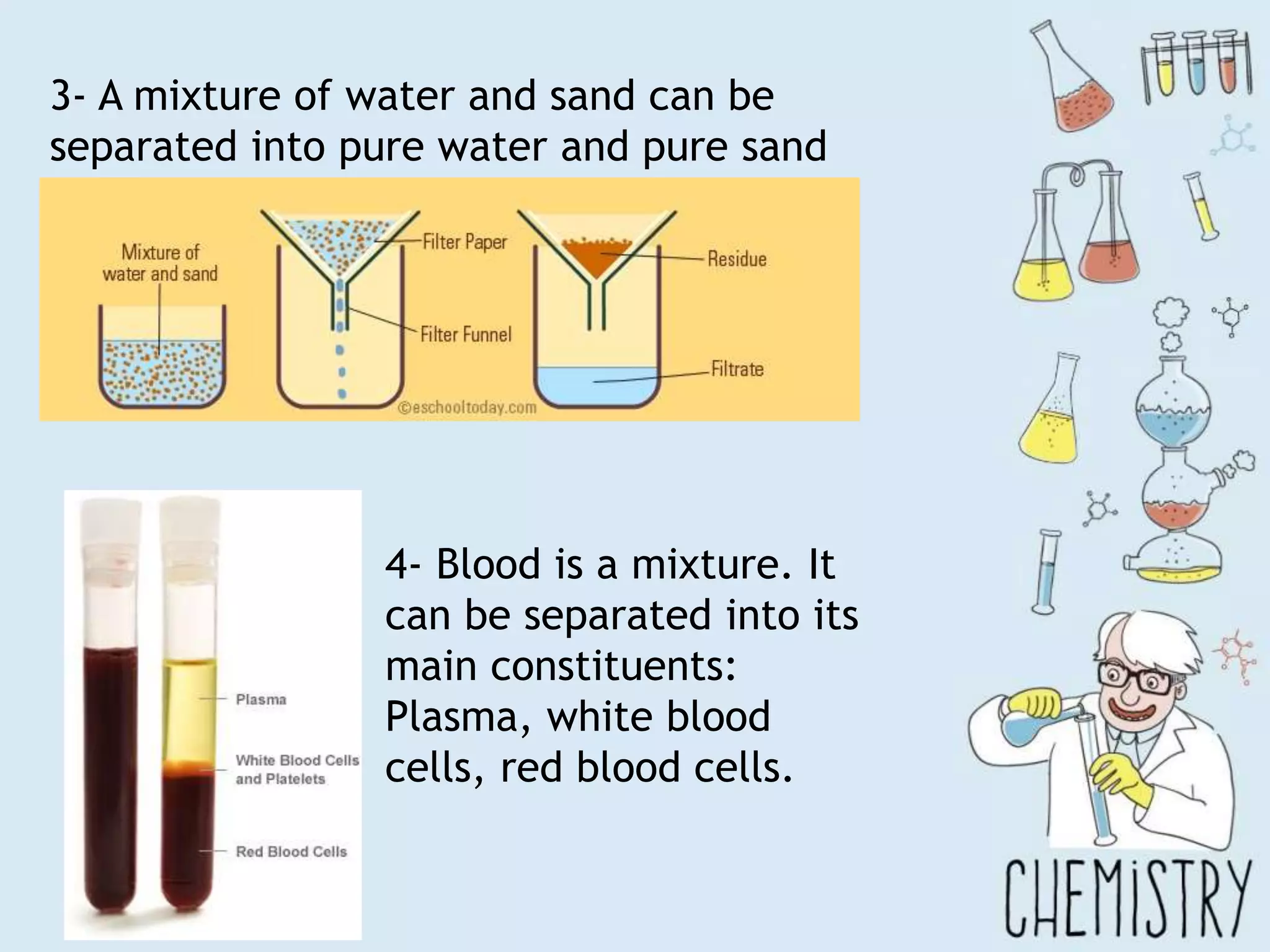
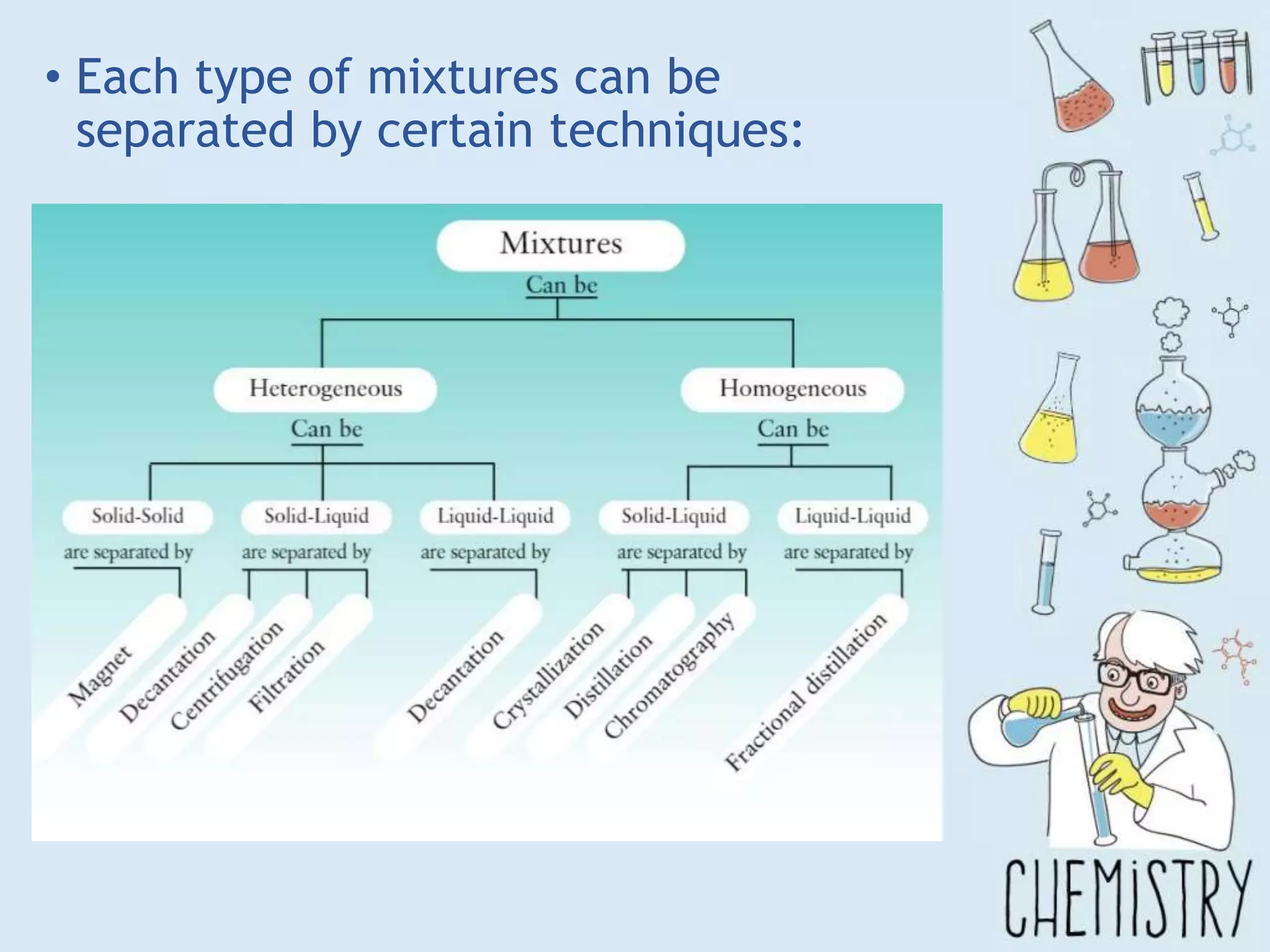
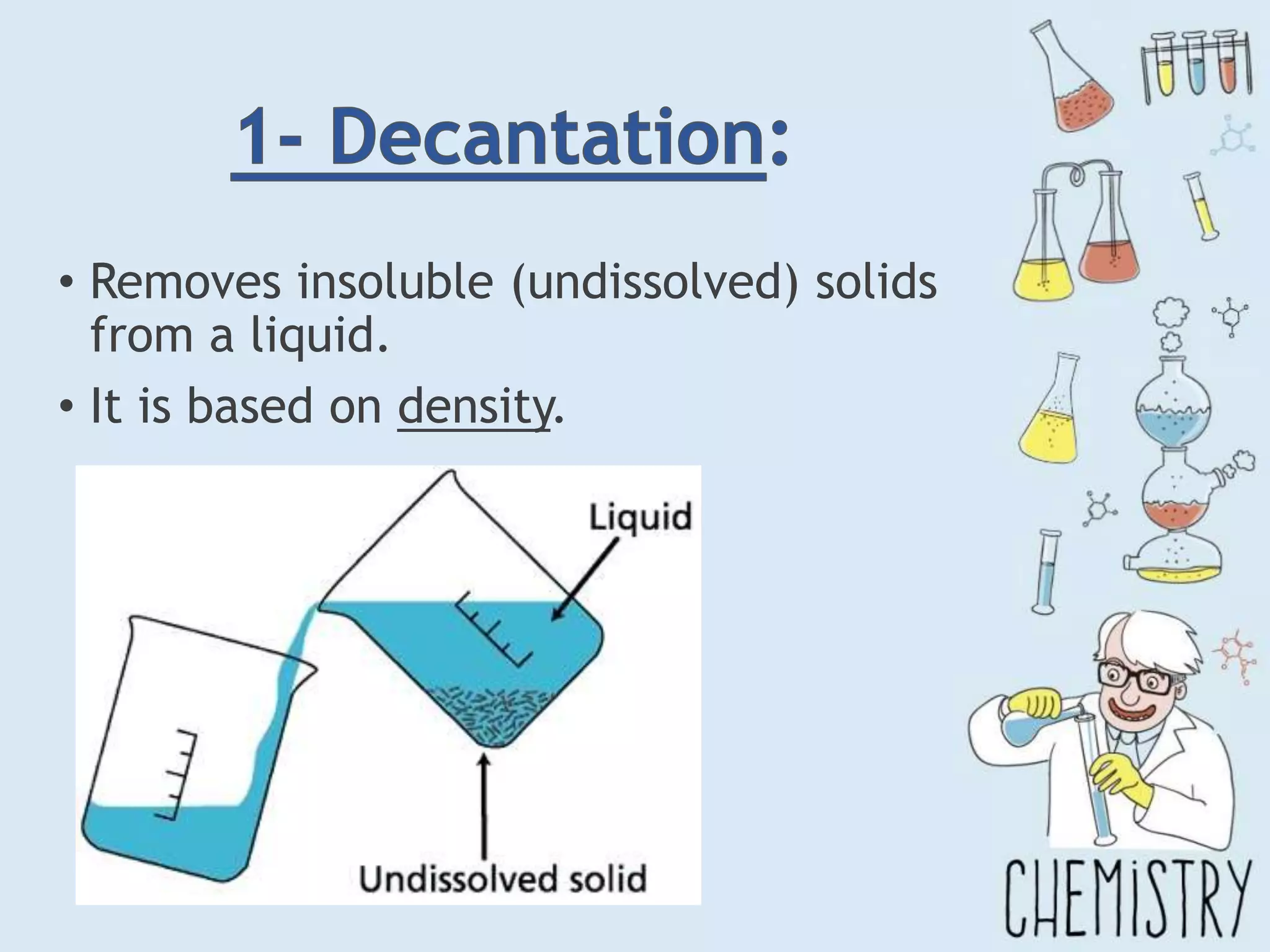
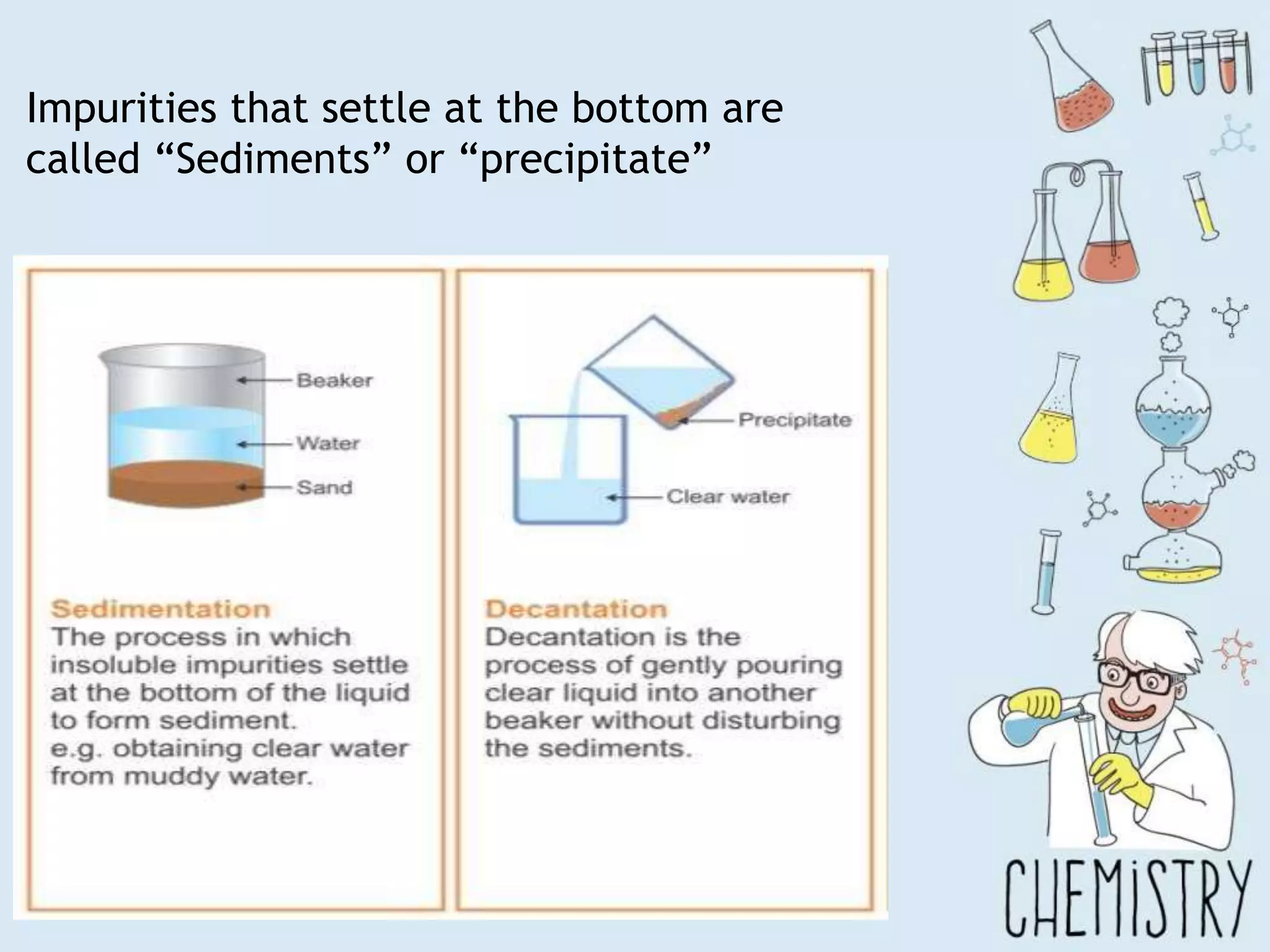
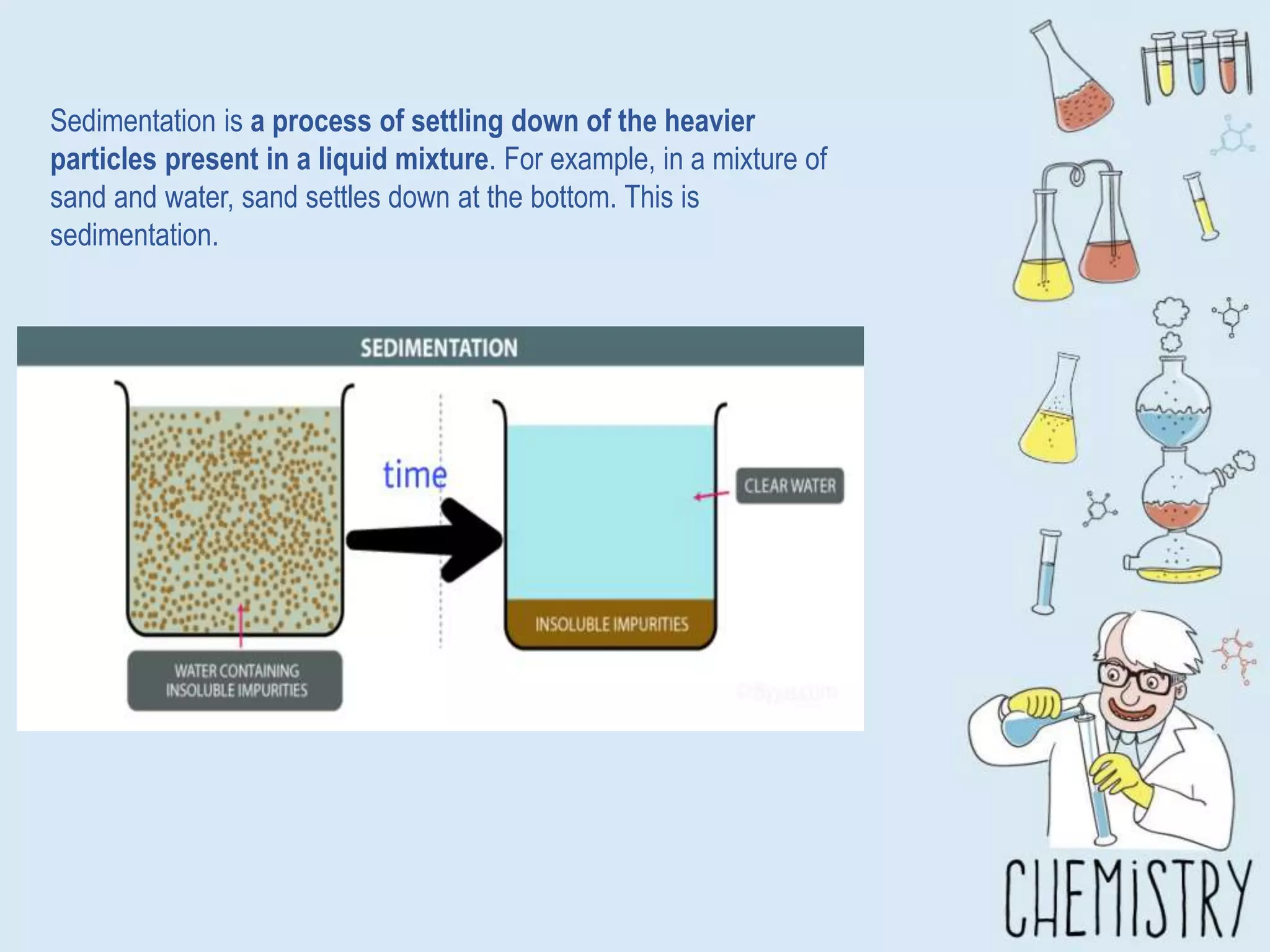
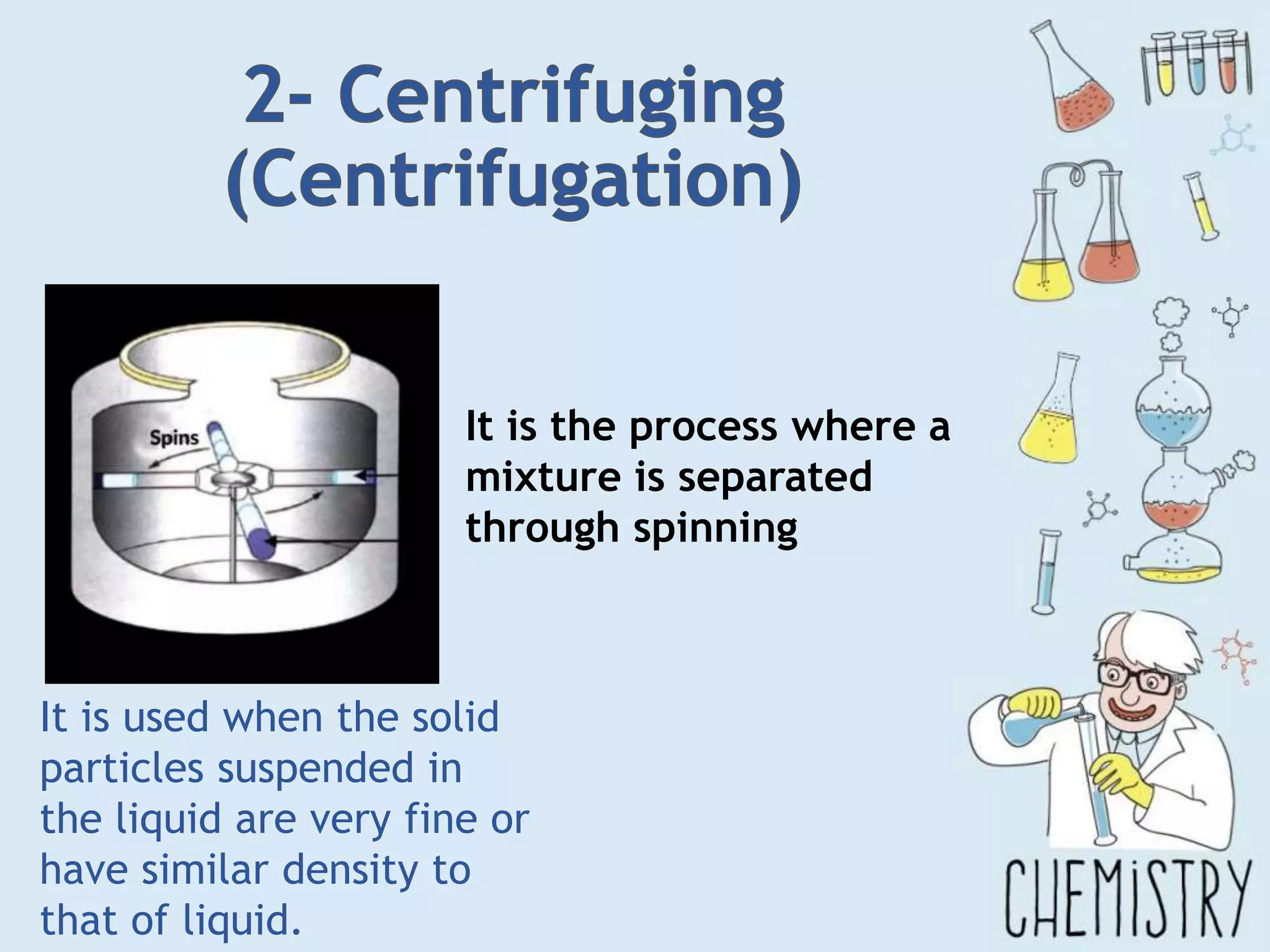
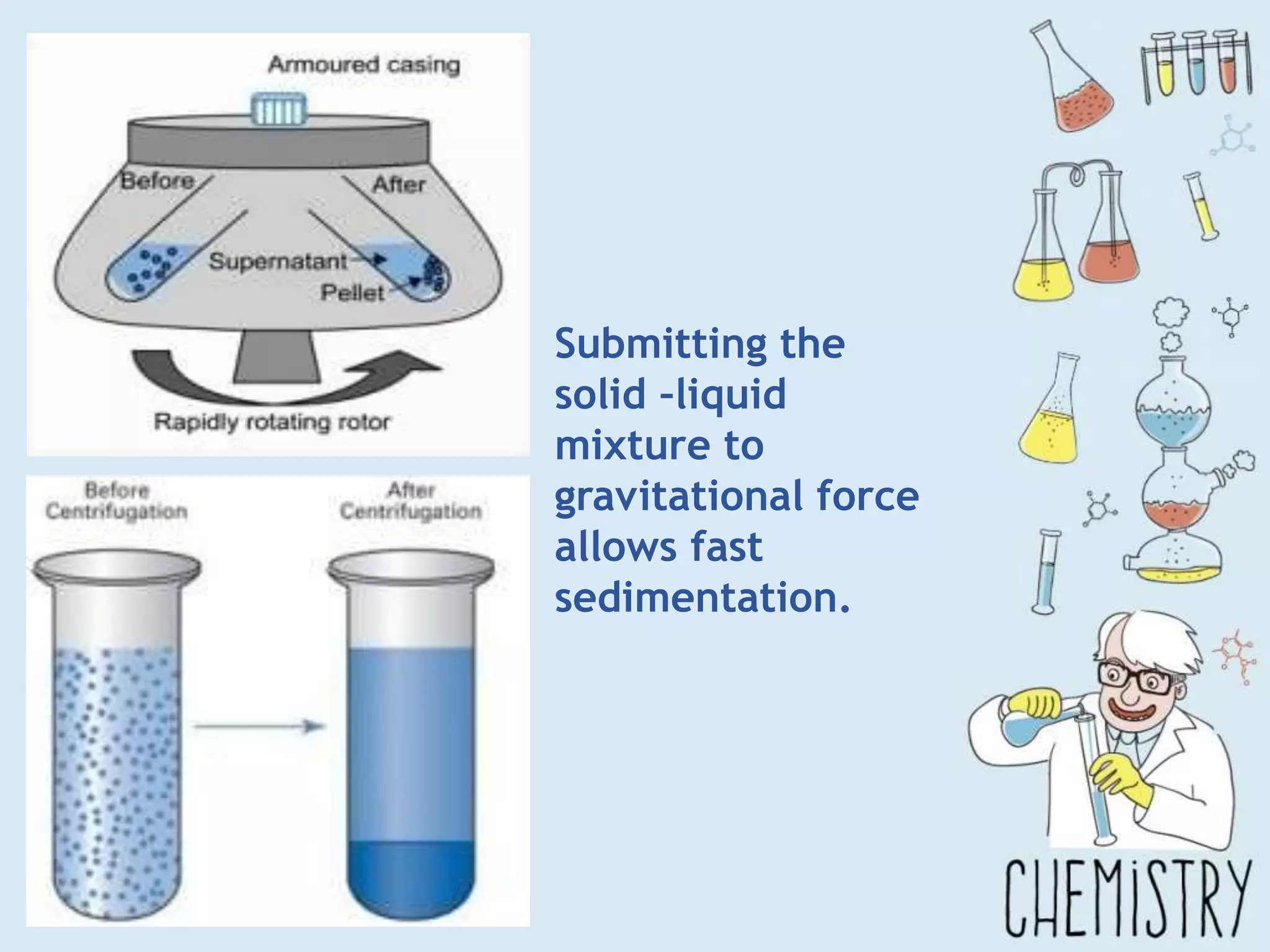
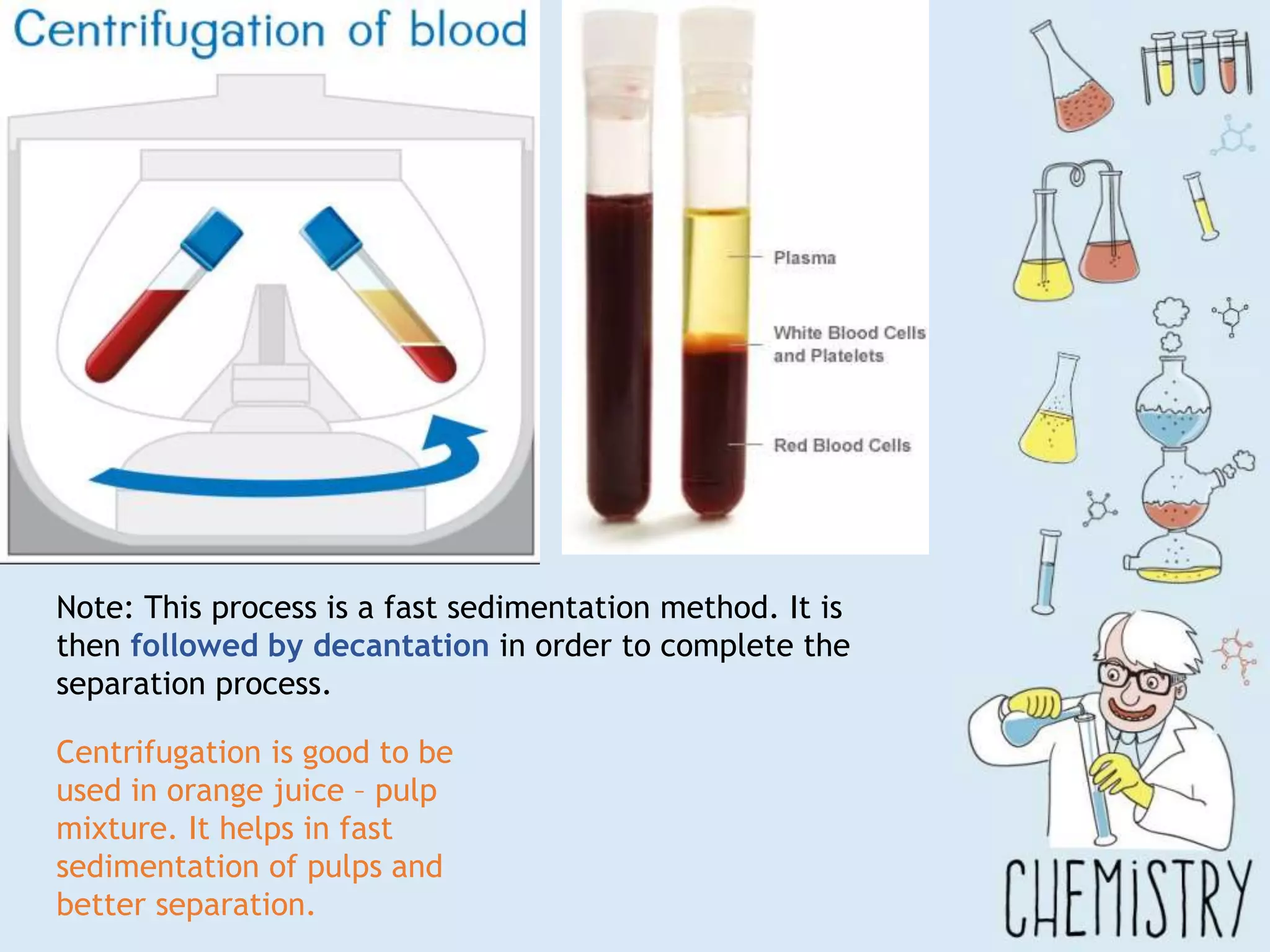
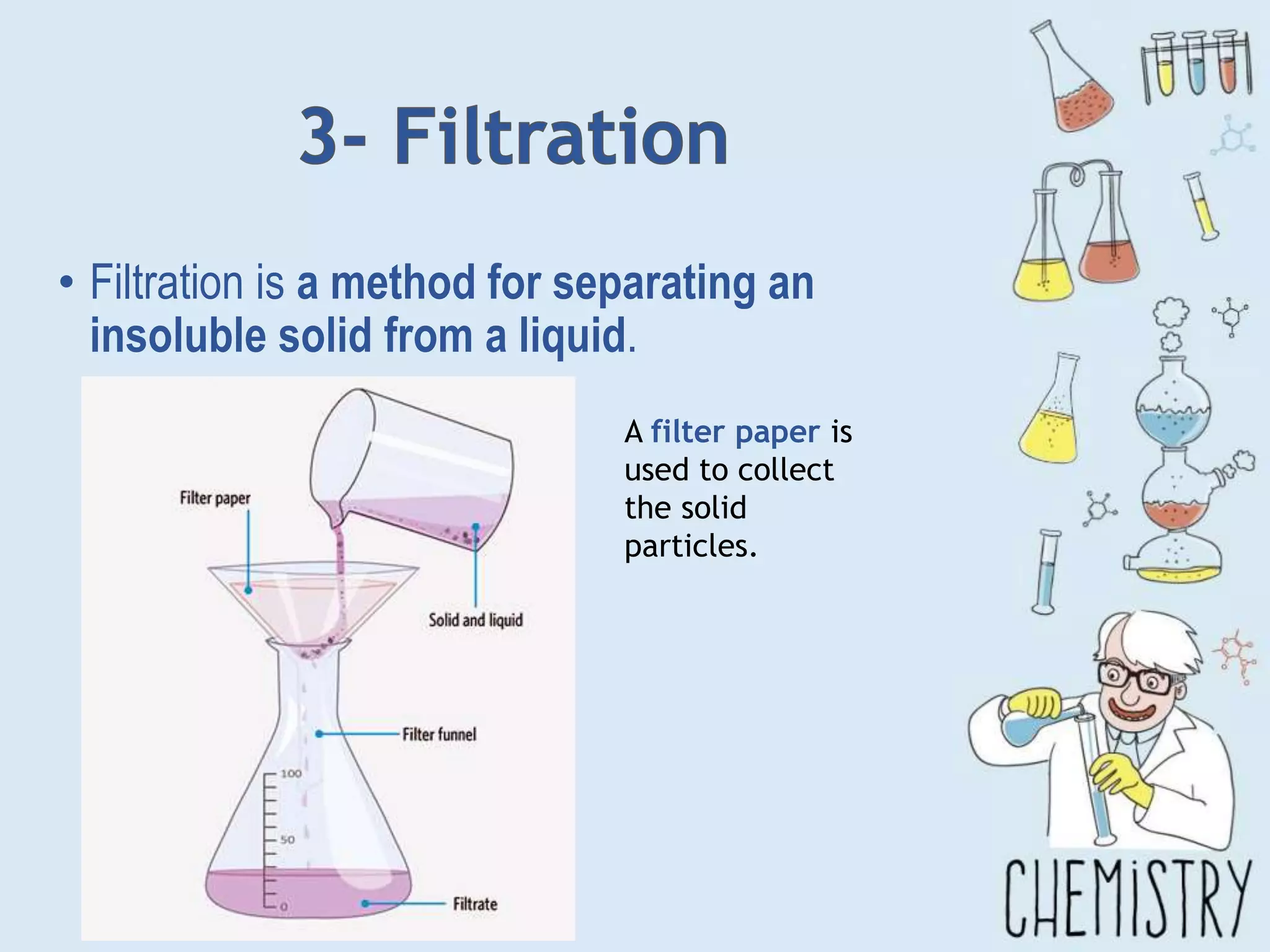
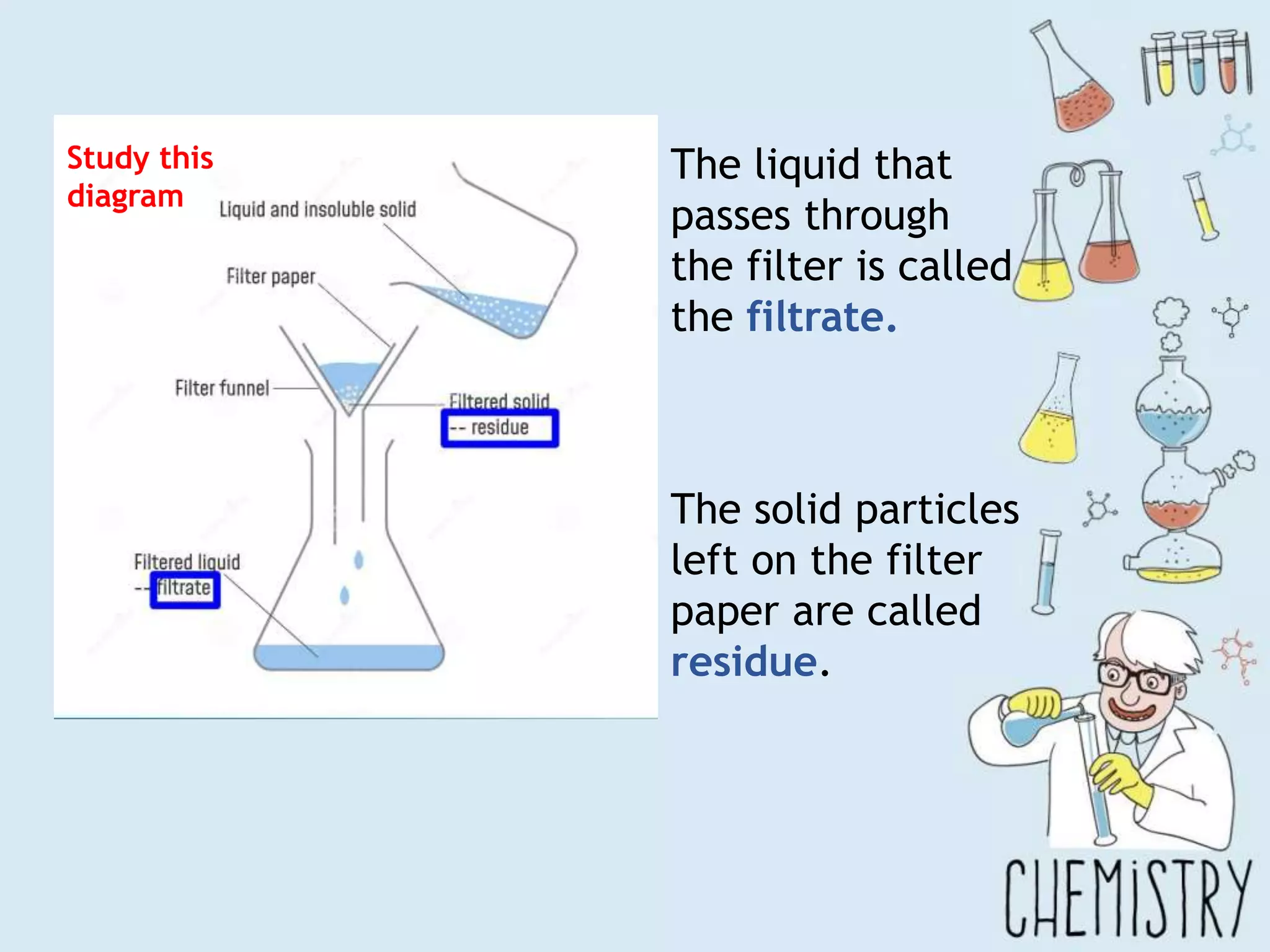
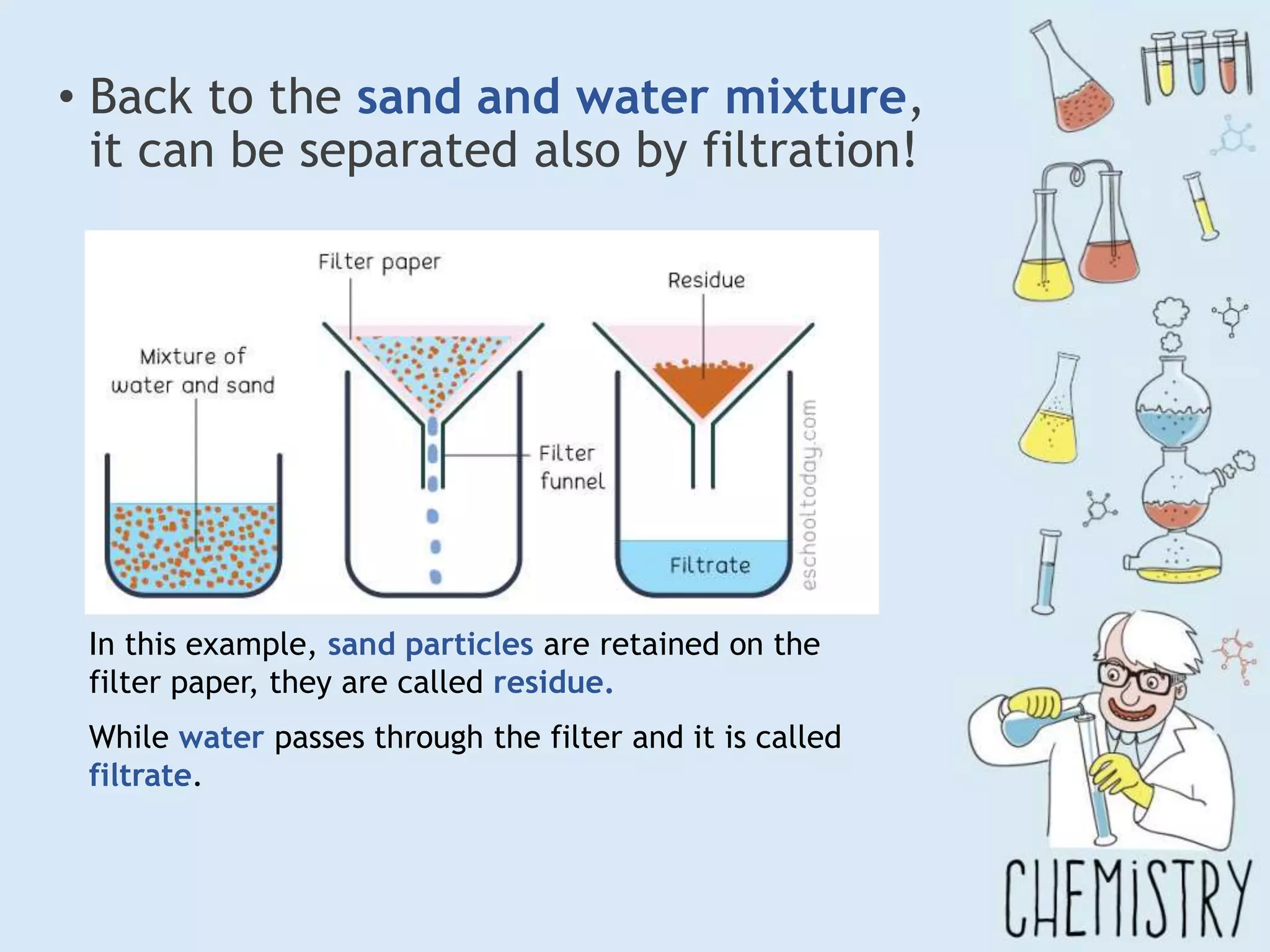
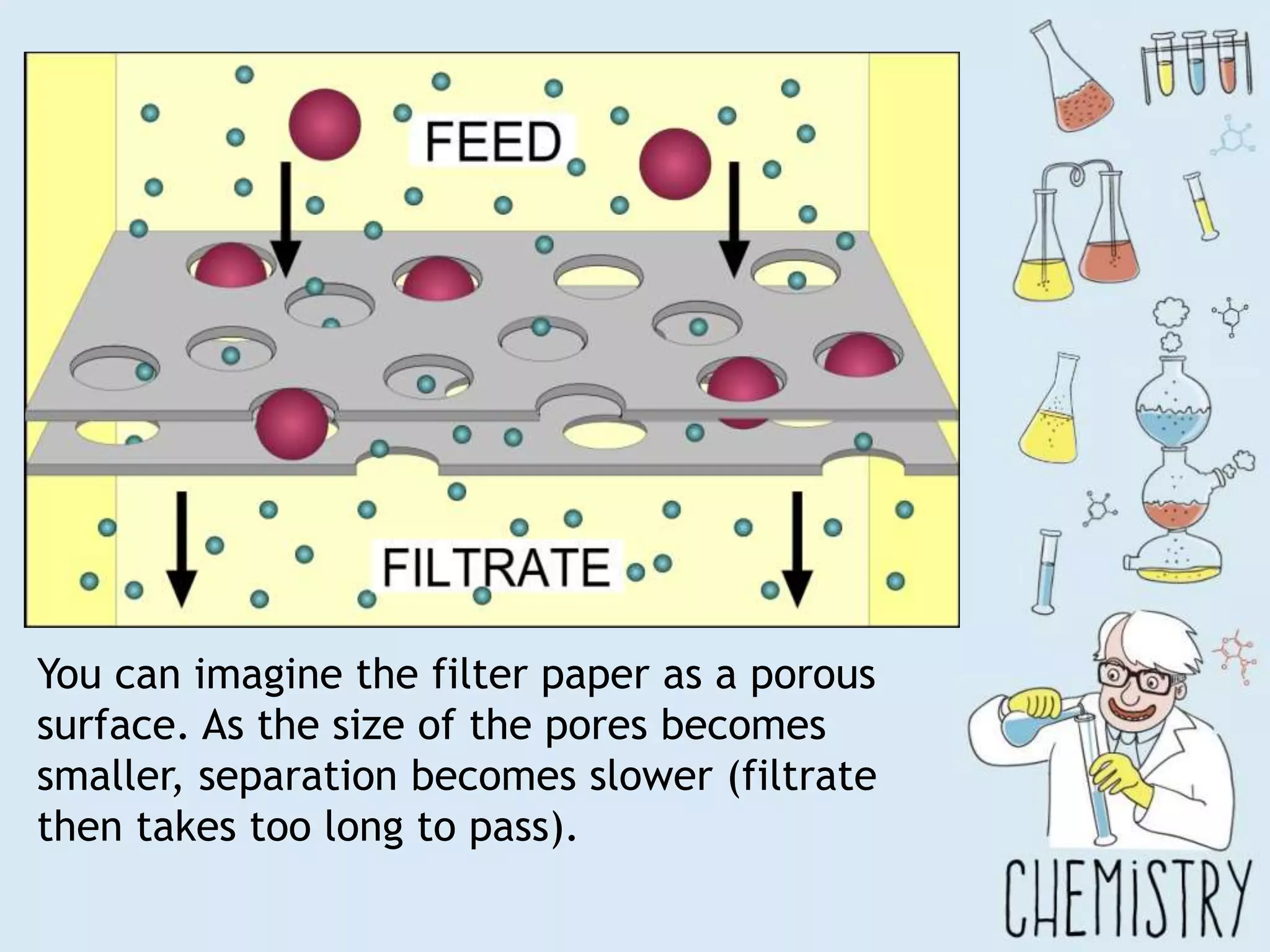
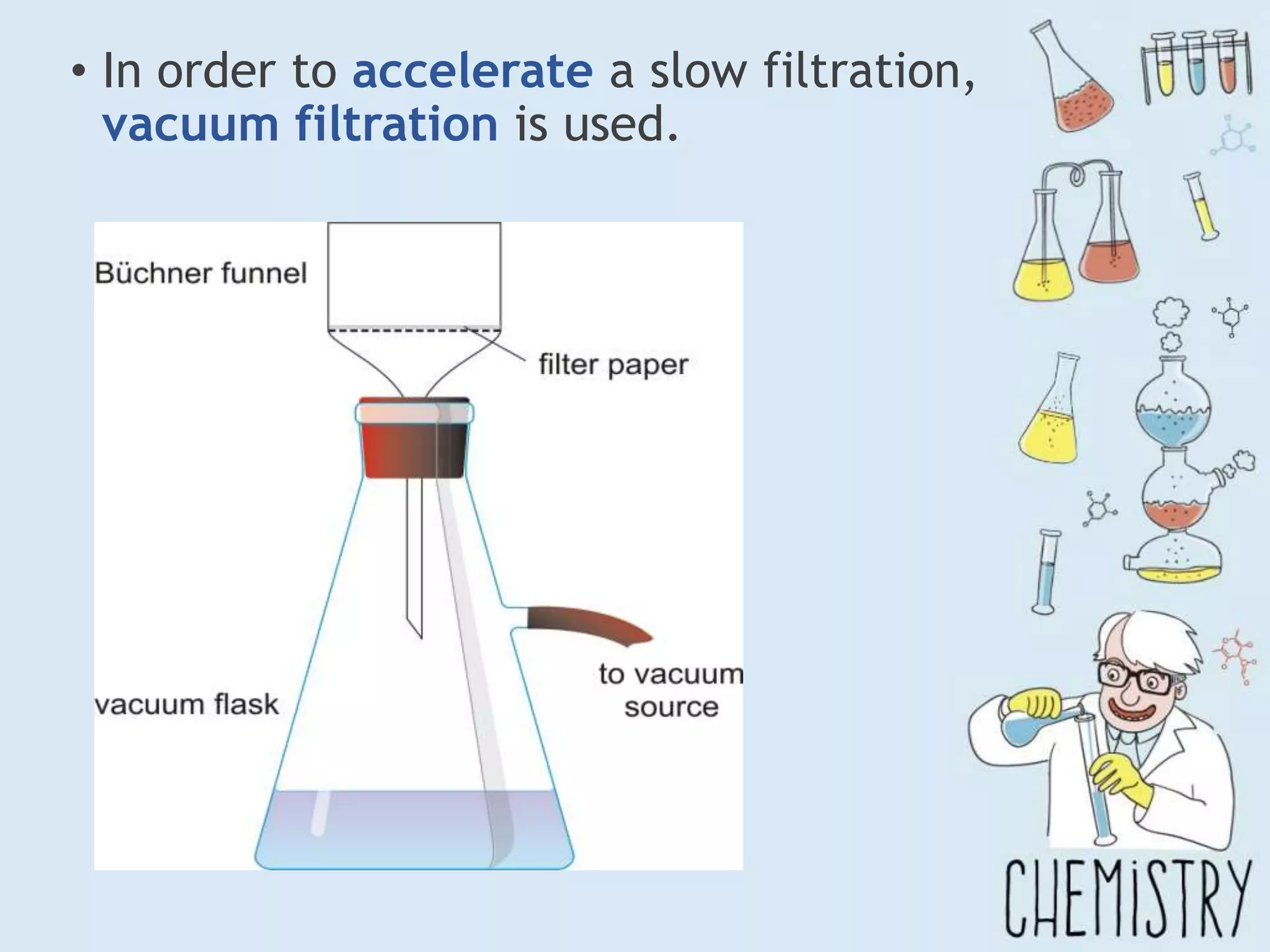
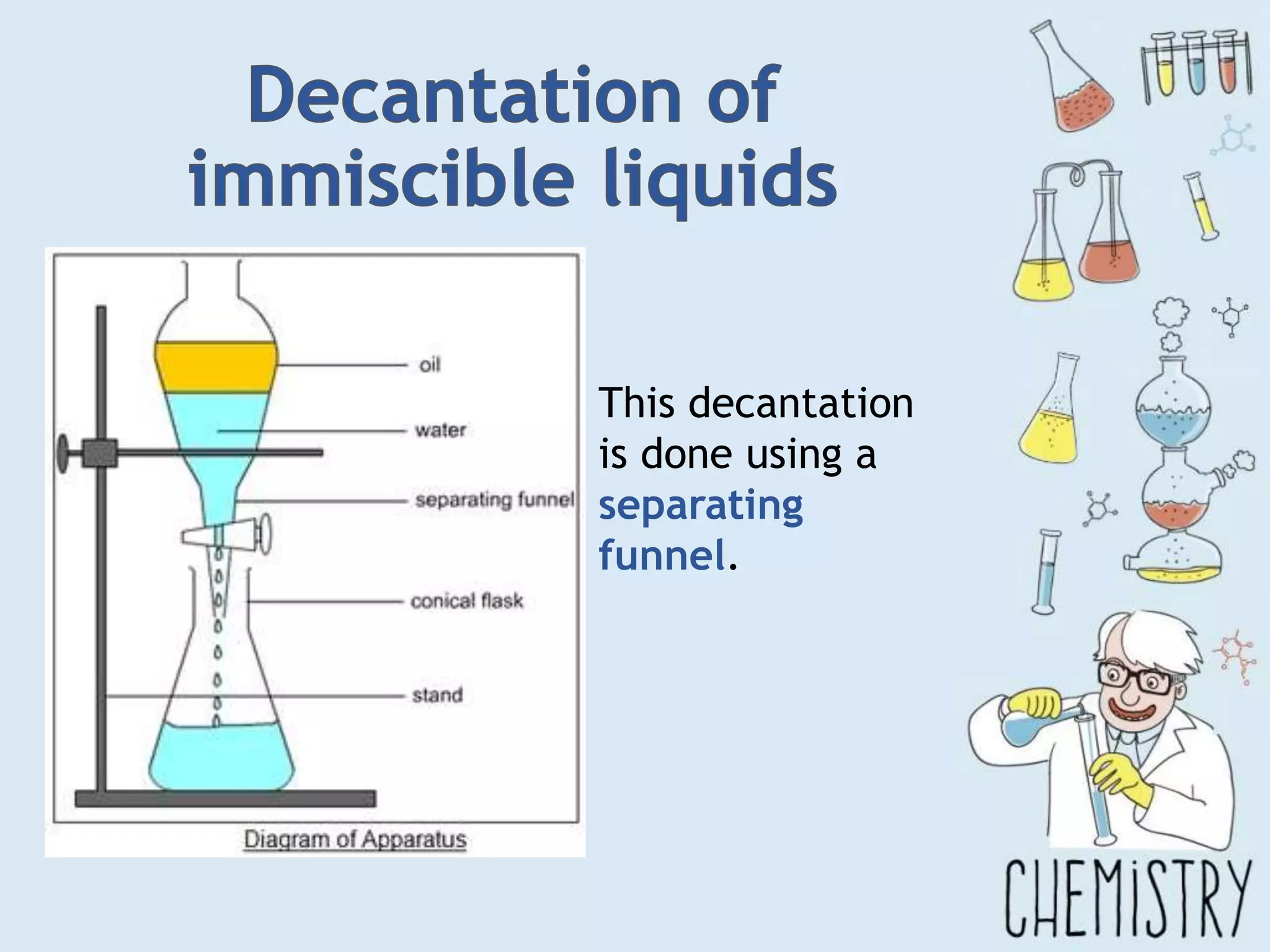
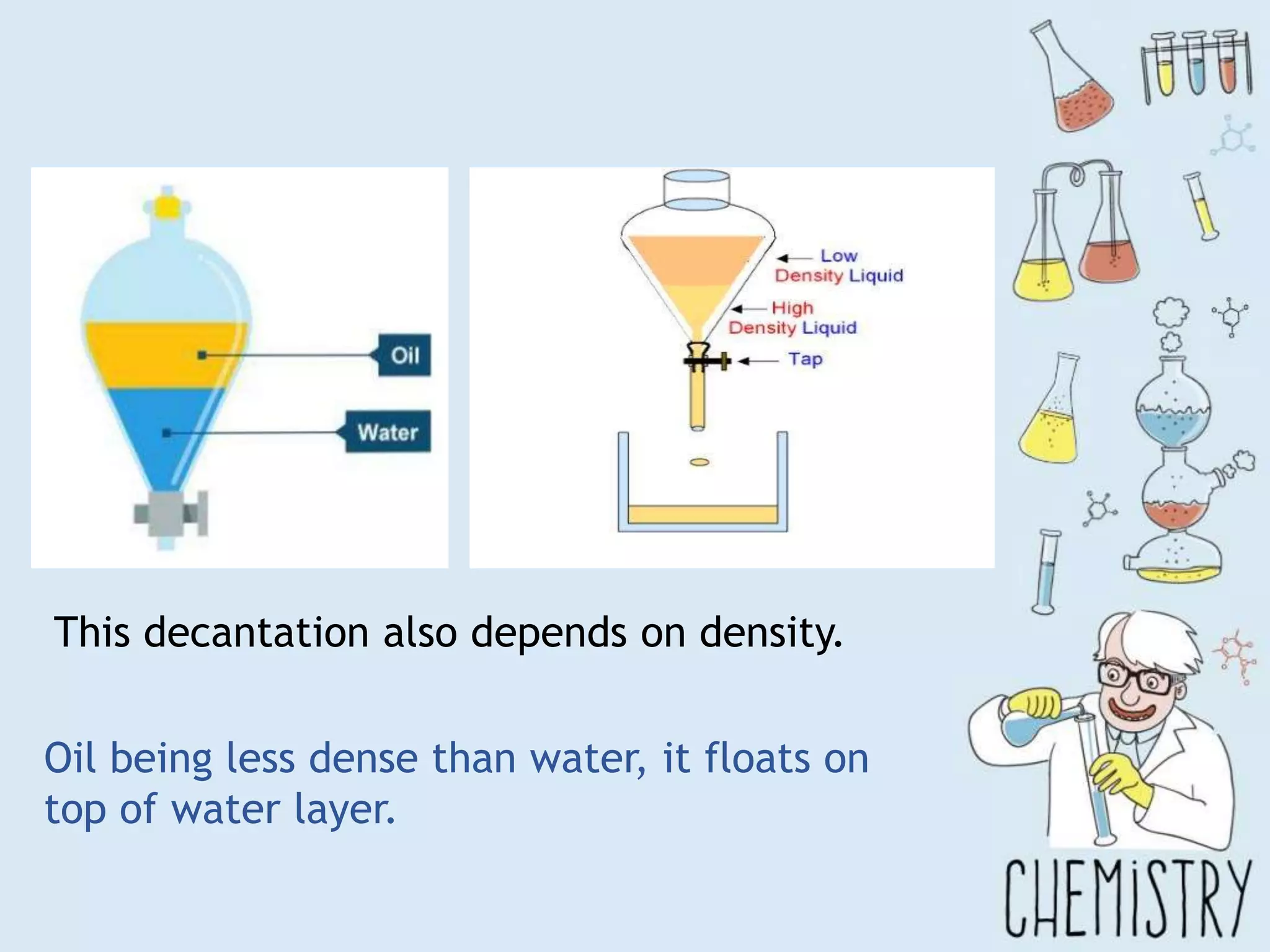
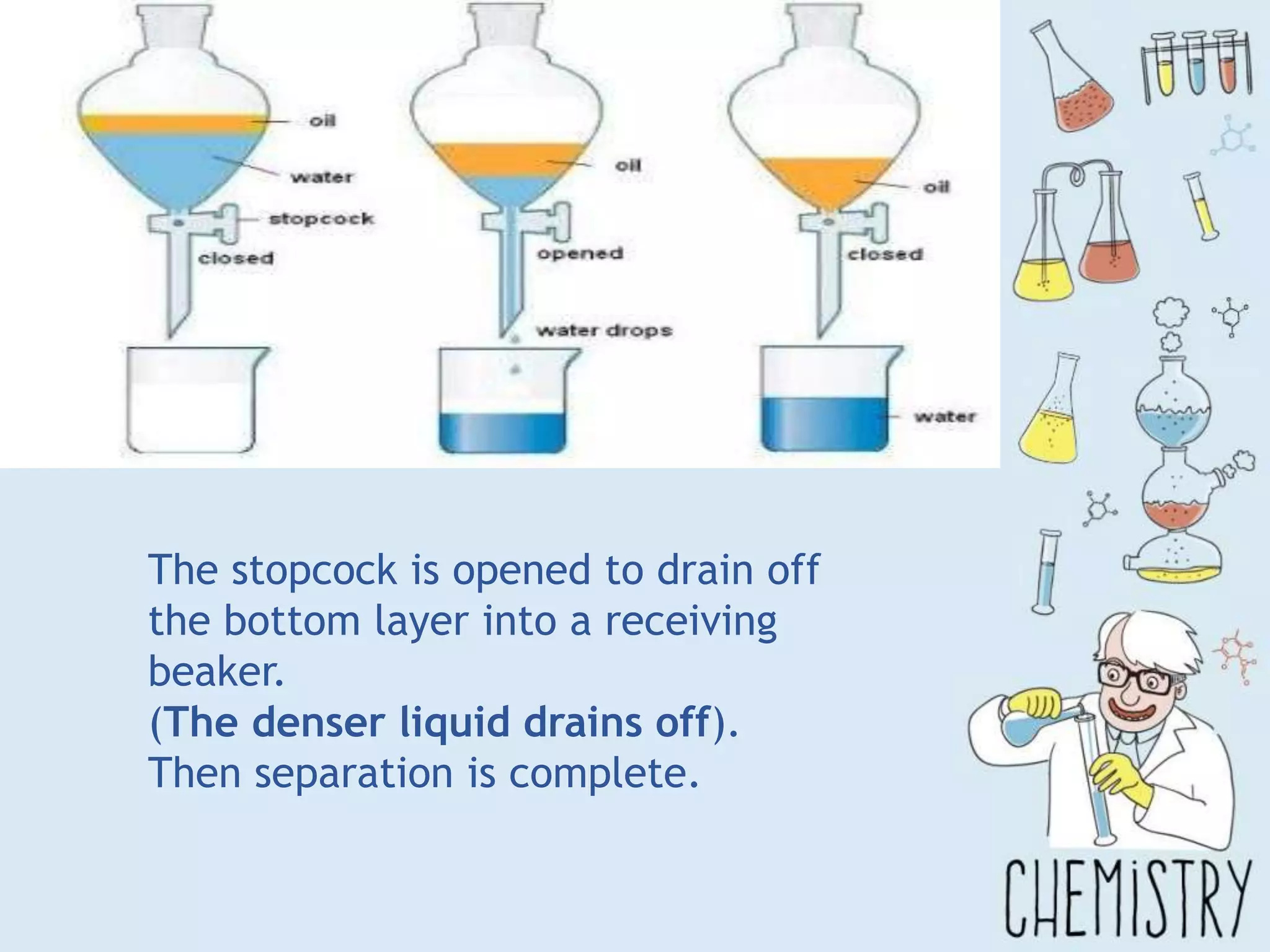
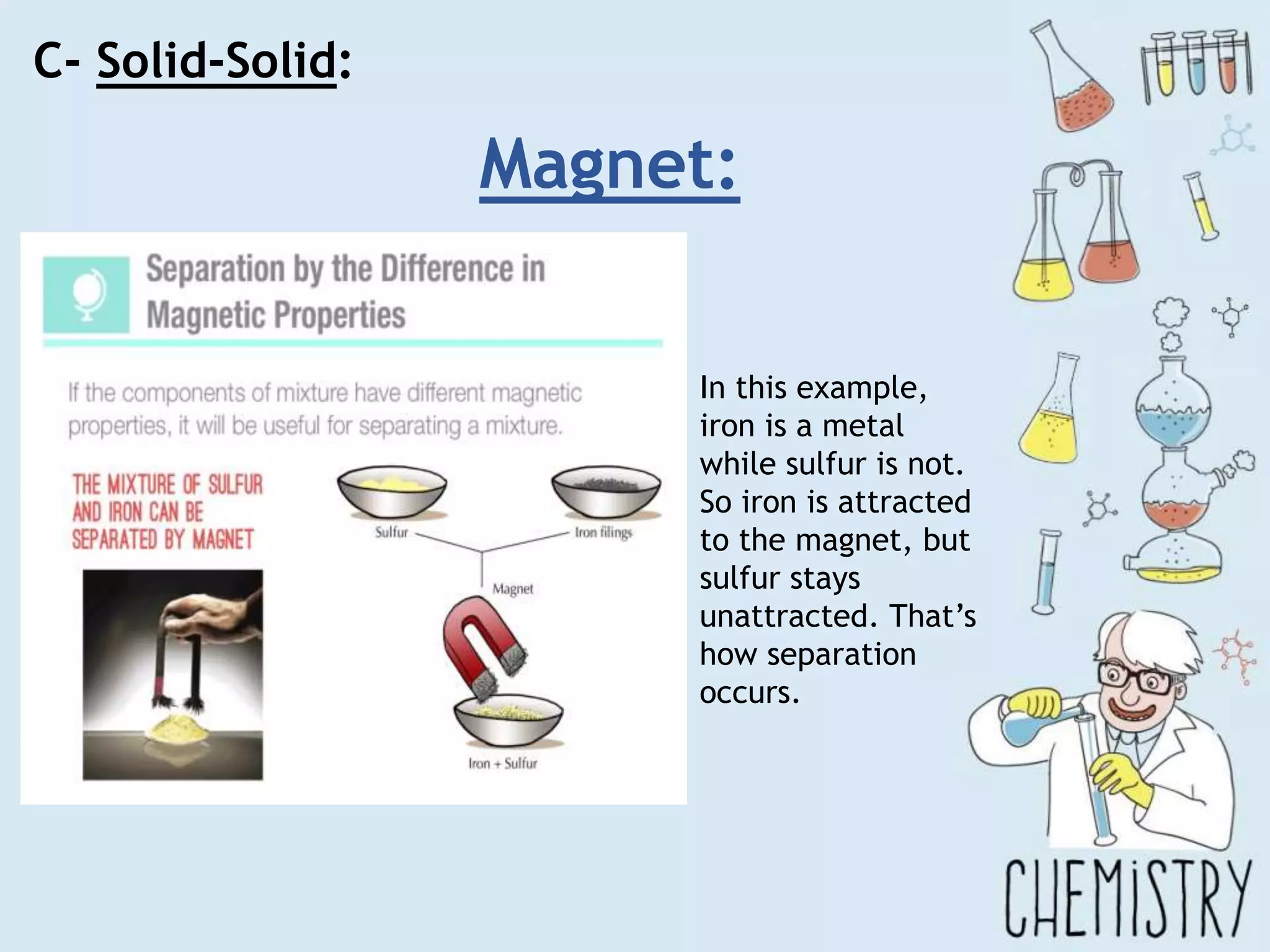
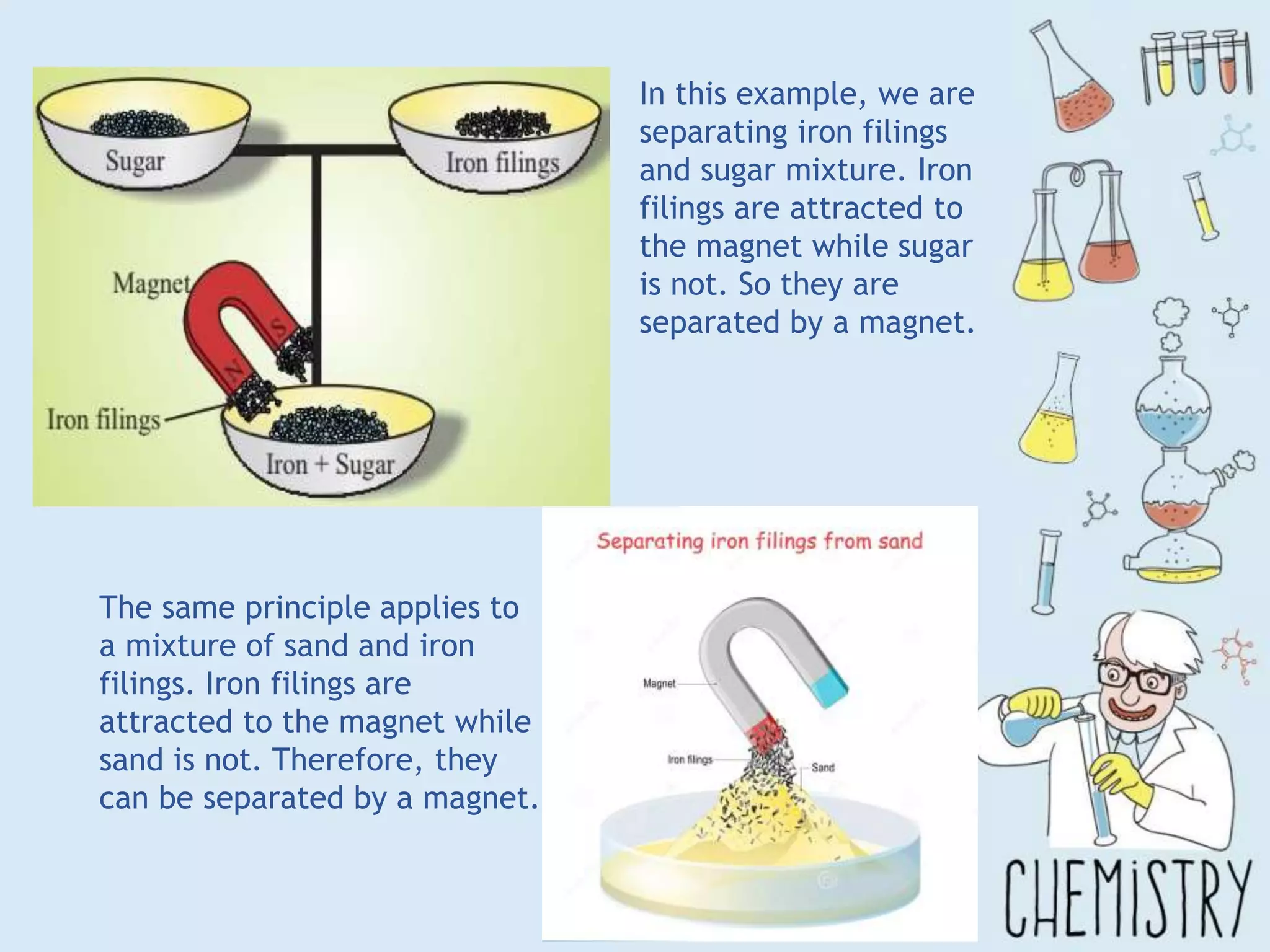
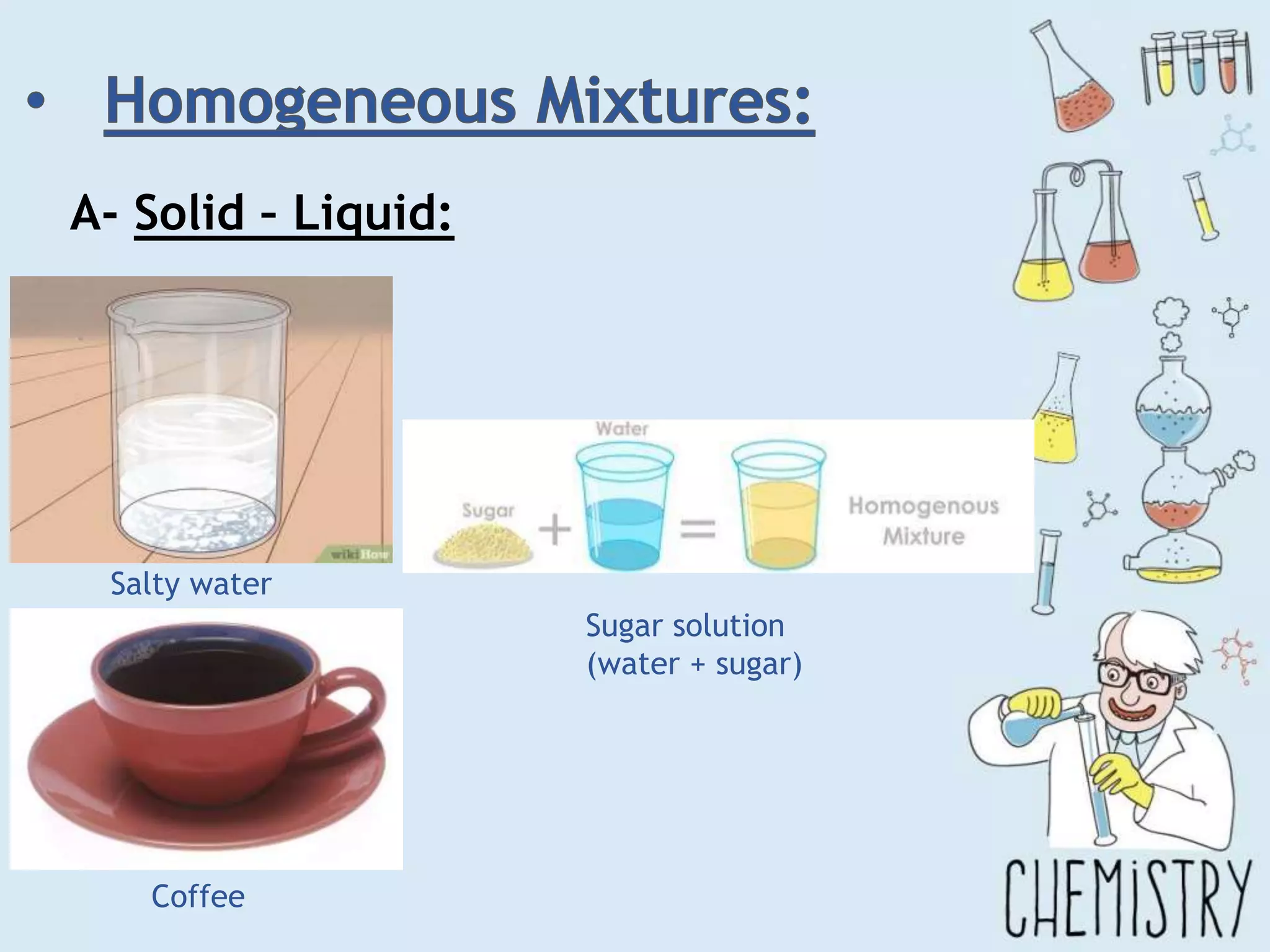
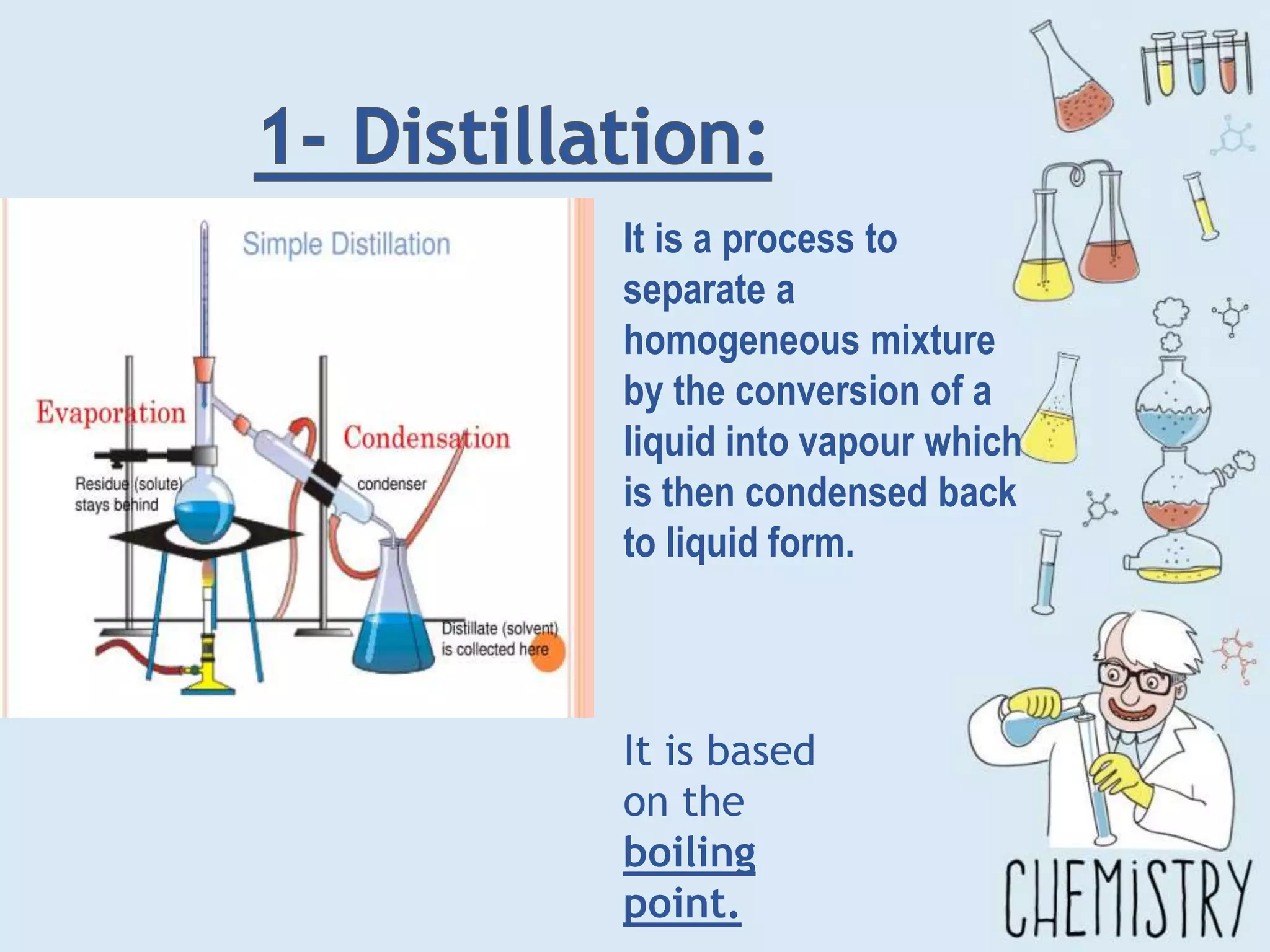
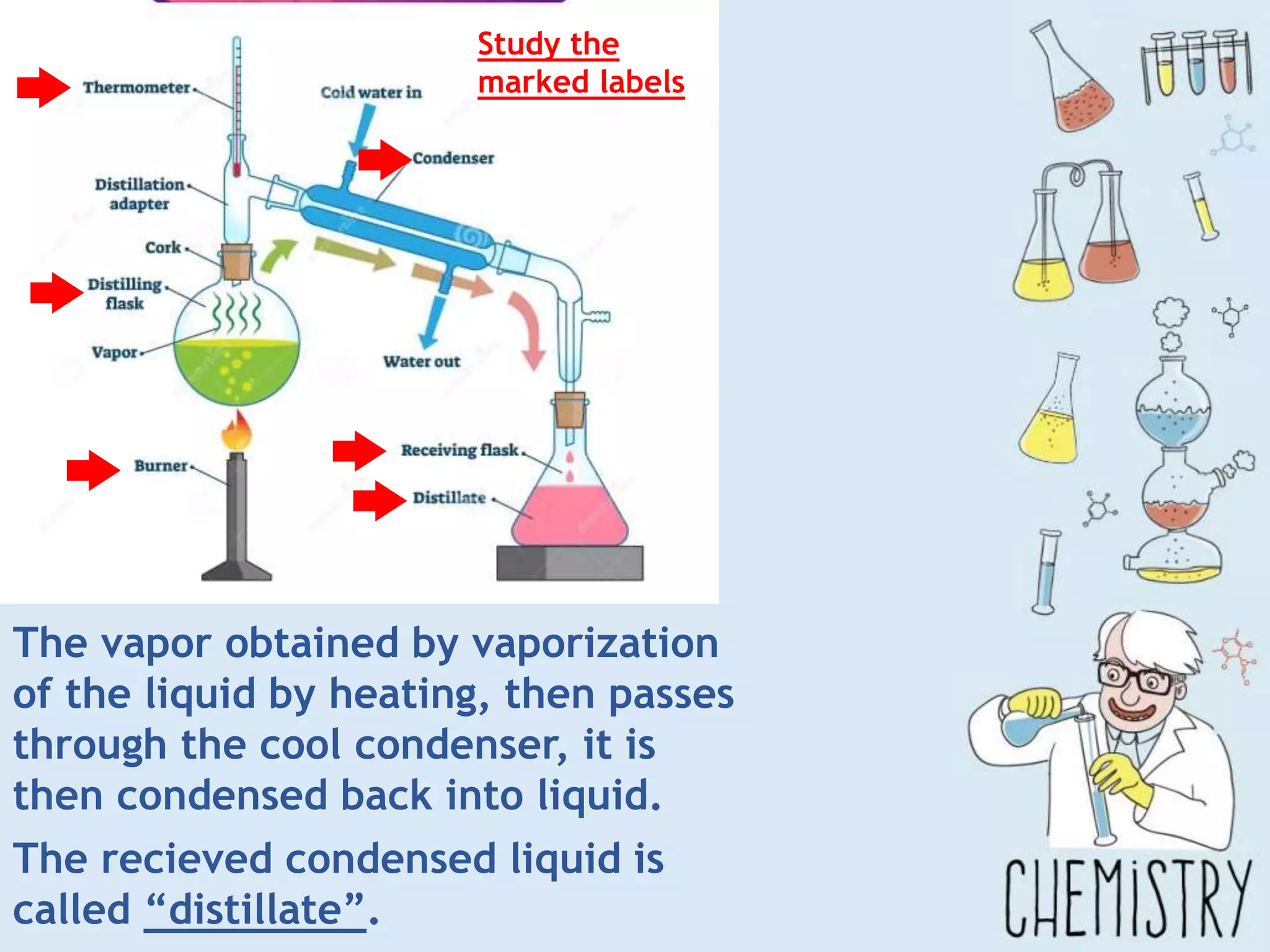
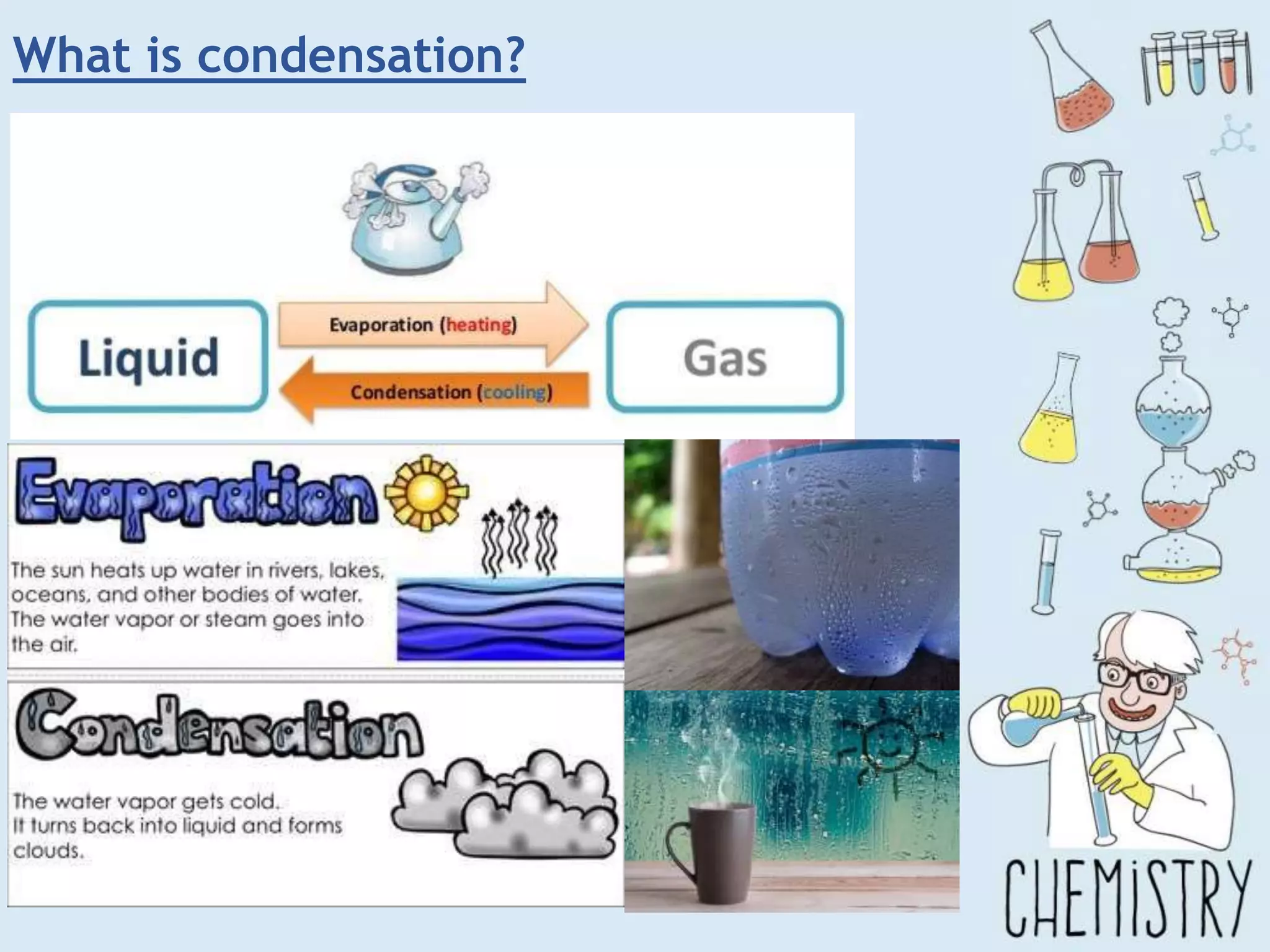
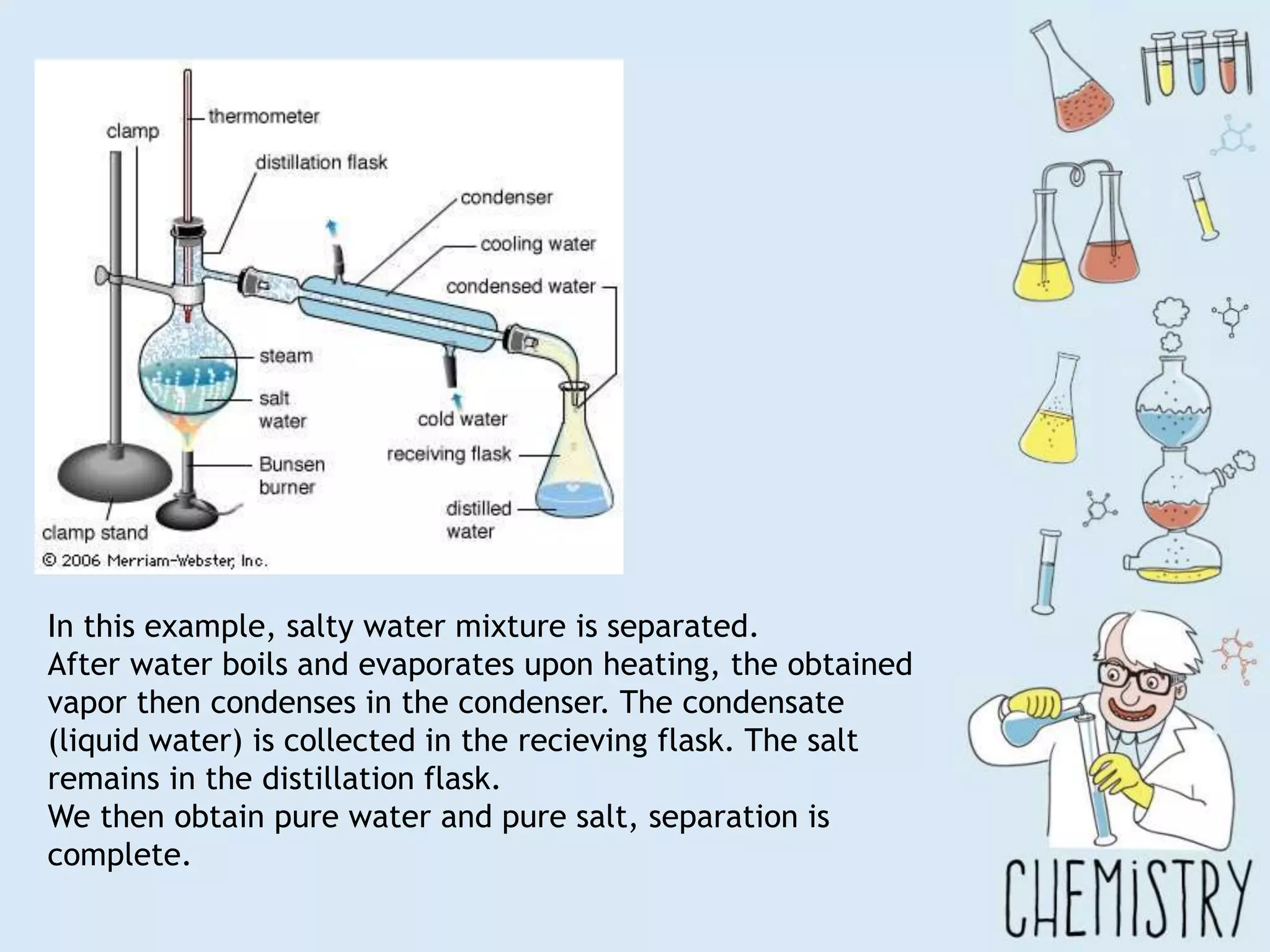
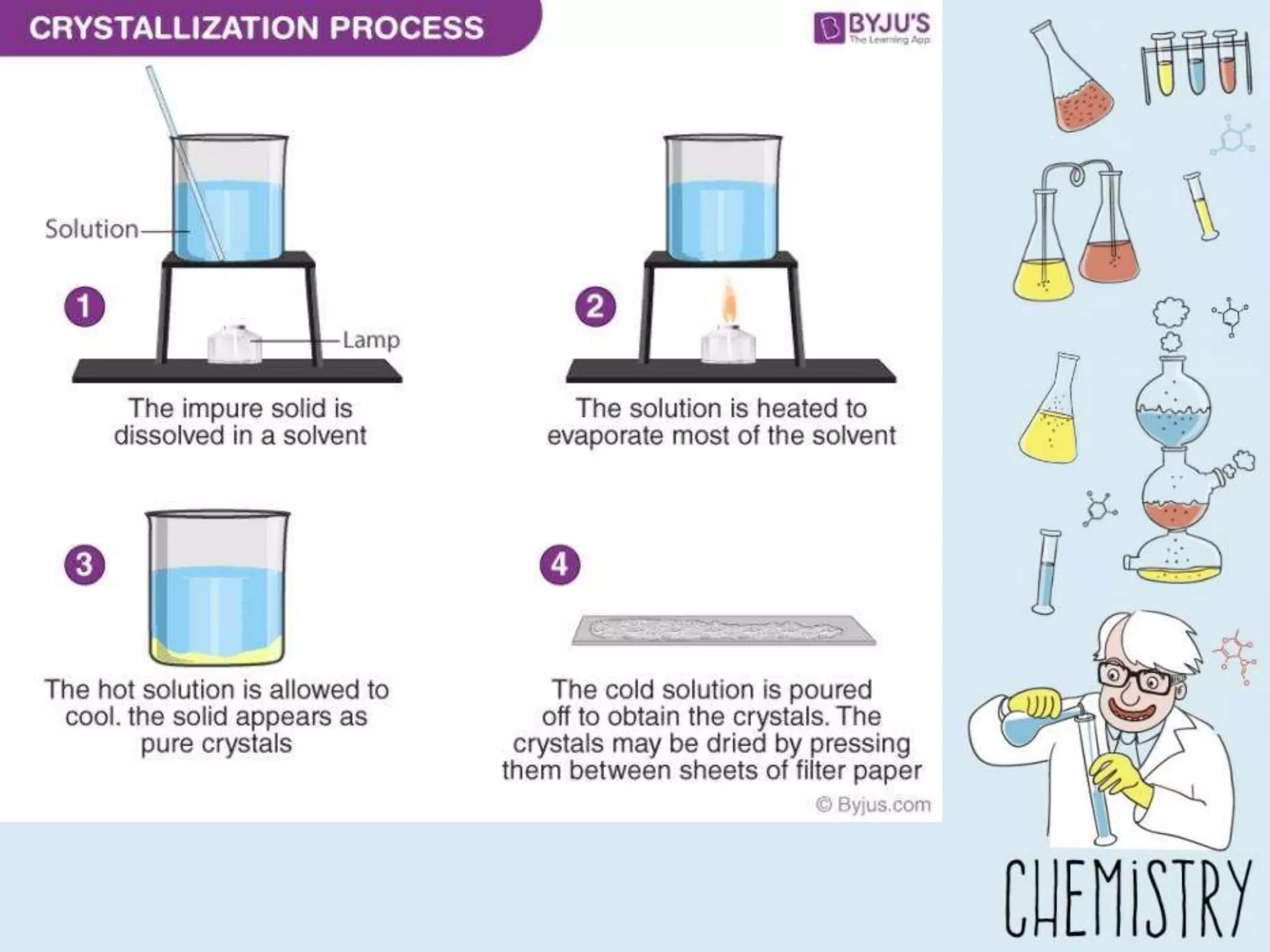
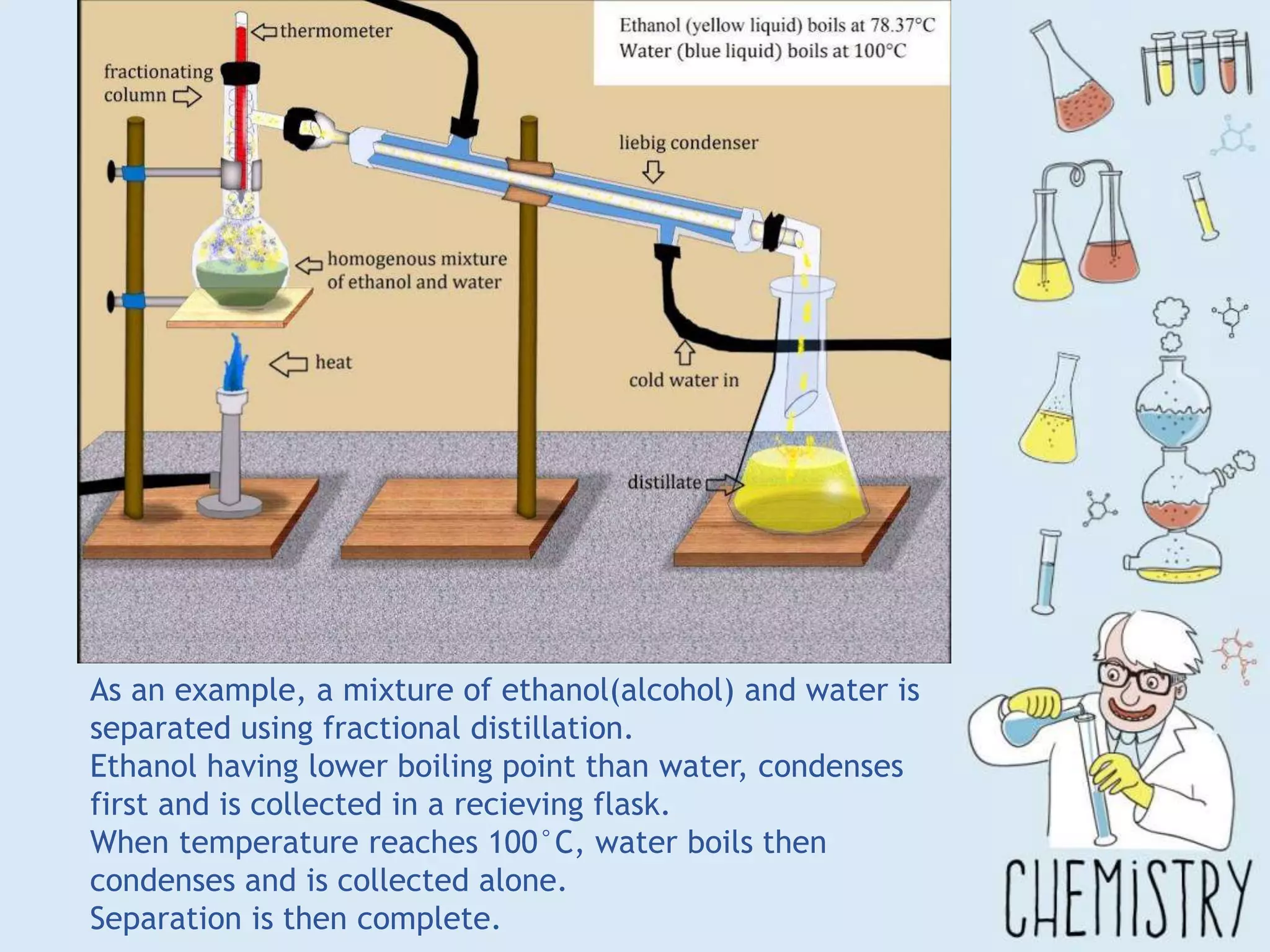
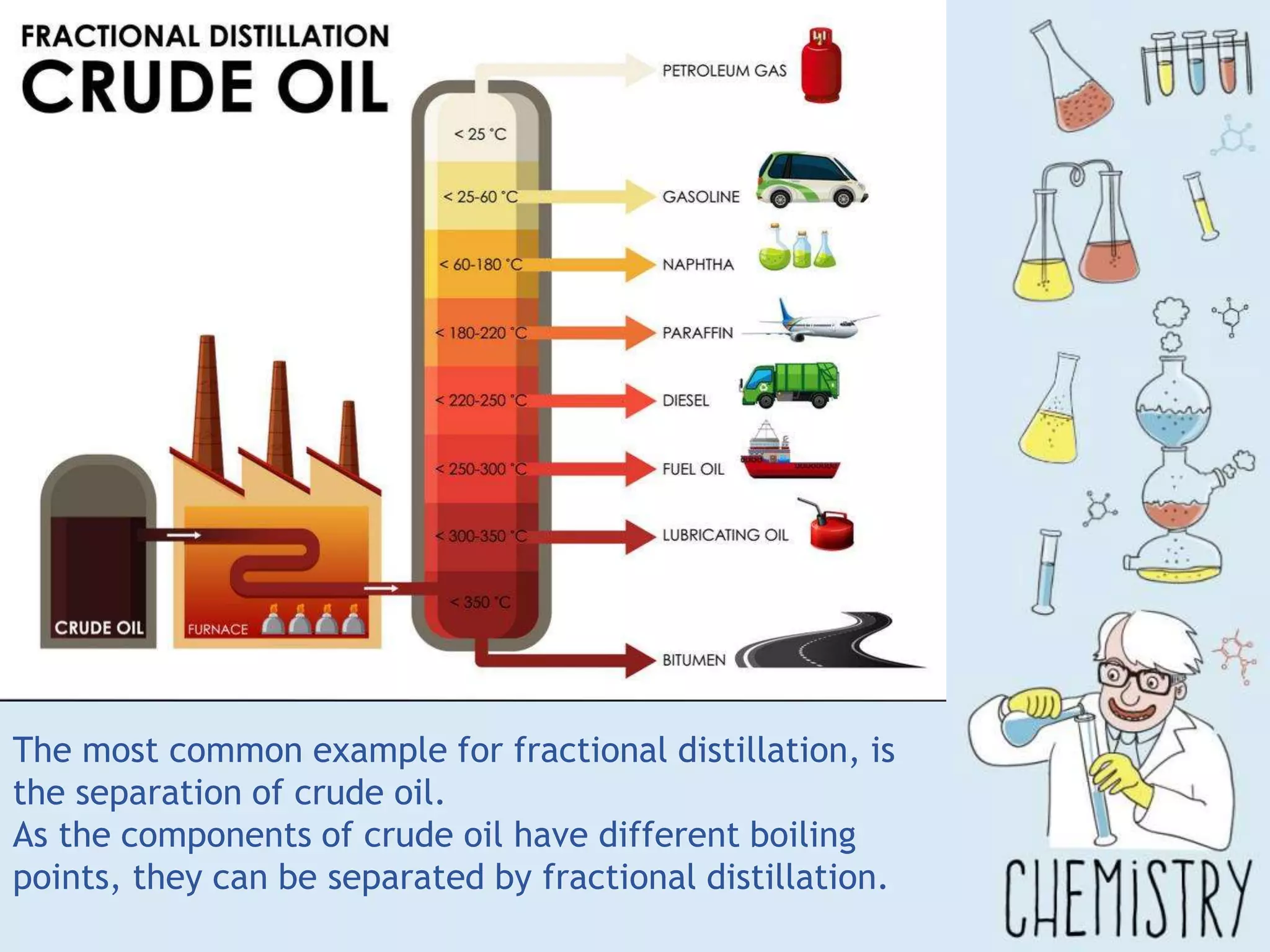
The document outlines various physical separation techniques for mixtures, such as decantation, filtration, distillation, and centrifugation, explaining their principles and applications. It highlights examples for separating solid-liquid, liquid-liquid, and solid-solid mixtures based on properties such as density and boiling points. Additionally, it includes exercises to reinforce understanding of these methods.